Verbal Menu
- Basic Grammar
- Speech and Voices
- Tenses
- Articles
- Tenses and Articles
- Idioms and Phrases
- Subject Verb Agreement
- Prepositions and Conjunction
- Selecting Words
- Relative Pronoun
- Sentence Completion
- Sentence Ordering
- Contextual Vocabulary
- Jumbled Sentence
- Sentence Formation
- Error Identification
- Sentence Improvement and Construction
- Cloze Test
- Fill in the blanks
- Paragraph Ordering
- Para Jumbles
- Synonyms and Antonyms
- Synonyms
- Antonyms
- Reading Comprehension
- Get Off-campus Drive Updates
- Get Hiring Updates
- Contact US
PREPINSTA PRIME
Rules For Tenses And Articles
Rules For Tenses and Articles
Introduction
The Rules for Tenses and Articles is one of the most basic structures that needs to be known in grammar.
While Tenses form the base for any form of verb in three different time periods or time zones, Articles form the basic structure to address any type of Noun or adjective.
On this page below you will get all the details about how Tenses and Articles are used in Grammar and how they shouldn’t be used.

Tenses and Articles Rules
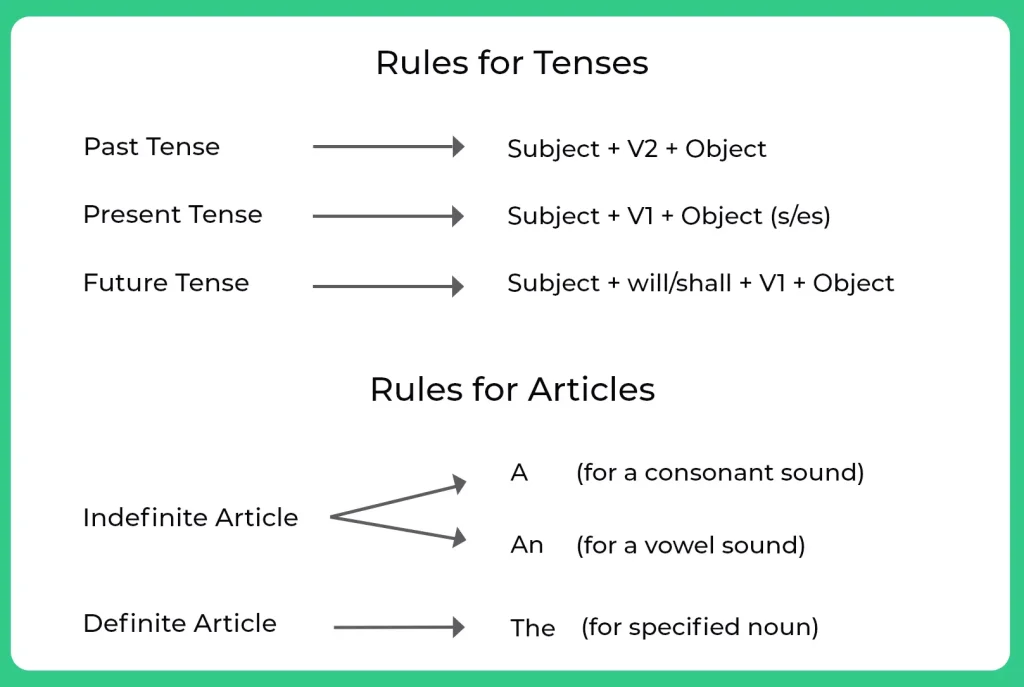
Rules for Tenses
Verbs can take only three types of Tenses. The three forms of Verbs are Past, Present, and Future.
- The Past is used to explain things that have already happened (e.g., Yesterday, last week, five years ago).
- The present tense is used to explain things that are happening right now or things that are continuous. (e.g., I am cooking, I am walking).
- The future tense explain things that have yet to happen; or is going to happen. (e.g., tomorrow, next week, next year, three years from now).
Present Tense
1. Simple present tense- These type are tense used in present action.
2. Present perfect tense- Is used in action which is completed but not expired.
3. Present continuous tense- Is used in continuous, which goes on and will go on.
4. Present perfect continuous tense- Are used in an action which is started earlier and still going on.
Past Tense
1. Simple past tense- Are used when a action is completed.
2. Past perfect tense- Are used when an action is completed and expired.
3. Past continuous tense- Are used when the duration of an work is completed
4. Past perfect continuous tense- Are used when work started earlier and was going on for a certain time period and was stopped in the past time.
Future Tense
1. Future tense- Are used for a future work or an action.
2. Future perfect tense- Are used to have a strong pledge for a future.
3. Future continuous tense- Are used for the duration of the action of a future action
4. Future perfect continuous tense- Are used when a works starts in future for a continuous action.
Miscellaneous Tense Rules
1. Pure present tense- Are used to provide someone’s present status / places / position
2. Pure past tense- Are used to provide someone’s past position/ status/ place
3. Additional present tense- Are used for future distance possibility/rare ability/assumption/frequent ability/regular habitual/advisable manner
4. Additional past tense- Are used for work past assumption/past ability/past pledge
5. Additional present continuous tense- Are same as additional present tense and with providing importance to the duration of the work and action.
6. Additional past continuous tense- Are same as additional past tense and with providing importance to the duration of the work and action.
7. Future in the past tense- Is an action that are occurred in past time but for a reverse angle.
8. Future in the past continuous tense- Are same as above and with providing importance to the duration of the action.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Present Tense Rule Table
| Present Tense Type | Usage / Function | Structure / Rule | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Present | – Daily routines – General truths – Facts and habits | Subject + base verb (add s/es for he/she/it) | She writes every day. They play football. |
| Present Continuous | – Actions happening right now – Temporary actions – Future planned events | Subject + is/am/are + verb+ing | I am studying English. They are watching a movie. |
| Present Perfect | – Actions completed recently – Actions with relevance to the present | Subject + has/have + past participle | She has finished her homework. We have seen that movie. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | – Actions that started in the past and are still continuing – Focus on duration | Subject + has/have been + verb+ing | He has been working since morning. I have been learning French for a year. |
Past Tense Rule Table
| Past Tense Type | Usage / Function | Structure / Rule | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Past | – Completed actions in the past – Specific time references | Subject + past verb | We visited the museum. She called me yesterday. |
| Past Continuous | – Actions happening at a specific moment in the past – Interrupted past actions | Subject + was/were + verb+ing | She was reading when I called. They were playing football. |
| Past Perfect | – An action completed before another past action | Subject + had + past participle | He had left before I arrived. We had finished dinner by 9 PM. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | – Past action in progress before another past event – Focus on duration | Subject + had been + verb+ing | They had been working for 3 hours. I had been studying all night. |
Future Tense Rule Table
| Future Tense Type | Usage / Function | Structure / Rule | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Future | – Actions that will happen in the future – Promises, decisions, predictions | Subject + will/shall + base verb | I will travel next week. She will call you soon. |
| Future Continuous | – Actions that will be in progress at a certain time in the future | Subject + will be + verb+ing | They will be studying at 9 PM. She will be driving to work. |
| Future Perfect | – Actions that will be completed before a certain point in the future | Subject + will have + past participle | We will have finished the project by Friday. He will have left before noon. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | – Emphasizes the duration of an action up to a point in the future | Subject + will have been + verb+ing | She will have been working here for 5 years. I will have been waiting for an hour. |
Rules for Articles
Articles-Rules
Articles ares always used with noun or an adjective. There are different usage for different types of articles which is explained below:There are a total of 3 articles and using
them correctly can make your sentence accurate and meaningful.
(i) Definite article – THE
(used before a definite (specified subject or noun or plural noun)
(ii) Indefinite article – A / AN
A is used before a singular noun beginning with a consonant sound
AN is used before a singular noun beginning with a vowel sound
| Rule #1 Specific unknown identity | a, an | (no article) |
| Rule #2 Specific known identity | the | the |
| Rule #3 All things or things in general | (no article) | (no article) |
Also Check:
- Basic Grammar – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Speech and Voices – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Tenses – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Tenses and Articles – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Idioms and Phrases – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Subject Verb Agreement – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Prepositions and Conjunction – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Selecting Words – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Relative Pronoun – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Sentence Completion- Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
Also Check Out
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others

 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates




Login/Signup to comment