Verbal Menu
- Basic Grammar
- Speech and Voices
- Tenses
- Articles
- Tenses and Articles
- Idioms and Phrases
- Subject Verb Agreement
- Prepositions and Conjunction
- Selecting Words
- Relative Pronoun
- Sentence Completion
- Sentence Ordering
- Contextual Vocabulary
- Jumbled Sentence
- Sentence Formation
- Error Identification
- Sentence Improvement and Construction
- Cloze Test
- Fill in the blanks
- Paragraph Ordering
- Para Jumbles
- Synonyms and Antonyms
- Synonyms
- Antonyms
- Reading Comprehension
- Get Off-campus Drive Updates
- Get Hiring Updates
- Contact US
PREPINSTA PRIME
Rules for Sentence Completion
Rules for Sentence Completion
The Rules for Sentence Completion are necessary to know because this particular topic in grammar tests the skill to read the given information in an incomplete sentence and then choose words / sentence that can complete them.
It aims to analyze a student’s vocabulary and logical skills pertaining to a contextual sentence

Rules for Sentence Completion
Before starting off with the main rules for Sentence Completion, let’s look at its types:
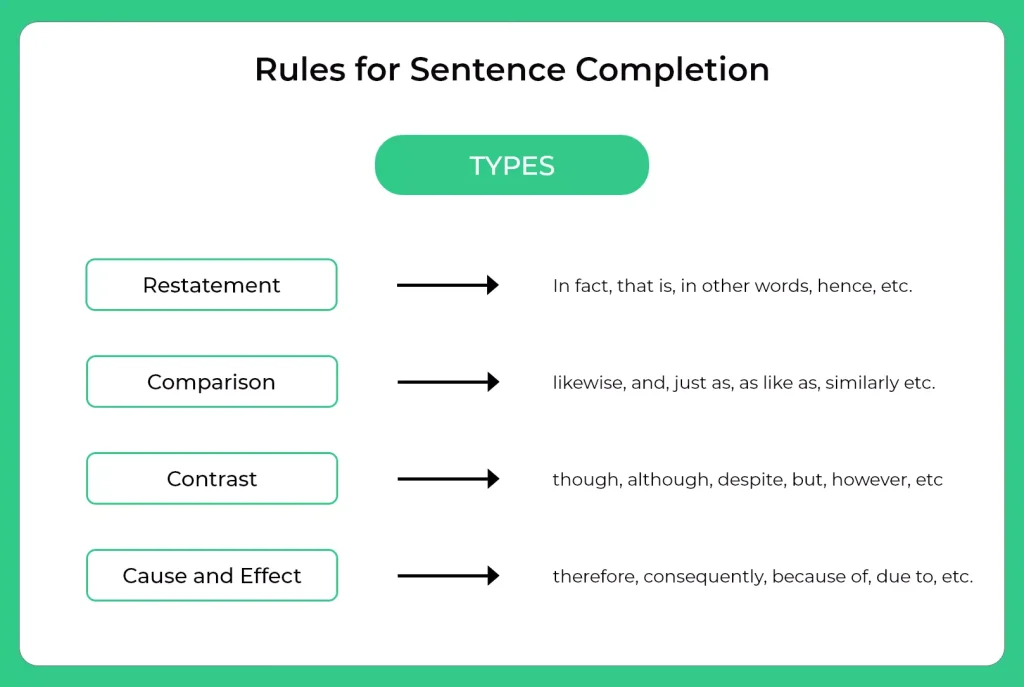
There are approximately four types of Sentence / Word Completion:
Restatement:
These are the words that we use to amplify the importance of the first clause or add more information to the already stated facts.
Example:
In other words, in fact, that is, etc.
Question:
The boy was too lazy to even move about during the day, in other words, he was ________.
a. slumber
b. promt
c. trickster
d. lethargic
Answer – Lethargic.
Since we use the phrase ‘in other words’ it means that we need to use a word that re-states the already given description.So lethargic can be the answer.
Comparison:
The words that we use in this type reflect a comparison between two subjects in the two clauses.
Example:
likewise, and, just as, as like as, similarly etc.
Question:
Just as we hope to be forgiven, so we should ______ others.
a. burden
b. forgive
c. criticize
d. conspire
Answer:
Here, we have used the comparison word, ‘just as’ which means that the second clause should have a word that presents a similar meaning in the first clause. So we use ‘forgive’.
Contrast:
This type comprises the words that reflect a stark and definite contrast between two or more clauses.
Example:
though, yet, although, despite, but, on the other hand, but, however, despite, or, on the contrary, etc.
Question:
Although her son is a happy to go soul, her daughter is _______ and grumpy
a. rude
b. peaceful
c. merry
d. casual
Answer:
Here the answer should be ‘rude’ because we are presenting a contrast between the natures of her son and daughter. While the son is peaceful and happy, the daughter is rude and grumpy.
Cause and effect:
The Cause and Effect type comprises words that act as a consequential evidence of some previous action or cause or present an impactful situation post an action.
Example:
therefore, consequently, because of, due to, as a result, leads to, etc.
Question:
Ginger practiced everyday for the competition, as a result, she _______ it.
a. lost
b. eliminated
c. won
d. ditched
Answer:
Here the answer is ‘won’ because ginger practiced regularly and so she won it. her efforts resulted in her win.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Sentence Completion Rules
Once we are done with the types of words used in sentence completion, let’s had over to the practical types of the same:
TYPE – 1: Quantity Based
A Quantity Based Question means the number of blanks that we get in a sentence.It can be divided into:
- One Blank
- Two or More Blanks
TYPE – 2: Length Based
A Length Based Question means the length of the question that is given to us. It can be divided into two parts:
- Sentence Based – the question is only 20-35 words long.
- Paragraph / Passage based – the sentence given to us in compiled into a bigger passage with multiple blanks to fill in.
TYPE – 3: Element Based
A Sentence Completion Question that is element based means the type of answer that we need to fill in to complete the sentence / passage.
- Word – based: It requires us to fill the blank with a single word.
- Phrase – based: This type needs us to choose a phrase in order to complete the sentence given to us
- Sentence – based: It requires us to insert a complete sentence in the blank. This type is mostly used in passage-based questions.
For Example:
These are just two examples of the multiple possible combinations of questions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Sentence Completion
| Mistake | What to Do Instead |
| Ignoring context | Read the full sentence carefully before choosing an option. |
| Missing connector clues | Watch for clue words like but, although, however, therefore. |
| Grammatical mismatch | Check subject-verb agreement, tense, and parts of speech. |
| Falling for distractor words | Choose words based on sentence tone and logic, not appearance. |
| Ignoring collocations | Select words that naturally pair together (e.g., make a decision). |
| Skipping elimination | Use elimination to remove irrelevant or grammatically incorrect options. |
| Overthinking simple answers | Trust the straightforward option if the tone suggests simplicity. |
| Ignoring dual blank relationship | Ensure both blanks fit together logically in tone and meaning. |
Quick Rules Table for Sentence Completion
| Step | Rule | Example/Tip |
| 1 | Understand the tone | Positive/Negative/Neutral |
| 2 | Spot clue words | but, because, however |
| 3 | Check grammar | Subject-Verb agreement, tense, parts of speech |
| 4 | Predict the word | Think before seeing options |
| 5 | Eliminate wrong choices | Use logic and tone clues |
Rules for Sentence Completion - Sample Questions
Below are few example for you to understand Sentence Completion:
Question 1:
The opposition parties allege that prices of essential commodities are __________ like a runaway balloon.
A. soaring
B. reviving
C. flying
D. leaping
Answer – Soaring
Explanation:
Since the sentence compares the prices with runaway balloon,it means that the prices are going up high. Out of all the options, Soaring means to go up high.
Question 2:
_______is a person who dabbles in art and letters.
A. chauvinist
B. connoisseur
C. philistine
D. dilettante
Answer – Dilettante
Explanation:
Here, the second clause of the sentence gives us the description or definition of the word that should be used in the first blank. Since it defines a person who dabbles (to take superficial interest) in art and letters, we can say hat the person is Dilettante.
Also Check Out
Also Check:
- Basic Grammar – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Speech and Voices – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Tenses – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Tenses and Articles – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Idioms and Phrases – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Subject Verb Agreement – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Prepositions and Conjunction – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Selecting Words – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Relative Pronoun – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Sentence Completion- Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Basic Grammar
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Speech and Voices
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Tenses
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Tenses and Articles
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Idioms and Phrases
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Subject Verb Agreement
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Prepositions and Conjunction
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Selecting Words
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Relative Pronoun
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Sentence Completion
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others

 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates




Login/Signup to comment