Verbal Menu
- Basic Grammar
- Speech and Voices
- Tenses
- Articles
- Tenses and Articles
- Idioms and Phrases
- Subject Verb Agreement
- Prepositions and Conjunction
- Selecting Words
- Relative Pronoun
- Sentence Completion
- Sentence Ordering
- Contextual Vocabulary
- Jumbled Sentence
- Sentence Formation
- Error Identification
- Sentence Improvement and Construction
- Cloze Test
- Fill in the blanks
- Paragraph Ordering
- Para Jumbles
- Synonyms and Antonyms
- Synonyms
- Antonyms
- Reading Comprehension
- Get Off-campus Drive Updates
- Get Hiring Updates
- Contact US
PREPINSTA PRIME
How To Solve Tenses And Articles Problems Quickly
How to Solve Tense and Articles
The Rules for How to Solve Tenses and Articles are fairly easy once you know how to use them in the questions. Below we have mentioned some rules in brief that can be used to solve question which needs you to answer in terms of Tenses or Articles.
If you want to learn about how to solve Tenses and Articles in details read the page thoroughly

How to Solve Tenses and Articles
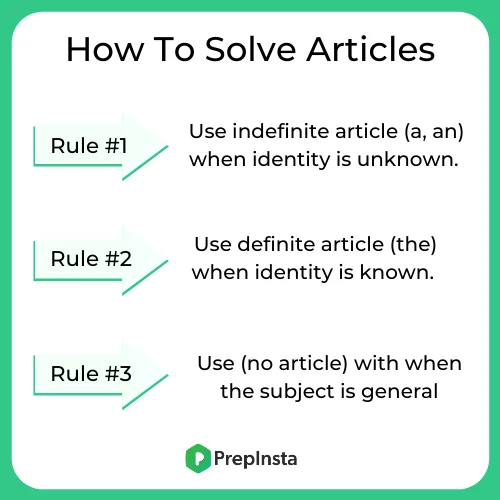
How to Solve Articles
Rule 1:
When specific identity is not known use the indefinite article ‘a’ or ‘an’ only with a singular count noun. We can use ‘a’ and ‘an’
- To highlight any non-specified member of a group or category.
- Example, I think an animal is in the room.
- To indicate one in number.
- Example, I own a cat.
- To indicate an unspecified, limited amount.
- Example, An apple a day, keeps the doctor away.
- We use ‘a’ before words that start with consonants and ‘an’ before words that begin with vowels.
- Example, The first letter of the word honest is a consonant, but it’s unpronounced. In spite of its spelling, the word honest begins with a vowel sound. Therefore, we use an as an article before the word honest.
Rule 2:
When specific identity is known use the definite article ‘the’ with singular or plural, count or non-count noun. We can use ‘the’
- When a particular noun has already been mentioned previously.
- Example, I ate an apple yesterday. The apple was red in color.
- An adjective, phrase, or clause describing the noun clarifies or restricts its identity.
- Example, Thank you for the present that you gave me yesterday.
- When the noun refers to something or someone that is unique.
- Example, The Taj mahal was built by Shah Jahan.
Rule 3:
Use no article with plural count nouns or any non-count nouns used to mean all or in general.
There are also some common noun which do not take any article such as name of languages, sports, academic subjects.
Example,
- I don’t like tea.
- Cricket is my favorite sport.
- Mr. Smith teaches us biology.
- Paint is hard to remove.
- I wanted to learn French.
- She was asking for advice.
- Women generally live longer than men.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Practice Questions - How to Solve Articles
Type 1: Indefinite Article
Question 1:
There is ——— white chemistry book on the writing desk.
A. a
B. an
C. the
D. no article
Answer: option A
Explanation:
Article “a” is used with words starting with consonant sounds.
Question 2:
My friend likes to be ________________engineer.
A. a
B. an
C. the
D. no article
Answer: option B
Explanation:
Article an is used with words starting with vowel sounds
Question 3:
Manjari can do the work if she has __ patience.
A. a
B. an
C. the
D. no article
Answer: option D
Explanation:
Here the sentence is general in nature which does not require either a or an hence no article is used.
Type 2: Definite Article
Question 1:
_____________ Dal Bati you cooked tasted good.
A. a
B. an
C. the
D. no article
Answer: The
Explanation:
Here the speaker is talking about the dish that was cooked yesterday that means a particular dish, hence we use ‘THE’.
Question 2:
Shilpa works for a group to help ___________ disabled.
A. a
B. an
C. the
D. no article
Answer: The
Explanation:
“The” is used before a noun. It is also used with the non-profitable organizations.
Question 3:
When we stayed at my Grannie’s house, we went to _____ lake every Sunday.
A. a
B. an
C. the
D. no article
Answer: option C
Explanation:
“The” is used before a noun. Because there is only one lake near to grannie’s house, “the” will be used.
How to Solve Tenses
Tenses denote the time of action. They show when the work was done, being done or will be done.
There are three types of tenses majorly as,
- Past Tense
- Present Tense
- Future Tense
We have discussed them one by one below and explained how to use them to solve Tenses questions.
Past Tense
The past tense in English grammar talks about the past. It is further divided into four types.
Simple Past
Used to indicate an action completed in the past.
Rule – Subject + Second form of verb (V2)
- Assertive Sentence: Subject + V2 + Object
For Example- She wrote an article. - Negative Sentences: Subject + didn’t + V1 + Object
For Example: She didn’t write an article. - Interrogative Sentences : Did + Subject + V1 + Object
For Example: Did she write an article? - Interrogative Negative Sentences: Did + Subject + not + V1 + Object
For Example: Did she not write an article?
Past Continuous Tense
Used to denote an action going on at some time in the past.
Rule – Subject + was/were + verb + ing
- Assertive Sentence: Subject + was/were + V1+ ing + Object
For Example: I was watching a movie. - Negative Sentences: Subject + was/were + not + ing + Object
For Example: I was not watching a movie - Interrogative Sentences: Was/were + Subject + ing+ Object
For Example: Was she watching a movie? - Interrogative Sentences: Was/were + Subject + not + ing+ Object
For Example: Was she not watching a movie?
Past Perfect Tense
Used to describe an action completed before a certain moment in the past, usually a long time ago. If two actions happened in the past, past perfect is used to show the action that took place earlier.
Rule – Subject + had + V3
- Assertive Sentences: Subject + had + V3 + Object
For Example: He had gone to Paris when I called him. - Negative Sentences: Subject + had + not + Object
For Example: He had not gone to Paris when I called him. - Interrogative Sentences: Had + Subject + V3 + Object
For Example:Had he gone to Paris when you called him? - Interrogative Negative Sentences: Had + Subject + not + V3 + Object
For Example: Had he not gone to Paris when you called him?
Present Tense
The present tense in English grammar is used to describe actions happening now, habitual actions, general truths, and near future events. It has four types:
Simple Present Tense
Used to express general truths, habits, and regular activities.
Rule – Subject + base form of verb (V1)
- Assertive Sentence: Subject + V1 (or V1+s/es) + Object
Example: She reads books every day. - Negative Sentences: Subject + do/does + not + V1 + Object
Example: She does not read books every day. - Interrogative Sentences: Do/Does + Subject + V1 + Object
Example: Does she read books every day? - Interrogative Negative Sentences: Do/Does + Subject + not + V1 + Object
Example: Does she not read books every day?
Present Continuous Tense
Used to describe actions happening right now or ongoing actions.
Rule – Subject + is/am/are + verb + ing
- Assertive Sentence: Subject + is/am/are + V1 + ing + Object
Example: He is playing football. - Negative Sentences: Subject + is/am/are + not + V1 + ing + Object
Example: He is not playing football. - Interrogative Sentences: Is/Am/Are + Subject + V1 + ing + Object
Example: Is he playing football? - Interrogative Negative Sentences: Is/Am/Are + Subject + not + V1 + ing + Object
Example: Is he not playing football?
Present Perfect Tense
Used to describe actions completed recently or actions with results connected to the present.
Rule – Subject + has/have + V3
- Assertive Sentence: Subject + has/have + V3 + Object
Example: She has finished her homework. - Negative Sentences: Subject + has/have + not + V3 + Object
Example: She has not finished her homework. - Interrogative Sentences: Has/Have + Subject + V3 + Object
Example: Has she finished her homework? - Interrogative Negative Sentences: Has/Have + Subject + not + V3 + Object
Example: Has she not finished her homework?
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Used to describe an action that started in the past and is still continuing.
Rule – Subject + has/have + been + verb + ing
- Assertive Sentence: Subject + has/have + been + V1 + ing + Object
Example: They have been studying since morning. - Negative Sentences: Subject + has/have + not + been + V1 + ing + Object
Example: They have not been studying since morning. - Interrogative Sentences: Has/Have + Subject + been + V1 + ing + Object
Example: Have they been studying since morning? - Interrogative Negative Sentences: Has/Have + Subject + not + been + V1 + ing + Object
Example: Have they not been studying since morning?
Future Tense
Future tense is used to talk about actions that will happen in the future. It has four types:
Simple Future Tense
Used to describe actions that will happen in the future.
Rule – Subject + will/shall + base form of verb (V1)
- Assertive Sentence: Subject + will/shall + V1 + Object
Example: She will start her new job tomorrow. - Negative Sentences: Subject + will/shall + not + V1 + Object
Example: She will not start her new job tomorrow. - Interrogative Sentences: Will/Shall + Subject + V1 + Object
Example: Will she start her new job tomorrow? - Interrogative Negative Sentences: Will/Shall + Subject + not + V1 + Object
Example: Will she not start her new job tomorrow?
Future Continuous Tense
Used to describe actions that will be ongoing at a certain time in the future.
Rule – Subject + will/shall + be + verb + ing
- Assertive Sentence: Subject + will/shall + be + V1 + ing + Object
Example: He will be working on the project tomorrow. - Negative Sentences: Subject + will/shall + not + be + V1 + ing + Object
Example: He will not be working on the project tomorrow. - Interrogative Sentences: Will/Shall + Subject + be + V1 + ing + Object
Example: Will he be working on the project tomorrow? - Interrogative Negative Sentences: Will/Shall + Subject + not + be + V1 + ing + Object
Example: Will he not be working on the project tomorrow?
Future Perfect Tense
Used to describe actions that will be completed before a certain time in the future.
Rule – Subject + will/shall + have + V3
- Assertive Sentence: Subject + will/shall + have + V3 + Object
Example: She will have completed the task by evening. - Negative Sentences: Subject + will/shall + not + have + V3 + Object
Example: She will not have completed the task by evening. - Interrogative Sentences: Will/Shall + Subject + have + V3 + Object
Example: Will she have completed the task by evening? - Interrogative Negative Sentences: Will/Shall + Subject + not + have + V3 + Object
Example: Will she not have completed the task by evening?
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Used to describe actions that will continue up to a point in the future.
Rule – Subject + will/shall + have been + verb + ing
- Assertive Sentence: Subject + will/shall + have been + V1 + ing + Object
Example: He will have been working here for five years by next month. - Negative Sentences: Subject + will/shall + not + have been + V1 + ing + Object
Example: He will not have been working here for five years by next month. - Interrogative Sentences: Will/Shall + Subject + have been + V1 + ing + Object
Example: Will he have been working here for five years by next month? - Interrogative Negative Sentences: Will/Shall + Subject + not + have been + V1 + ing + Object
Example: Will he not have been working here for five years by next month?
Also Check Out
Also Check:
- Basic Grammar – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Speech and Voices – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Tenses – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Tenses and Articles – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Idioms and Phrases – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Subject Verb Agreement – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Prepositions and Conjunction – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Selecting Words – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Relative Pronoun – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Sentence Completion- Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Basic Grammar
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Speech and Voices
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Tenses
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Tenses and Articles
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Idioms and Phrases
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Subject Verb Agreement
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Prepositions and Conjunction
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Selecting Words
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Relative Pronoun
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Sentence Completion
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others

 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates





Login/Signup to comment