Verbal Menu
- Basic Grammar
- Speech and Voices
- Tenses
- Articles
- Tenses and Articles
- Idioms and Phrases
- Subject Verb Agreement
- Prepositions and Conjunction
- Selecting Words
- Relative Pronoun
- Sentence Completion
- Sentence Ordering
- Contextual Vocabulary
- Jumbled Sentence
- Sentence Formation
- Error Identification
- Sentence Improvement and Construction
- Cloze Test
- Fill in the blanks
- Paragraph Ordering
- Para Jumbles
- Synonyms and Antonyms
- Synonyms
- Antonyms
- Reading Comprehension
- Get Off-campus Drive Updates
- Get Hiring Updates
- Contact US
PREPINSTA PRIME
Rules For Reading Comprehension
Rules For Reading Comprehension
Rules for Reading Comprehension are the key steps that help you read, understand, and remember information effectively.
On this page, you will find a complete guide to mastering reading comprehension – from identifying the main idea to spotting important details, understanding tone, and making inferences. These rules will help you read smarter, answer questions faster, and improve your overall accuracy.

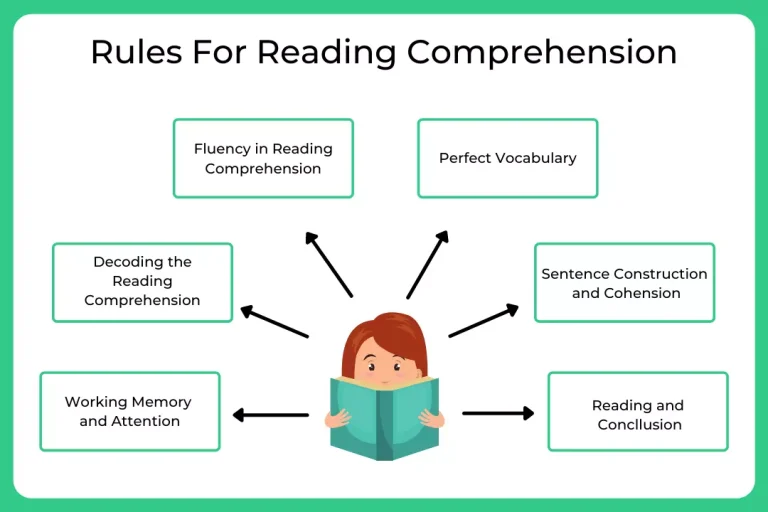
Skills Required for Reading Comprehension
Here are five essential skills needed for reading comprehension, and tips on what can help kids improve this skill.
Decoding the Reading Comprehension
Decoding is a vital step in the reading process. Decoding relies on an early language skill called Phonemic awareness. (This skill is part of an even broader skill called phonological awareness.)
Decoding also relies on connecting individual sounds to letters.
Fluency in Reading Comprehension
Fluency speeds up the rate at which they can read and understand the text.
Sounding out or decoding every word can take a lot of effort. Word recognition is the ability to recognize whole words instantly by sight, without sounding them out.
When kids can read quickly and without making too many errors, they are “fluent” readers.
Fluent readers read smoothly at a good pace. Reading fluency is essential for good reading comprehension.
Vocabulary
To understand what you’re reading, you need to understand most of the words in the text. Having a strong vocabulary is a key component of reading comprehension. Students typically learn the meaning of words through everyday experience and also by reading.
Sentence Construction and Cohesion
Most readers relate what they’ve read to what they know. So kids need to have the background or prior knowledge about the world when they read. They also need to be able to “read between the lines” and pull out meaning even when it’s not literally spelled out.
Example: A child is reading a story about a poor family in the 1930s. Knowing the Great Depression can provide insight into what’s happening in the story.
Reasoning and Conclusion
The capacity or the efficiency to reason a given passage and then draw conclusion from the stated facts is highly instrumental in solving a reading comprehension question. This is mostly required in an inferential based passage. Being able to understand the underlying meaning and idea.
Working Memory and Attention
When kids read, attention allows them to take in information from the text. Working memory allows them to hold on to that information and use it to gain meaning and build knowledge from what they’re reading.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Rules for Reading Comprehension
1. Read the Questions First
Before reading the passage, quickly glance at the questions. This helps you:
- Know what information to look for.
- Save time by focusing on relevant parts.
- Avoid rereading the passage multiple times.
Example:
If a question asks “What is the main reason the author mentions climate change in paragraph 2?” you will know to read paragraph 2 carefully and note any reasons given.
2. Skim Before You Read in Detail
Do a quick scan to understand the general topic and tone.
- Read headings, subheadings, and any highlighted words.
- Notice the first and last sentence of each paragraph.
- Identify keywords.
Tip: This step gives you a mental map of the passage.
3. Understand the Main Idea
Every passage has one central idea. Ask yourself:
- What is the author trying to say overall?
- Is the passage explaining, arguing, describing, or telling a story?
Example:
In an article about renewable energy, the main idea might be “Renewable energy is essential for a sustainable future.”
4. Pay Attention to Keywords and Transition Words
Transition words like however, therefore, in contrast, for example help you understand the flow of ideas.
- However = contrast
- Therefore = cause/effect
- For example = illustration
Why important? They help identify shifts in opinion, reasons, and conclusions.
5. Break Down Complex Sentences
Long sentences can hide the real meaning.
- Find the subject and verb first.
- Remove extra information (clauses) to understand the core idea.
Example:
“The policy, which was introduced by the government last year to control inflation, has had mixed results.”
Core idea: The policy has had mixed results.
6. Watch for Tone and Attitude
Tone shows the writer’s feelings. Is it positive, negative, neutral, sarcastic, or serious?
Clues come from:
- Word choice (fantastic vs terrible).
- The type of examples given.
7. Don’t Assume —Stick to the Text
Your answer must come from the passage, not from your own knowledge.
Even if you know extra facts, they may not match the author’s point of view.
8. Practice Inference
Some answers are not directly written — you must read between the lines.
- Look for hints, suggestions, or indirect meanings.
- Combine facts from the passage with logical thinking.
Example:
If the passage says “She closed the book and sighed deeply,” you might infer she felt disappointed or sad.
9. Manage Your Time
If you are stuck on a question:
- Skip it and return later.
- Avoid spending too much time on one answer.
- Keep an eye on the clock.
10. Review Before Submitting
If time allows:
- Recheck tricky answers.
- Ensure your answers match the question type (e.g., main idea vs detail).
- Look out for “except” or “not” in the question.
Rules for Reading Comprehension: Sample Question
Passage: 1
Read the comprehension below and answer the following questions.
Climate change is a pressing global issue that has far-reaching implications for our planet and future generations. It refers to long-term shifts in temperature patterns and weather conditions, largely resulting from human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation. The consequences of climate change are evident across the globe, affecting various aspects of the environment, economy, and society.
One of the most noticeable effects of climate change is the rise in global temperatures. As greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, accumulate in the atmosphere, they trap heat and contribute to the warming of the Earth. This phenomenon leads to melting glaciers, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events like hurricanes and heat waves.
Another consequence of climate change is the disruption of ecosystems and loss of biodiversity. Many plant and animal species struggle to adapt to the changing conditions, resulting in habitat loss and increased risk of extinction. Coral reefs, for example, are particularly vulnerable to rising ocean temperatures, leading to widespread coral bleaching and the collapse of these vibrant ecosystems.
In addition to environmental impacts, climate change poses significant challenges for human societies. Changing weather patterns affect agricultural productivity, leading to crop failures and food insecurity. Rising sea levels threaten coastal communities, displacing populations and increasing the risk of flooding. Moreover, the health of individuals is compromised as extreme heatwaves and the spread of diseases become more prevalent.
Addressing climate change requires global cooperation and concerted efforts. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, implementing sustainable land-use practices, and adopting greener transportation options are some of the measures needed to mitigate the effects of climate change. It is crucial to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and develop strategies to adapt to the changes already occurring.
Question: 1
What is climate change primarily caused by?
Options:
- Natural weather patterns.
- Human activities.
- Volcanic eruptions.
- Astronomical events.
Answer : Human activities
Question: 2
What is one noticeable effect of climate change?
Options:
- Decrease in global population.
- Expansion of polar ice caps.
- Increase in extreme weather events.
- Preservation of biodiversity.
Answer: Increase in extreme weather events.
Question: 3
How do greenhouse gases contribute to climate change?
Options:
- By cooling the Earth’s atmosphere.
- By causing ocean acidification.
- By trapping heat in the atmosphere.
- By preventing the formation of clouds.
Answer: By trapping heat in the atmosphere.
Common Types of Reading Comprehension Questions
- Main Idea – What is the central theme of the passage?
- Supporting Details – Which statement supports the author’s argument?
- Vocabulary in Context – What does the word ‘reluctant’ mean in paragraph 3?
- Inference – What can be understood from the author’s statement?
- Author’s Tone – What is the tone of the passage?
- Cause and Effect – What caused the change described in paragraph 4?
- Fact vs Opinion – Which statement is an opinion?
Also Check Out
Also Check:
- Basic Grammar – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Speech and Voices – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Tenses – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Tenses and Articles – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Idioms and Phrases – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Subject Verb Agreement – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Prepositions and Conjunction – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Selecting Words – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Relative Pronoun – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Sentence Completion- Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Basic Grammar
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Speech and Voices
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Tenses
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Tenses and Articles
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Idioms and Phrases
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Subject Verb Agreement
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Prepositions and Conjunction
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Selecting Words
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Relative Pronoun
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts - Sentence Completion
Questions
Rules
How to Solve Quickly
Tricks & Shortcuts
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others

 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates




Login/Signup to comment