0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
Searching In A Binary Search Tree In C++
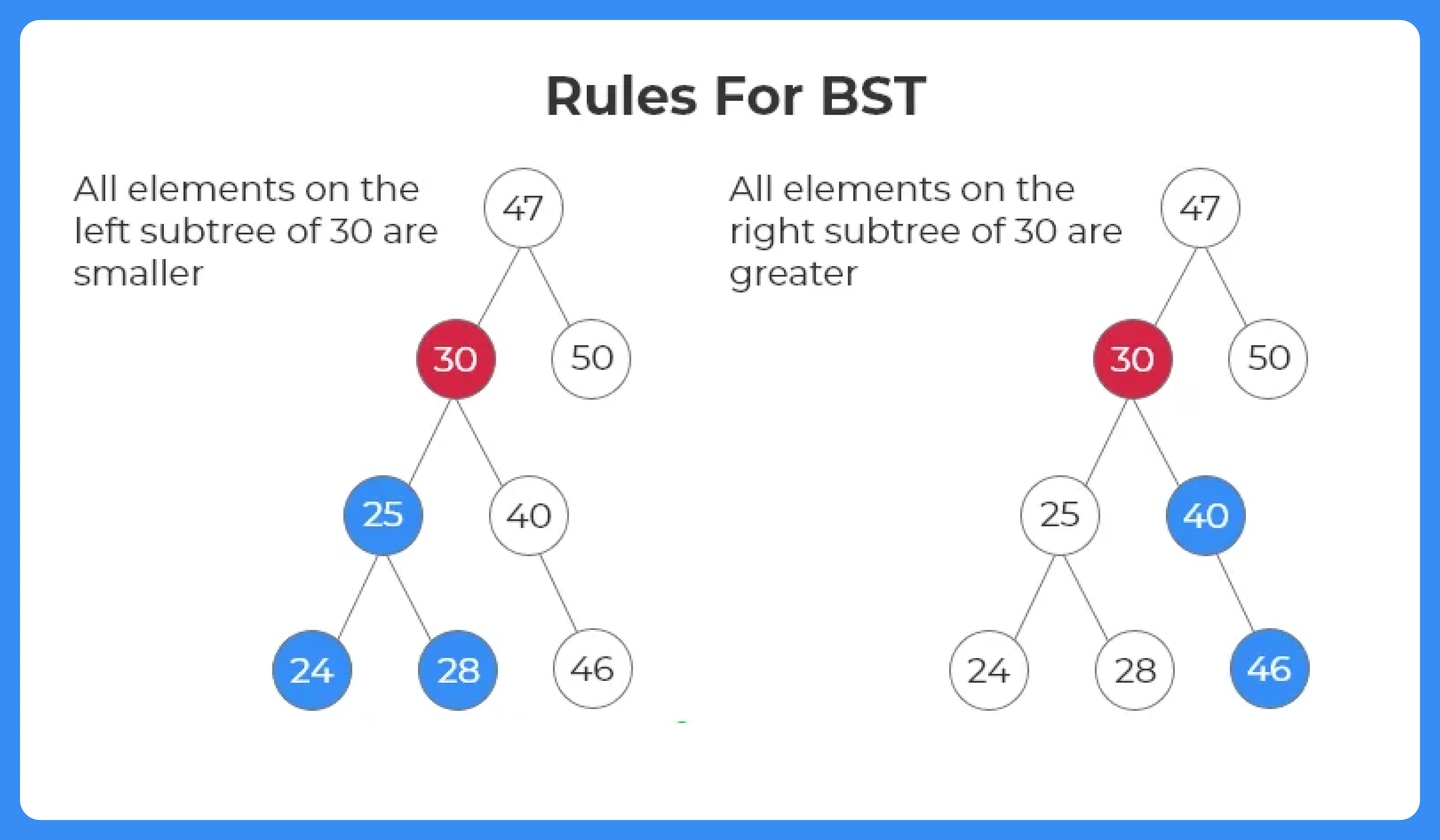
Searching In A Binary Search Tree
A binary search tree is a tree in which the data in left subtree is less than the root and the data in right subtree is greater than the root.Given a Binary Search tree and a key, check whether the key is present in the tree or not.

Code Implementation of Binary Search Tree Program in C++
Run
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Tree
{
public:
int data;
Tree *left = NULL, *right = NULL;
// Constructor initialised
Tree (int x)
{
data = x;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
int search (Tree * root, int value)
{
while (root != NULL)
{
if (value > root->data)
root = root->right;
else if (value < root->data)
root = root->left;
else
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void inorder_traversal (Tree * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder_traversal (root->left);
cout << root->data << " ";
inorder_traversal (root->right);
}
Tree *insert_node (Tree * root, int x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
Tree *temp = new Tree (x);
return temp;
}
if (root->data > x)
{
root->left = insert_node (root->left, x);
}
else
{
root->right = insert_node (root->right, x);
}
return root;
}
Tree *Delete (Tree * root, int x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
cout << "Node not found ";
return NULL;
}
if (root->data > x)
{
root->left = Delete (root->left, x);
}
else if (root->data < x)
{
root->right = Delete (root->right, x);
}
else
{
if (root->left == NULL)
{
Tree *temp = root->right;
free (root);
return temp;
}
else if (root->right == NULL)
{
Tree *temp = root->left;
free (root);
return temp;
}
else
{
Tree *temp = root->right;
while (temp->left != NULL)
temp = temp->left;
root->data = temp->data;
root->right = Delete (root->right, temp->data);
}
}
return root;
}
int main ()
{
Tree *root = new Tree (15);
root->left = new Tree (13);
root->right = new Tree (18);
root->left->left = new Tree (8);
root->left->right = new Tree (14);
root->right->left = new Tree (16);
root->right->right = new Tree (19);
int delete_item = 18;
cout << "Inorder Traversal :";
inorder_traversal (root);
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "17 inserted \n";
insert_node(root,17);
cout << "Inorder Traversal :";
inorder_traversal (root);
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "18 deleted \n";
Delete (root, delete_item);
cout << "Inorder Traversal :";
inorder_traversal (root);
cout << endl;
cout<< "Searching for element 15 \n";
cout << search (root, 15);
}
Output: Inorder Traversal :8 13 14 15 16 18 19 17 inserted Inorder Traversal :8 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 18 deleted Inorder Traversal :8 13 14 15 16 17 19 Searching for element 15
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others

 0
0



Login/Signup to comment