Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS)
Tree Traversals: Breadth First Search (BFS)
The term traversal means to visit each node in a tree exactly once. In linear lists the order of traversal is vividly first to last. However, in trees there exists no such natural linear order.
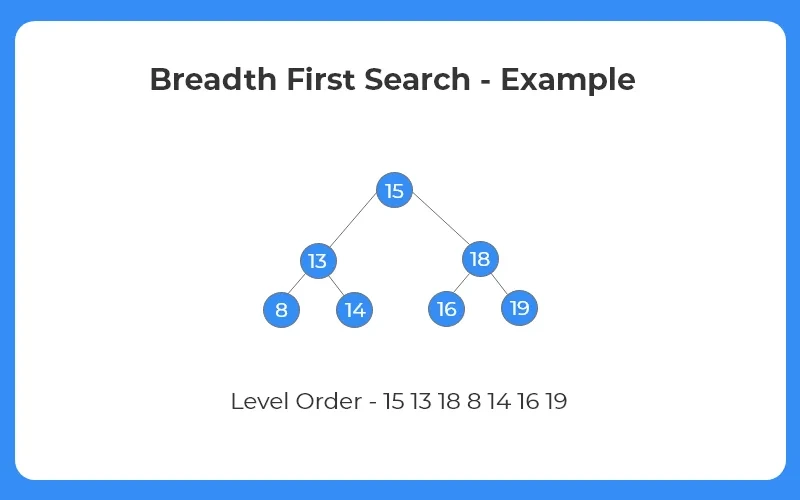
In Tree Traversal : Breadth-First Search (BFS) traversal visits tree nodes level by level, starting from the root and moving left to right at each level. It uses a queue data structure to ensure nodes are processed in the order they are discovered. This traversal is especially useful for finding the shortest path and analyzing the structure of a tree.

More Information About BFS:
- BFS can be defined as an algorithm dedicated to traversing a tree structure, level by level or depth by depth.
- This category of tree traversal initializes from the root node and explores all the adjacent nodes on a current level and then moves on to the next level, and so on.
Why Queue is better to traverse than Recursion?
- Queues improves the time complexity because recursion gives the time complexity of O(2^n) in the worst case, whereas queue gives time complexity of O(n).
- Height of the tree is first calculated to print level order but this is not required in queue.
- Implementation is shorter in queues.
Algorithm (Queue):
- If the root is NULL, return.
- Otherwise push the root in queue.
- Print the node’s data and add its left and right child.
- Pop the node from the queue.
- Repeat until the queue is empty.
Algorithm (Recursion):
- Calculate height of tree.
- Initialize loop from 0 to height
- Recursive call for left and right subtree and decrease level by 1.
- If level is 0, print the nodes
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Code Implementation for Tree Traversal : Breadth-First Search (BFS) in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode (int x):val (x), left (NULL), right (NULL)
{ }
};
void bfs (TreeNode * root)
{
queue <TreeNode*>q;
q.push (root);
while (!q.empty ())
{
int num_nodes = q.size ();
for (int i = 0; i < num_nodes; i++)
{
TreeNode *curr_node = q.front ();
q.pop ();
cout << curr_node->val << " "; if (curr_node->left)
{
q.push (curr_node->left);
}
if (curr_node->right)
{
q.push (curr_node->right);
}
}
}
}
int main ()
{
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode (10);
root->left = new TreeNode (20);
root->right = new TreeNode (30);
root->left->left = new TreeNode (40);
root->left->right = new TreeNode (50);
cout<<"BFS Traversal of the tree is : ";
bfs (root);
return 0;
}
Output:
10 20 30 40 50
Explanation:
- The code defines a TreeNode structure where each node stores a value and pointers to its left and right child.
- The bfs() function performs Breadth First Search using a queue to traverse the tree level by level.
- The root node is pushed into the queue first, and nodes are processed until the queue becomes empty.
- For every node removed from the queue, its value is printed and its left and right children are added to the queue if they exist.
- In main(), a binary tree is manually created and the BFS traversal is called to display nodes in level order.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| BFS Traversal | O(n) | O(n) |
| Queue Operations | O(1) per operation | O(n) |
| Tree Node Creation | O(1) per node | O(1) |
| Total Program Execution | O(n) | O(n) |
Conclusion:
Breadth First Search (BFS) is an important tree traversal technique that visits nodes level by level, starting from the root node. By using a queue, it ensures that all nodes at the current level are processed before moving to the next level, making the traversal systematic and easy to understand.
BFS is widely used in problems where level-wise processing is required, such as finding the shortest path or checking the structure of a tree. Its simple logic and predictable traversal order make it a reliable choice for many tree-based applications.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment