Binary Search Tree Program in C++
Binary Search Tree Program in C++
Binary Search Tree Program in C++ – A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a special type of binary tree that keeps its elements in a sorted manner. In a BST, for every node, the left child holds a smaller value, and the right child holds a larger value. This makes searching, inserting, and deleting elements efficient.
A binary search tree is a tree in which the data in left subtree is less than the root and the data in right subtree is greater than the root. In this article , we will cover all the basics of binary search tree.

Rules of a Binary Search Tree in C++
Before writing the program, it’s important to understand the fundamental rules that define a Binary Search Tree:
Each node has at most two children – a left child and a right child.
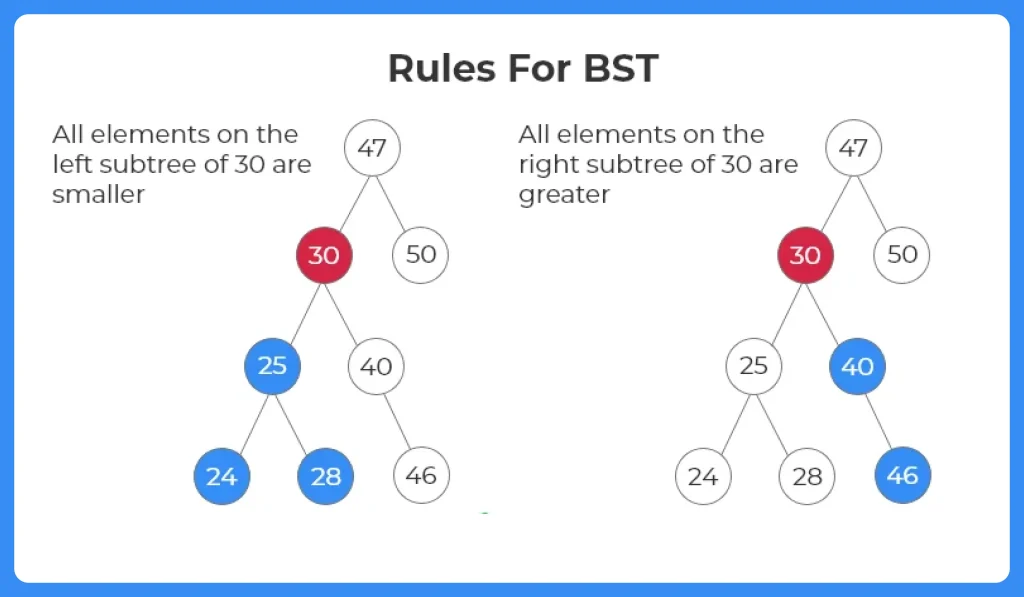
- Left Subtree Rule – All nodes in the left subtree of a node must have values less than the value of the node.
- Right Subtree Rule – All nodes in the right subtree of a node must have values greater than the value of the node.
- No duplicate nodes – A BST does not allow duplicate elements (each value is unique).
- Recursive Structure – The left and right subtrees themselves must also be binary search trees.
These rules ensure that operations like search, insert, and delete can be done efficiently, typically in O(log n) time if the tree is balanced.

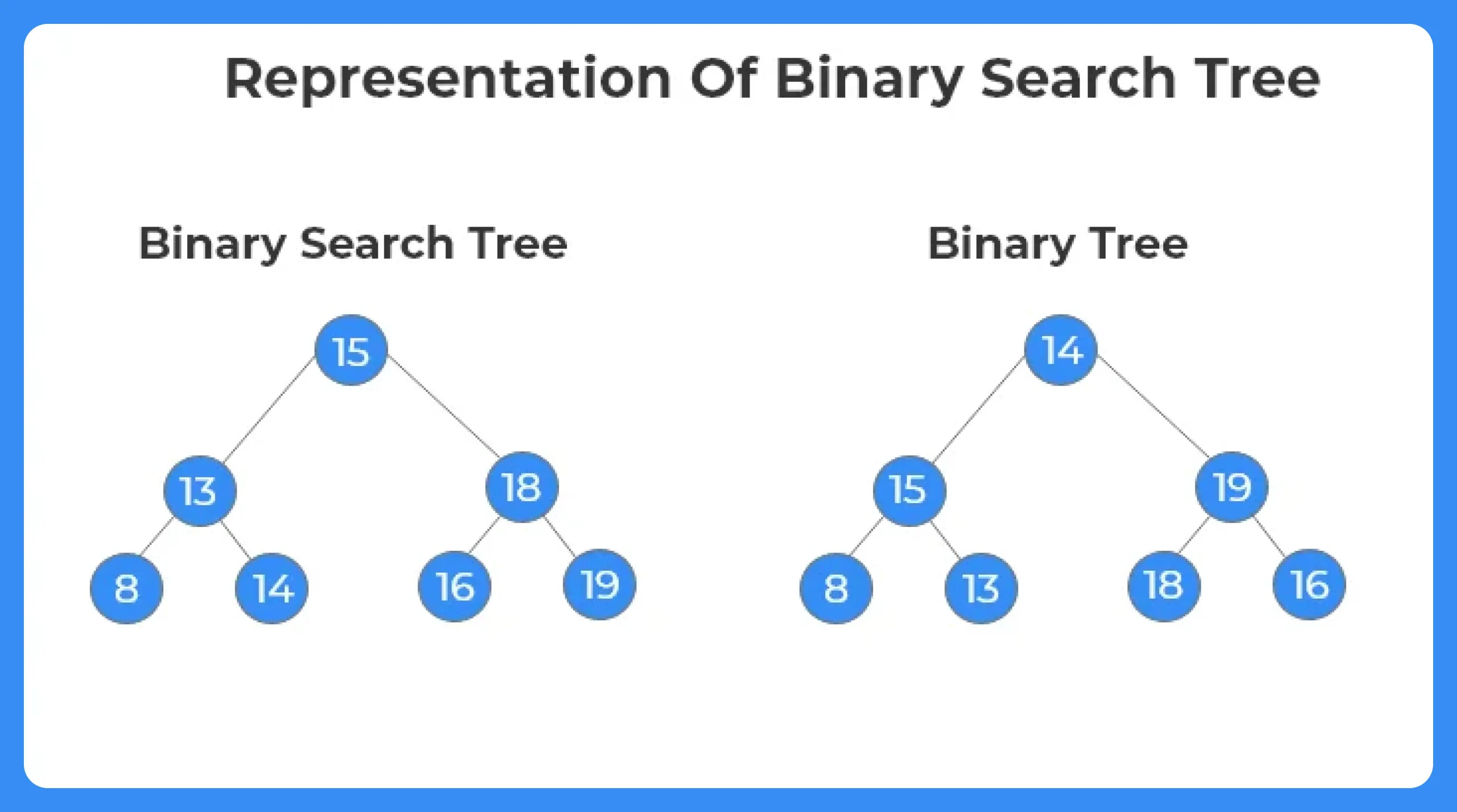
Reprsentation Of BST:
- The representation of a BST is similar to that of a binary tree. The order of a BST is ‘2’. Each node can have at most two children.
- Only difference between the two is that there is a certain criteria of arrangement or insertion of the elements based on their comparisons with the root node and the sub tree segment they are added to.

Operations In A BST:
- Traversal
- Searching
- Insertion
- Deletion
Features Of A BST:
- Fast look-up.
- Efficient addition and removal of items.
- Used to implement dynamic set of items

Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Code For Binary Search Tree
Binary Search Tree code helps in organizing data so that searching, inserting, and deleting elements becomes faster and more efficient. It follows a structured left-right pattern that keeps operations predictable and optimized.
- Each node stores a value where the left child holds smaller values and the right child holds larger values, ensuring quick lookup.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
};
struct node *create_node (int data)
{
struct node *new_node = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
new_node->data = data;
new_node->left = NULL;
new_node->right = NULL;
return new_node;
}
struct node *insert_node (struct node *root, int data)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return create_node (data);
}
if (data < root->data)
{
root->left = insert_node (root->left, data);
}
else
{
root->right = insert_node (root->right, data);
}
return root;
}
struct node *search_node (struct node *root, int data)
{
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
{
return root;
}
if (data < root->data)
{
return search_node (root->left, data);
}
else
{
return search_node (root->right, data);
}
}
void inorder (struct node *root)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
inorder_traversal (root->left);
printf ("%d ", root->data);
inorder_traversal (root->right);
}
}
int main ()
{
struct node *root = NULL;
root = insert_node (root, 50);
insert_node (root, 30);
insert_node (root, 20);
insert_node (root, 40);
insert_node (root, 70);
insert_node (root, 60);
insert_node (root, 80);
inorder (root);
return 0;
}
Output :
20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Explanation:
- The code uses a structure node to represent each Binary Search Tree (BST) node, storing data along with left and right pointers to its children.
- The insert_node() function inserts values into the BST recursively by comparing the new value with the root and placing it in the correct left or right subtree.
- The search_node() function follows the same BST property to quickly find a node by moving left for smaller values and right for larger ones.
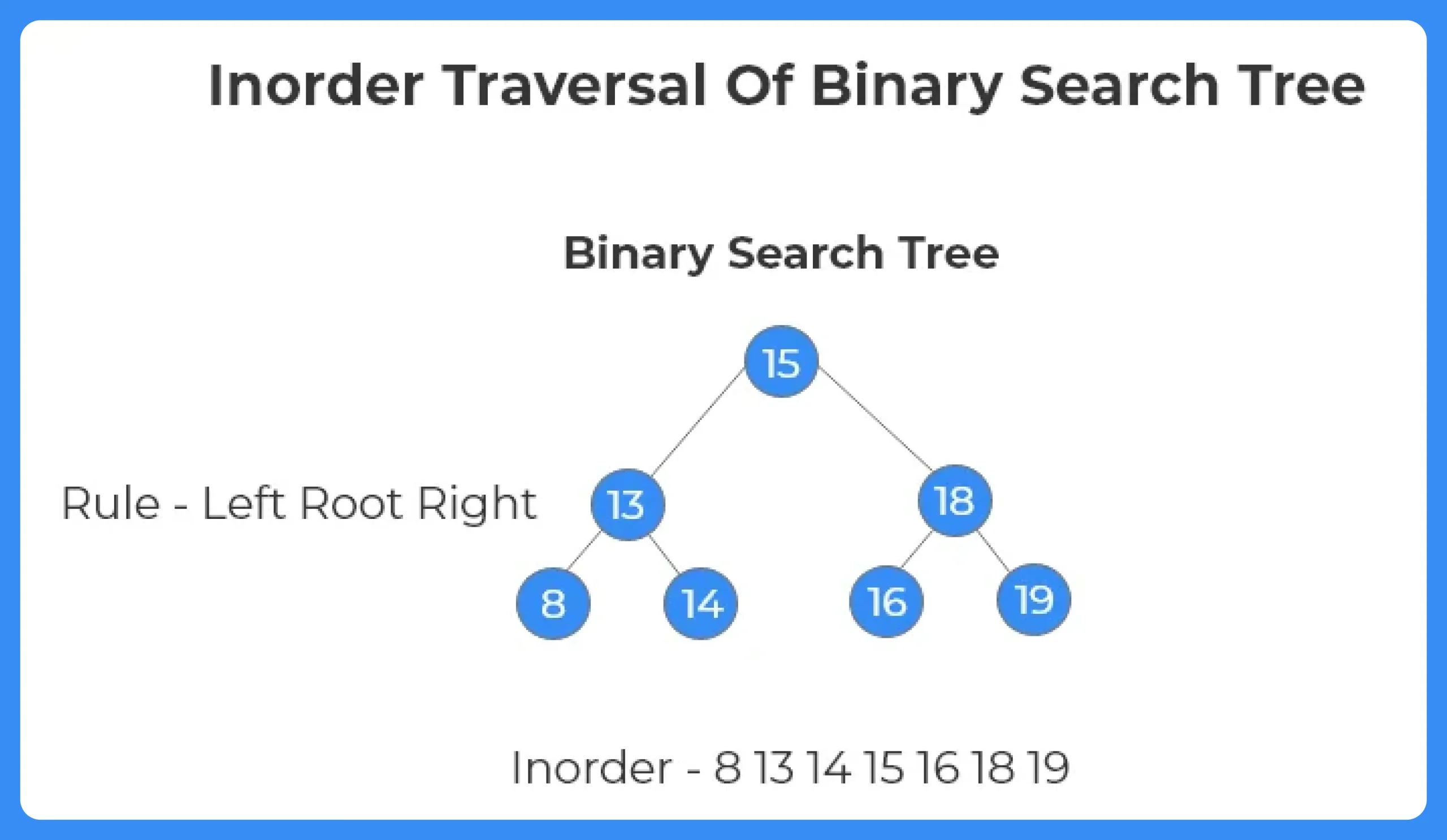
- The inorder() traversal visits the left subtree, prints the node, and then visits the right subtree, resulting in a sorted sequence of the BST values.
- In main(), multiple values are inserted into the BST, and an inorder traversal prints the elements in ascending order: 20 30 40 50 60 70 80.
Time & Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion in BST | O(h) — h = height of tree (Best: O(log n), Worst: O(n)) | O(h) |
| Search in BST | O(h) — h = height of tree (Best: O(log n), Worst: O(n)) | O(h) |
| Inorder Traversal | O(n) | O(n) — recursion stack |
| Overall Complexity | O(n) | O(n) |
Advantages Of BST:
- Inorder Traversal gives sorted order of elements.
- Easy to implement order statistics.
- Helpful in range queries.
Disadvantages Of BST:
- The cost of operations may be high.
- Shape of tree depends on insetions and may be degenerated.
To Wrap It Up:
Binary Search Trees (BSTs) are one of the most important topics in data structures. They help us store and manage data in a sorted way, which makes searching, inserting, and deleting values much faster compared to basic data structures like arrays or linked lists.
In a BST, each value is placed in a specific position by following some simple rules smaller values go to the left and larger ones to the right. This keeps the tree organized and easy to work with.
In this blog, we learned how to create a BST in C++, how to insert values, how to search for a specific number, and how to print all values in sorted order using inorder traversal.
FAQs - Binary Search Tree Program in C++
FAQs - Binary Search Tree Program in C++
Deleting a node in a BST is tricky because you must maintain the BST rules. There are 3 cases:
- Case 1: Node has no children (Leaf Node) – Just remove the node.
- Case 2: Node has one child – Replace the node with its child.
- Case 3: Node has two children – Find the inorder successor (smallest in the right subtree) or inorder predecessor (largest in the left subtree), replace the node’s value with it, and delete that successor/predecessor node.
- Average case time complexity: O(log n)
- Worst case time complexity: O(n)
This worst case happens when the tree becomes unbalanced — for example, inserting sorted elements creates a skewed tree (like a linked list), where each node only has one child.
You can check using inorder traversal. If the values from the traversal are in strictly increasing order, it’s a BST.
Another way is to use a recursive function and check if each node lies between a valid range:
- Left subtree: values should be < current node
- Right subtree: values should be > current node
A regular BST does not guarantee balance, so operations can take O(n) time in the worst case.
A Balanced BST like AVL or Red-Black Tree keeps the height minimal using rotations. This ensures all operations (insert, delete, search) stay close to O(log n) even in the worst case.
By default, BSTs do not allow duplicates. But if needed, you can:
- Store duplicates in the left or right subtree consistently (e.g., duplicates go right).
- Or, modify the node structure to include a count field to track how many times a value has occurred.
Instead of recursion, use a loop:
- Start at the root and traverse down the tree.
- Use a while loop to find the correct position based on the value.
- Create a new node and link it to its parent.
This method avoids the call stack and is useful when recursion depth becomes a concern in large trees.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment