Insertion In B-Tree C++
Insertion in B-Tree C++
Insertion In B-Tree C++ – A B – Tree can be defined as a multi-way search tree of order m. All the values of a node that appear on the leftmost child of the node are smaller than the first value of that node. Similarly, all the values that appear on the rightmost child of a node are greater than the last value of that node.
B-Trees are self-balancing tree data structures widely used in databases and file systems where large blocks of data are handled. Unlike binary search trees, B-Trees can store multiple keys in a single node and have more than two children. This makes them ideal for systems that read and write large chunks of data at once. One of the most essential operations in a B-Tree is insertion.
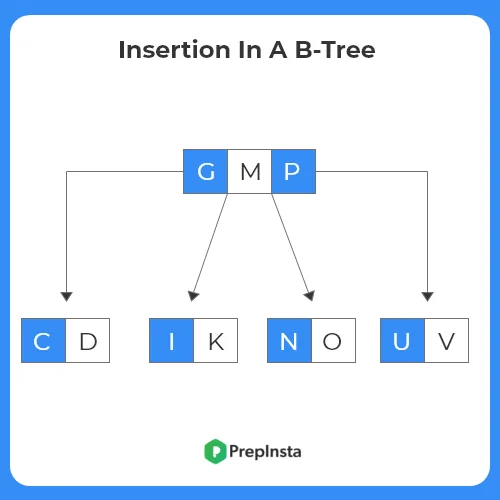
Insertion Operation in B-Tree
The goal of insertion in a B-Tree is to add a new key while maintaining the sorted order and balanced structure of the tree.
Here’s how it works:
- If the node where we want to insert is not full, we simply insert the key in the correct position.
- If the node is full, we split it into two nodes and move the middle key up to the parent.
- This process may propagate all the way to the root, potentially increasing the height of the tree.
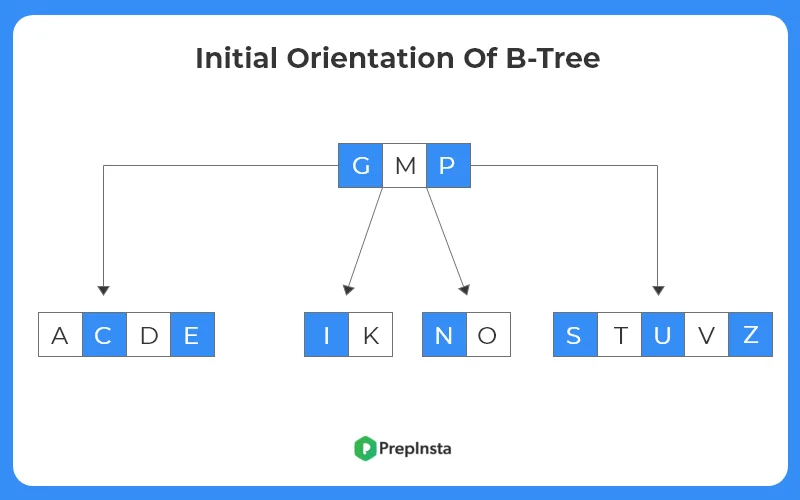

- If we see the image, the last node violates the properties of the B-tree, since it contains 5 keys.
- The node splits from the middle element ‘ U ‘ , which moves upwards to the parent node.
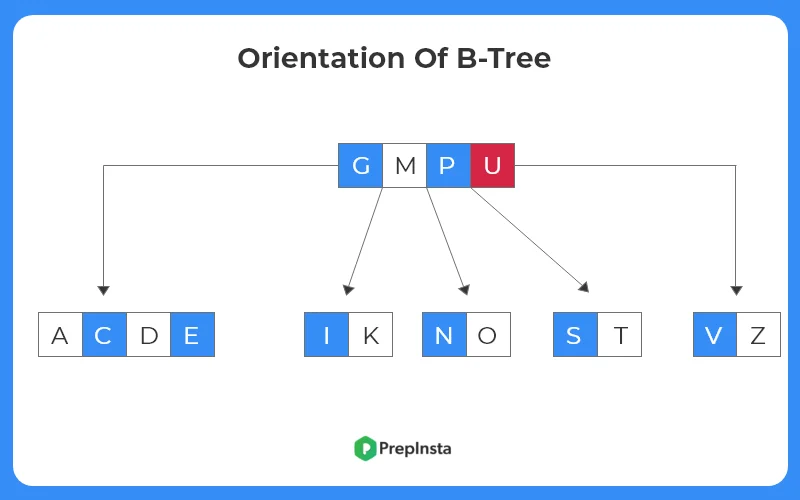

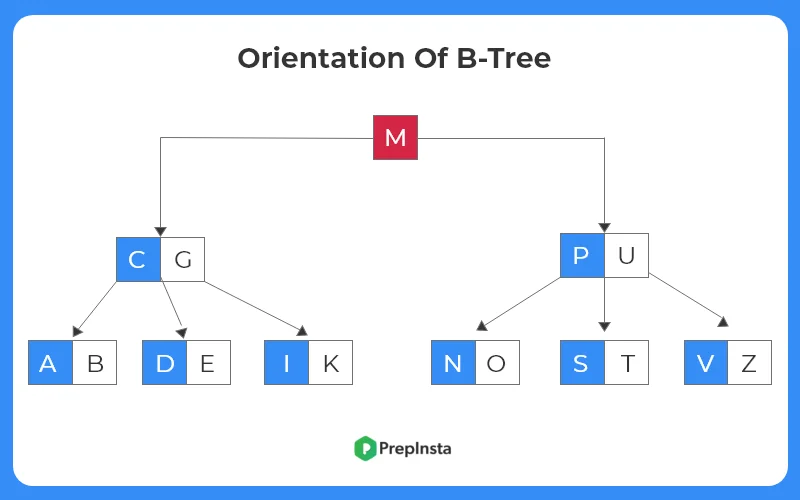
Insert ‘ B ‘
- Now, let us insert an element to the B-tree.
- Let the element to be inserted is ‘ B ‘.
- Since ‘ B ‘ comes before ‘ G ‘ in alphabetical order, it is to be inserted in the node 2.
- The node tree structure after insertion as follows.
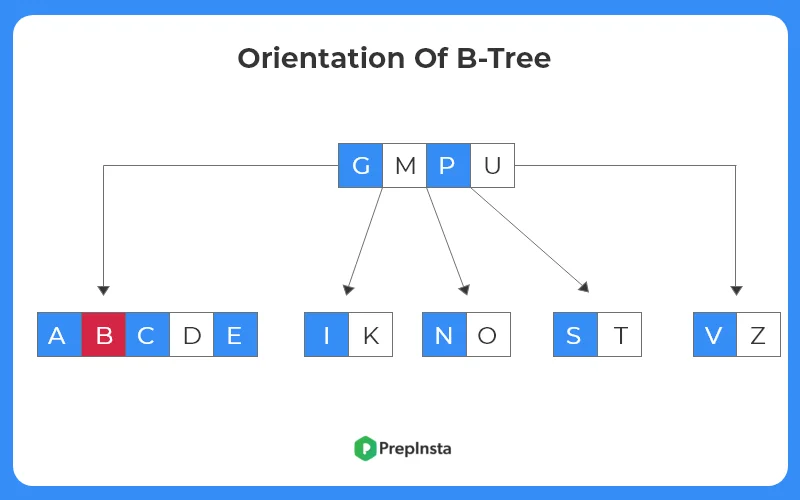

- As discussed before, each node can have at most 4 keys, we can see here, the root node violates this property.
- Hence, the root node is split from the middle.
- The middle element ‘ M ‘ moves upward and becomes the new root to the tree structure.
- The tree structure after alteration is shown as follows

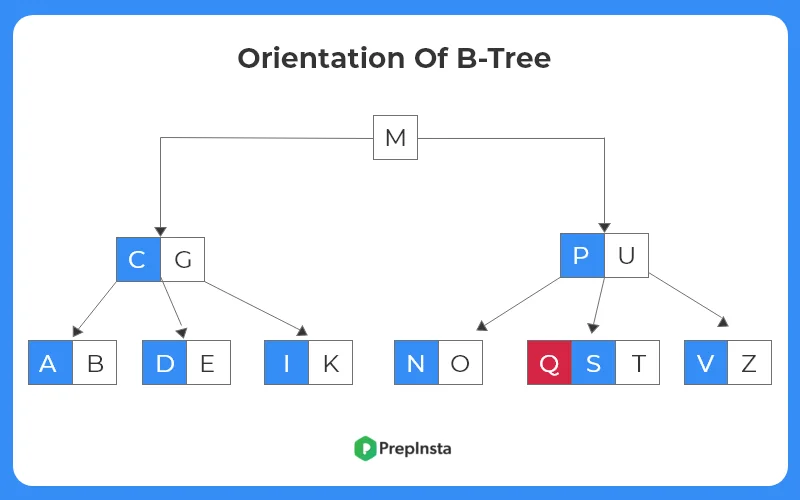
Insert ‘ Q ‘
- If we see the alphabetical order, the new node to be inserted Q lies after P.
- Thus Q, will be inserted in the second last node before ‘ S ‘ and ‘ T ‘.
- The tree structure after new insertion is shown as follows.

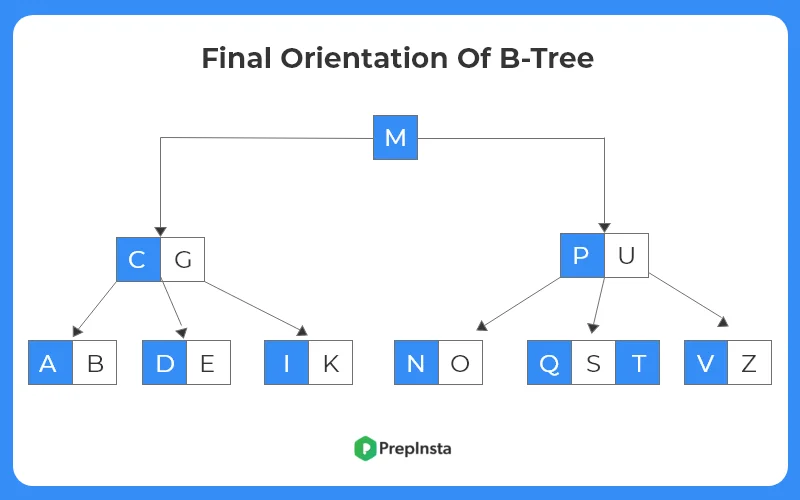
- Since Q is inserted at the leaf node which could accommodate more nodes.
- The final tree structure is shown as follows.

Code for Implementation of Insertion in B-Tree in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class BTreeNode {
int *keys;
int t; // Minimum degree
BTreeNode **C;
int n;
bool leaf;
public:
BTreeNode(int _t, bool _leaf);
void insertNonFull(int k);
void splitChild(int i, BTreeNode *y);
void traverse();
friend class BTree;
};
class BTree {
BTreeNode *root;
int t;
public:
BTree(int _t) {
root = nullptr;
t = _t;
}
void traverse() {
if (root != nullptr) root->traverse();
}
void insert(int k);
};
BTreeNode::BTreeNode(int t1, bool leaf1) {
t = t1;
leaf = leaf1;
keys = new int[2*t - 1];
C = new BTreeNode *[2*t];
n = 0;
}
void BTree::insert(int k) {
if (root == nullptr) {
root = new BTreeNode(t, true);
root->keys[0] = k;
root->n = 1;
} else {
if (root->n == 2*t - 1) {
BTreeNode *s = new BTreeNode(t, false);
s->C[0] = root;
s->splitChild(0, root);
int i = (s->keys[0] < k) ? 1 : 0; s->C[i]->insertNonFull(k);
root = s;
} else {
root->insertNonFull(k);
}
}
}
void BTreeNode::insertNonFull(int k) {
int i = n - 1;
if (leaf) {
while (i >= 0 && keys[i] > k) {
keys[i + 1] = keys[i];
i--;
}
keys[i + 1] = k;
n++;
} else {
while (i >= 0 && keys[i] > k)
i--;
if (C[i + 1]->n == 2*t - 1) {
splitChild(i + 1, C[i + 1]);
if (keys[i + 1] < k) i++; } C[i + 1]->insertNonFull(k);
}
}
void BTreeNode::splitChild(int i, BTreeNode *y) {
BTreeNode *z = new BTreeNode(y->t, y->leaf);
z->n = t - 1;
for (int j = 0; j < t - 1; j++) z->keys[j] = y->keys[j + t];
if (!y->leaf) {
for (int j = 0; j < t; j++) z->C[j] = y->C[j + t];
}
y->n = t - 1;
for (int j = n; j >= i + 1; j--)
C[j + 1] = C[j];
C[i + 1] = z;
for (int j = n - 1; j >= i; j--)
keys[j + 1] = keys[j];
keys[i] = y->keys[t - 1];
n++;
}
void BTreeNode::traverse() {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (!leaf) C[i]->traverse();
cout << " " << keys[i]; } if (!leaf) C[i]->traverse();
}
// Example usage
int main() {
BTree t(3); // A B-Tree with minimum degree 3
t.insert(10);
t.insert(20);
t.insert(5);
t.insert(6);
t.insert(12);
t.insert(30);
t.insert(7);
t.insert(17);
cout << "Traversal of B-tree is: ";
t.traverse();
return 0;
}
Output:
Traversal of B-tree is: 5 6 7 10 12 17 20 30
Time Complexity:
- Best/Average Case (Search/Insert): O(log n)
- Worst Case (Split at each level): O(log n)
Space Complexity:
- O(n), where n is the number of keys in the tree.
Conclusion
Insertion in B-Trees is more complex than in binary search trees but highly efficient for large datasets, especially in disk-based storage systems. The key idea is to maintain the balance of the tree while allowing multiple keys in each node.
By properly handling splits and key promotions, we ensure fast search and insert operations in logarithmic time. Mastering B-Tree insertion builds a strong foundation for understanding advanced storage structures used in databases and file systems.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
FAQs - Insertion In B-Tree C++
FAQs - Insertion In B-Tree C++
The most challenging part of inserting into a B-Tree is handling node splits while maintaining the B-Tree properties.
Unlike a BST, where insertion is straightforward, in a B-Tree:
- When a node is full, it must be split into two nodes.
- The median key is moved up to the parent.
- If the parent is also full, this splitting process can cascade upward until the root, potentially increasing the tree height.
- This requires careful pointer adjustments and key shifting within arrays, making the logic more complex than BST insertion.
If the root is full before insertion:
- Create a new root node.
- Make the old root a child of the new root.
- Split the old root into two nodes, moving the middle key to the new root.
- Insert the new key into the correct subtree.
This process ensures the B-Tree height increases while still maintaining the minimum degree constraints.
The minimum degree t determines:
- The minimum number of keys per non-root node (t – 1).
- The maximum number of keys per node (2t – 1).
Impact on insertion: - Higher t means fewer splits, as nodes can hold more keys.
- Smaller t means more frequent splits, increasing insertion overhead.
- It directly impacts disk I/O in external storage applications, where large t reduces the number of node accesses.
Splitting before descent is essential because:
- If you try to insert into a full node, there’s no room for the new key.
- By splitting before descent, you ensure that you never try to insert into a full node, which simplifies the insertion logic.
- This pre-splitting approach also avoids unnecessary recursive restructuring.
Insertion in a B-Tree remains O(log n) because:
- The tree height is logarithmic relative to the number of keys due to its balanced nature.
- Even if multiple splits occur, each split takes O(1) time per node (moving keys and pointers).
- At most one split occurs per level, and there are only O(log n) levels.
Thus, insertion requires O(log n) node accesses.
When using arrays in C++:
- Keys and child pointers are stored in contiguous memory blocks.
- Splitting involves shifting elements within arrays, which can be done efficiently using memmove() or manual loops.
- Array indices make child navigation straightforward but require careful handling of capacity.
When using linked structures:
- Nodes are dynamically allocated, and child pointers are linked.
- Splitting involves creating new nodes and updating links rather than shifting array elements.
- This is more flexible but has higher memory overhead and less cache locality.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment