Deletion In AVL Tree In Java
Deletion in an AVL Tree
AVL tree is self balancing tree in which for all nodes, the difference of height between the left subtree and the right subtree is less than or equal to 1. In this article, we will see how to perform deletion in AVL tree.

Why AVL tree?
Most of the BST operations (e.g., search, max, min, insert, delete.. etc) take O(h) time where h is the height of the BST. The cost of these operations may become O(n) for a skewed Binary tree. If we make sure that height of the tree remains O(Logn) after every insertion and deletion, then we can guarantee an upper bound of O(Logn) for all these operations. The height of an AVL tree is always O(Logn) where n is the number of nodes in the tree
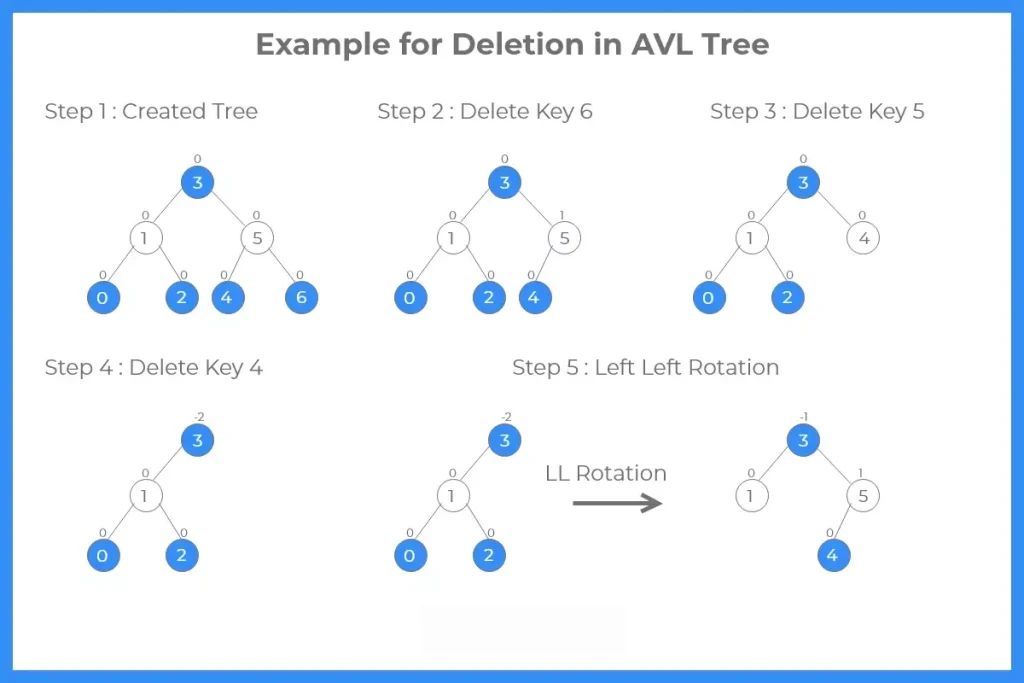
Deletion in an AVL Tree
- Deletion in an AVL tree is similar to that in a BST.
- Deletion of a node tends to disturb the balance factor. Thus to balance the tree, we again use the Rotation mechanism.
- Deletion in AVL tree consists of two steps:
- Removal of the node: The given node is removed from the tree structure. The node to be removed can either be a leaf or an internal node.
- Re-balancing of the tree: The elimination of a node from the tree can cause disturbance to the balance factor of certain nodes. Thus it is important to re- balance the b_fact of the nodes; since the balance factor is the primary aspect that ensures the tree is an AVL Tree.
Note: There are certain points that must be kept in mind during a deletion process.
- If the node to be deleted is a leaf node, it is simply removed from the tree.
- If the node to be deleted has one child node, the child node is replaced with the node to be deleted simply.
- If the node to be deleted has two child nodes then,
- Either replace the node with it’s inorder predecessor , i.e, the largest element of the left sub tree.
- Or replace the node with it’s inorder successor , i.e, the smallest element of the right sub tree.
class Node
{
int key, height;
Node left, right;
Node (int d)
{
key = d;
height = 1;
}
}
class AVLTree
{
Node root;
int height (Node N)
{
if (N == null)
return 0;
return N.height;
}
Node rotateRight (Node b)
{
Node a = b.left;
Node c = a.right;
a.right = b;
b.left = c;
b.height = Math.max (height (b.left), height (b.right)) + 1;
a.height = Math.max (height (a.left), height (a.right)) + 1;
return a;
}
Node rotateLeft (Node a)
{
Node b = a.right;
Node c = b.left;
b.left = a;
a.right = c;
a.height = Math.max (height (a.left), height (a.right)) + 1;
b.height = Math.max (height (b.left), height (b.right)) + 1;
return b;
}
int getBalance (Node N)
{
if (N == null)
return 0;
return height (N.left) - height (N.right);
}
Node insert (Node node, int key)
{
if (node == null)
return (new Node (key));
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert (node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert (node.right, key);
else
return node;
node.height = 1 + Math.max (height (node.left), height (node.right));
int balance = getBalance (node);
if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.key)
return rotateRight (node);
if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.key)
return rotateLeft (node);
if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.key)
{
node.left = rotateLeft (node.left);
return rotateRight (node);
}
if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.key)
{
node.right = rotateRight (node.right);
return rotateLeft (node);
}
return node;
}
Node minValueNode (Node node)
{
Node temp;
for (temp = node; temp.left != null; temp = temp.left);
return temp;
}
Node deleteNode (Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return root;
if (key < root.key)
root.left = deleteNode (root.left, key);
else if (key > root.key)
root.right = deleteNode (root.right, key);
else
{
if ((root.left == null) || (root.right == null))
{
Node temp = null;
if (temp == root.left)
temp = root.right;
else
temp = root.left;
if (temp == null)
{
temp = root;
root = null;
}
else
root = temp;
}
else
{
Node temp = minValueNode (root.right);
root.key = temp.key;
root.right = deleteNode (root.right, temp.key);
}
}
if (root == null)
return root;
root.height = Math.max (height (root.left), height (root.right)) + 1;
int balance = getBalance (root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance (root.left) >= 0)
return rotateRight (root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance (root.left) < 0)
{
root.left = rotateLeft (root.left);
return rotateRight (root);
}
if (balance < -1 && getBalance (root.right) <= 0)
return rotateLeft (root);
if (balance < -1 && getBalance (root.right) > 0)
{
root.right = rotateRight (root.right);
return rotateLeft (root);
}
return root;
}
void preOrder (Node node)
{
if (node != null)
{
System.out.print (node.key + " ");
preOrder (node.left);
preOrder (node.right);
}
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree ();
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 3);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 1);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 5);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 0);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 2);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 4);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 6);
System.out.println ("Preorder traversal is : ");
tree.preOrder (tree.root);
tree.root = tree.deleteNode (tree.root, 6);
tree.root = tree.deleteNode (tree.root, 5);
tree.root = tree.deleteNode (tree.root, 4);
System.out.println ("");
System.out.println ("Preorder traversal after " +
"deletion of [6,5,4] :");
tree.preOrder (tree.root);
}
}
Output:
Preorder traversal is : 3 1 0 2 5 4 6 Preorder traversal after deletion of [6,5,4] : 1 0 3 2
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment