Search a Node in a Binary search tree in C++
Searching in binary search tree
Here in this section , we will discuss the C++ program to search a node in binary search tree. Searching in Binary Search tree is the most basic program that you need to know, it has some set of rules that you need to follow, given below .
In a Binary Search Tree, searching is efficient because at each step we compare the key with the current node and move either to the left subtree (if the key is smaller) or to the right subtree (if the key is greater), reducing the search space by half.

What is Searching in a BST?
Searching in a Binary Search Tree means finding whether a given key (value) exists in the tree or not. This operation starts from the root node and compares the given key with the current node’s value. Based on the comparison, the search continues either in the left subtree or the right subtree.
Algorithm :
Consider the value that you need to search in a Binary search tree is called as data.
- Start from the root node of BST
- If the (root node value) == data, value found
- Else, if (root node value) > data, then iterate to the left subtree
- Else if (root node value) < data, then iterate to the right subtree
- Keep on doing this until you find the value
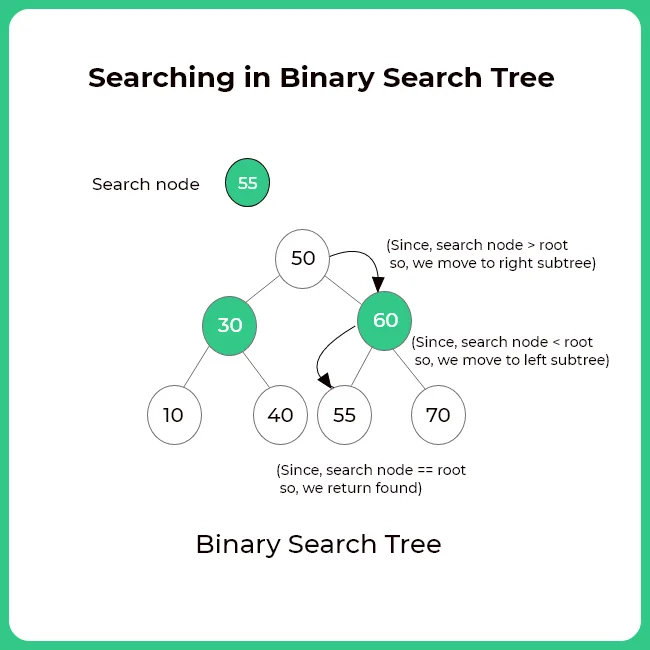
Rules for Searching in a Binary Search Tree (C++)
When searching for an element in a Binary Search Tree using C++, the following rules are applied:
- If the root pointer is NULL, the tree is empty and the element is not present.
- Start searching from the root node.
- If the value of the current node is equal to the key, the search is successful and the node is returned.
- If the key is less than the current node’s value, move to the left child (root->left).
- If the key is greater than the current node’s value, move to the right child (root->right).
- Repeat the comparison process recursively or iteratively until the key is found.
- If the pointer becomes NULL during traversal, the element does not exist in the Binary Search Tree.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Code Implementation for searching in a Binary Search Tree in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Tree
{
public:
int data;
Tree *left = NULL, *right = NULL;
// Constructor initialised
Tree (int x)
{
data = x;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
int search (Tree * root, int value)
{
while (root != NULL)
{
if (value > root->data)
root = root->right;
else if (value < root->data)
root = root->left;
else
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void inorder_traversal (Tree * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder_traversal (root->left);
cout << root->data << " "; inorder_traversal (root->right);
}
int main ()
{
Tree *root = new Tree (15);
root->left = new Tree (13);
root->right = new Tree (18);
root->left->left = new Tree (8);
root->left->right = new Tree (14);
root->right->left = new Tree (16);
root->right->right = new Tree (19);
cout << "Inorder Traversal of the Binary Search Tree:";
inorder_traversal (root);
cout << endl;
cout<< "Searching for element 15 \n";
cout <<"Element found? : "<< search (root, 15);
}
Output:
Inorder Traversal of the Binary Search Tree:8 13 14 15 16 18 19 Searching for element 15 Element found? : 1
Explanation:
- The Tree class defines a Binary Search Tree node with data, left, and right pointers.
- The constructor initializes the node value and sets child pointers to NULL.
- The search() function efficiently finds an element by comparing values and moving left or right.
- The inorder_traversal() function prints BST elements in sorted order using recursion.
- The main() function builds the BST, displays inorder traversal, and searches for a value.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Inorder Traversal | O(n) | O(h) |
| Search in BST | O(log n) / O(n) | O(1) |
| Tree Node Creation | O(1) per node | O(1) |
| Total Program Execution | O(n) | O(h) |
Conclusion:
The search algorithm in a Binary Search Tree works by comparing the target value with the current node and moving left or right accordingly. By following this structured approach, it efficiently reduces the search space and quickly determines whether the node exists in the tree.
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Thanks for the clarity on the concept.