0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
OS Menu
- OS Home
- Introduction
- CPU Scheduling
- What is Process?
- Process Lifecyle
- Process Control Block
- Process Scheduling
- Context Switching
- CPU Scheduling
- FCFS Scheduling
- SJF (non-preemptive)
- SJF (Preemptive - SRTF)
- Round Robin
- Priority Scheduling
- Convoy Effect
- Scheduler Vs Dispatcher
- Preemptive Vs non
- Preemptive scheduling
- Non preemptive scheduling
- Process Synchronization
- Deadlock
- Popular Algorithms
- Memory Management
- Memory Management Introduction
- Partition Allocation Method
- First Fit
- First Fit (Intro)
- First Fit in C
- First Fit in C++
- First Fit in Python
- First Fit in Java
- Best Fit
- Best Fit (Intro)
- Best Fit in C
- Best Fit in C++
- Best Fit in Java
- Worst Fit
- Worst Fit (Intro)
- Worst Fit in C++
- Worst Fit in C
- Worst Fit in Java
- Worst Fit in Python
- Next Fit
- First fit best fit worst fit (Example)
- Memory Management 2
- Memory Management 3
- Page Replacement Algorithms
- LRU (Intro)
- LRU in C++
- LRU in Java
- LRU in Python
- FIFO
- Optimal Page Replacement algorithm
- Optimal Page Replacement (Intro)
- Optimal Page Replacement Algo in C
- Optimal Page Replacement Algo in C++
- Optimal Page Replacement Algo in Java
- Optimal Page Replacement Algo in Python
- Thrashing
- Belady’s Anomaly
- Static vs Dynamic Loading
- Static vs Dynamic Linking
- Swapping
- Translational Look Aside Buffer
- Process Address Space
- Difference between Segmentation and Paging
- File System
- Off-campus Drive Updates
- Get Hiring Updates
- Contact us
What is an Operating System?
Operating System
An operating system is a software program that manages computer hardware and software resources, providing a platform for other software applications to run. It acts as an intermediary between the user and the computer hardware, enabling users to interact with the system and execute tasks effectively.

Purpose of an Operating System
The primary purpose of an operating system is to provide an environment in which applications can run smoothly and utilize the computer’s resources effectively. It manages memory, processors, input/output devices, and other system resources to ensure optimal performance and stability.
Evolution of Operating Systems:
Operating systems have evolved significantly over the years, adapting to the changing needs of computer users. Let’s take a brief look at the evolution of operating systems:
- Early Operating Systems:
In the early days of computing, operating systems were simple and mainly focused on managing hardware resources. Examples of early operating systems include the Batch Processing System and the Multiprogramming System. - Mainframe Operating Systems:
With the advent of mainframe computers, operating systems became more sophisticated and capable of supporting multiple users and tasks simultaneously. Examples of mainframe operating systems include IBM’s z/OS and UNIVAC’s EXEC 8. - Personal Computer Operating Systems:
The rise of personal computers brought about the need for operating systems tailored to individual users. Operating systems such as Microsoft Windows and Apple macOS became popular choices for personal computer users, offering user-friendly interfaces and a wide range of applications. - Modern Operating Systems:
Today, modern operating systems like Linux have gained popularity due to their open-source nature, flexibility, and robustness. Mobile operating systems like Android and iOS have also emerged, powering smartphones and tablets with advanced features and seamless app integration.
General Tasks carried by OS –
- Handling UI
- Handling input/output
- Process management
- File Management
- Memory Management
- Security
- other devices control like printer, SD card
Main Jobs handled by OS:
- Device Management
- File Management
- Memory Management
- Process Management
- UI Management
- Storage Management
- Application Handling
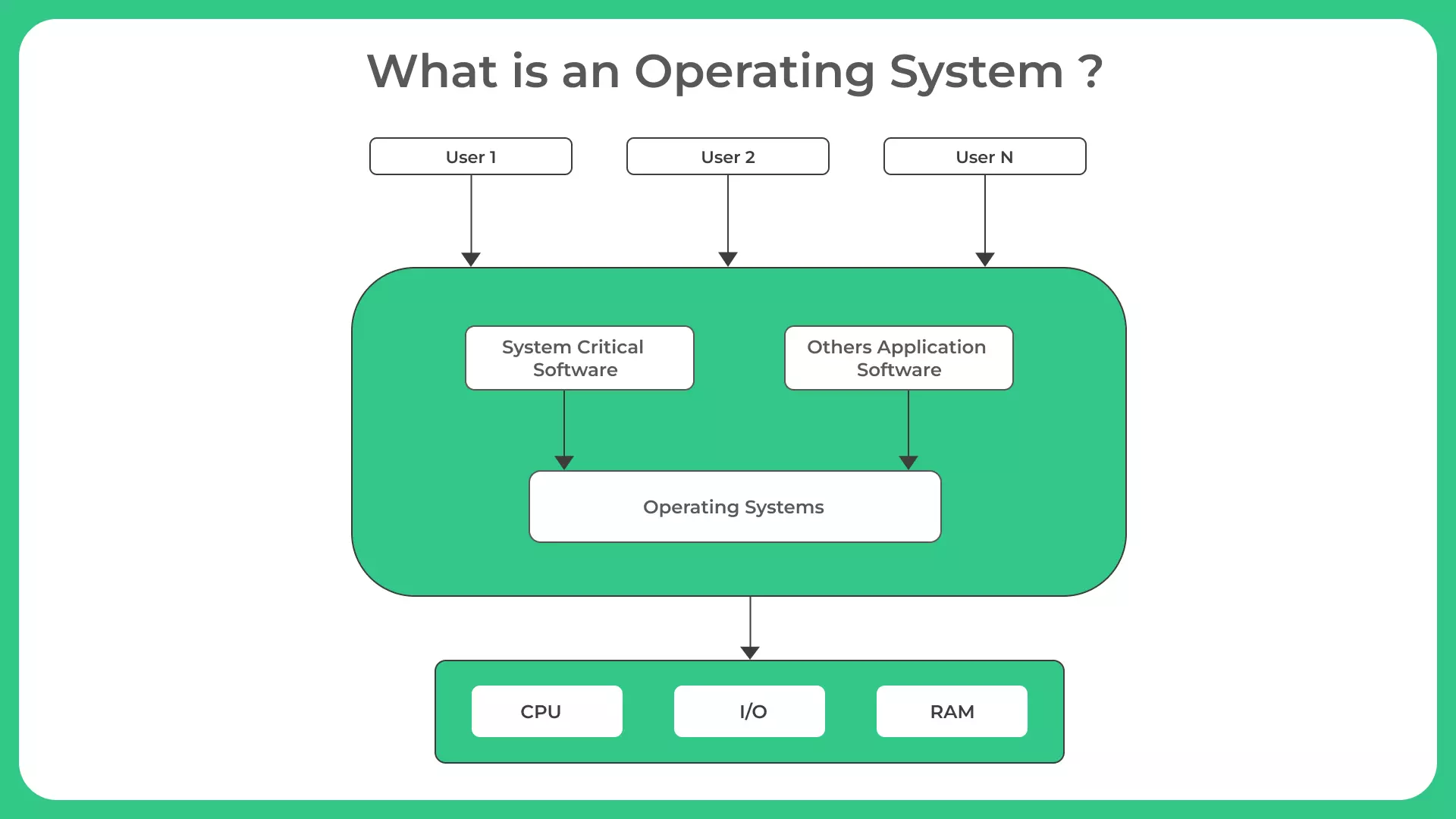
An operating system performs various functions to facilitate the operation of a computer system. These functions include:
Process management: It manages the execution of processes, scheduling them for execution, and allocating system resources to them.
Memory management: It controls the allocation and deallocation of memory space to processes, ensuring efficient memory utilization.
File system management: It provides a hierarchical structure for organizing and accessing files on storage devices.
Device management: It interacts with hardware devices, such as printers, scanners, and disk drives, to facilitate data transfer and communication.
User interface: It provides a means for users to interact with the system, such as through a command-line interface or a graphical user interface.
There are several popular operating systems in use today, catering to different computing needs. Let’s explore some of the widely used operating systems:
Windows
Microsoft Windows is a widely used operating system for personal computers. It offers a user-friendly interface, extensive software compatibility, and a range of features for both home and business users.
macOS
macOS is the operating system developed by Apple Inc. for its Macintosh computers. Known for its sleek design and seamless integration with other Apple devices, macOS provides a user-friendly and secure computing experience.
Linux
Linux is an open-source operating system that has gained popularity for its stability, security, and versatility. It powers a wide range of devices, from servers to smartphones, and offers a vast array of software options.
Android
Android is a mobile operating system developed by Google. It powers a majority of smartphones and tablets worldwide, offering a customizable user interface, extensive app ecosystem, and integration with Google services.
iOS
iOS is the operating system developed by Apple Inc. for its mobile devices, including iPhones and iPads. It provides a seamless and secure user experience, along with access to a wide range of apps optimized for Apple devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an operating system plays a crucial role in the functioning of a computer system. It acts as a bridge between the hardware and software, enabling users to interact with the system and run applications efficiently. Understanding the purpose, functions, types, and components of operating systems provides a solid foundation for navigating the world of computing.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others

 0
0


Login/Signup to comment