0
Notifications Mark All Read
No New notification
- Login
- Get Prime
Difference Between Scheduler and Dispatcher
Difference between Scheduler & Dispatcher
On this page, we will learn the concepts of scheduler and dispatcher and also compare the differences between the two.
Schedulers selects a process out of the several processes that need to be executed. Dispatcher performs the function of switching contexts, switching to user mode and many other.

Scheduler
Schedulers are system software that handle the removal of the running process from the CPU and the selection of another process. It selects a process out of several processes that need to be executed.
There are three types of schedulers in an operating system.
1. Long Term Scheduler
It is also known as a job. It decides the degree of multi-programming of the system. In simple words, when multiple processes are waiting for the execution, processes having small size are placed in the secondary storage. Then long term scheduler selects the processes from the job queue and brings that process to the ready queue in the main memory.
2. Medium-Term Scheduler
A running process needs input/output operations. The process goes to waiting state when not in need. This process is called suspended. However, CPU is used to its full utilization, while running the other process. Meanwhile, the suspended process is transferred back to the secondary memory. Now, the transferred process can return back to the main memory and continue its execution. This transfer of suspended process to the secondary memory is called swapping out and bringing the process back to the main memory is known as swapping in. It removes processes from memory, and thus, reduces the degree of multi-programming.
3. Short Term Scheduler
It is also known as CPU scheduler. It selects a process in the ready queue that should be allocated for execution. When it picks the process from the ready queue, the previous task goes to the waiting state. This process is completed in a fraction of seconds to avoid wasting the CPU time.
3. Short Term Scheduler
It is also known as CPU scheduler. It selects a process in the ready queue that should be allocated for execution. When it picks the process from the ready queue, the previous task goes to the waiting state. This process is completed in a fraction of seconds to avoid wasting the CPU time.
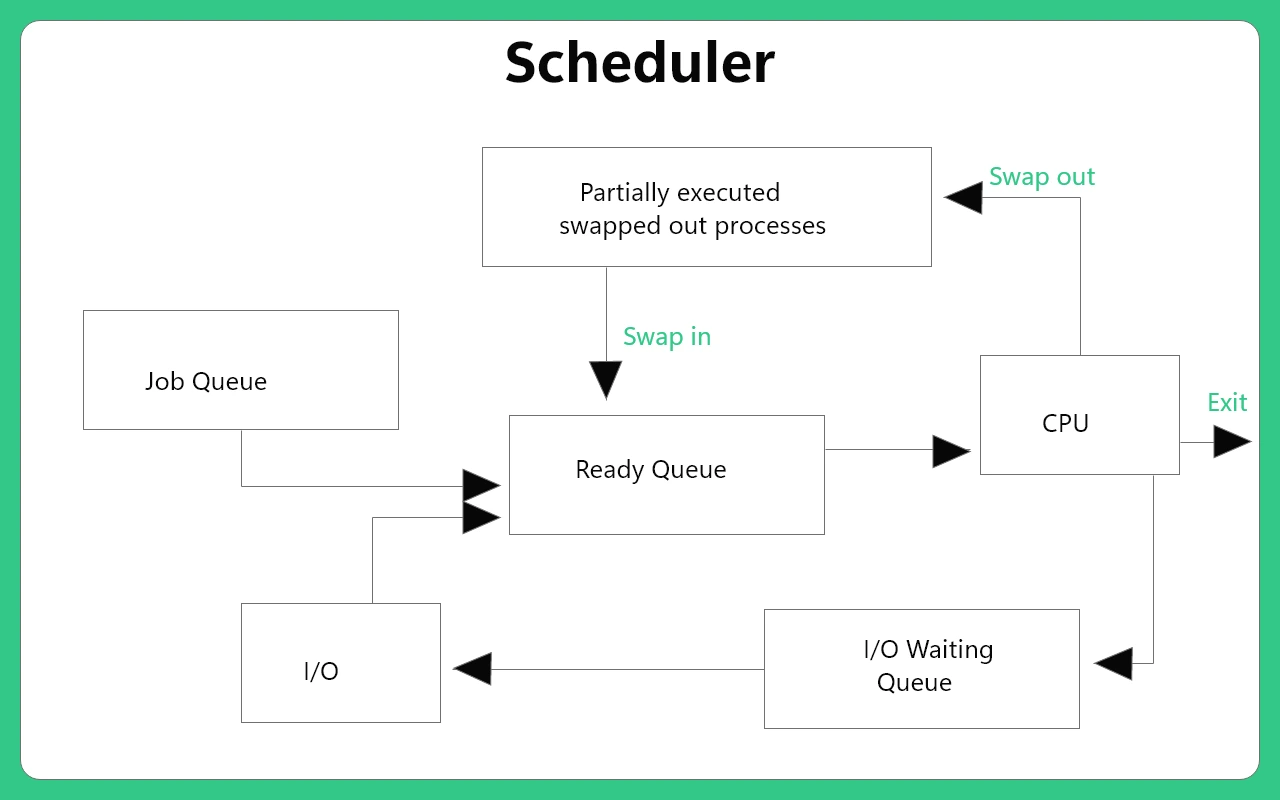
Difference between Scheduler and Dispatcher
[table id=624 /]Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






 0
0


Login/Signup to comment