0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
Difference Between Segmentation and Paging in Operating System (OS)
Segmentation And Paging
Memory management in the operating system is an important functionality, which allocates memory to the process for its execution and deallocates the memory when the process is no longer needed There are two management schemes called segmentation and paging in the operating system.
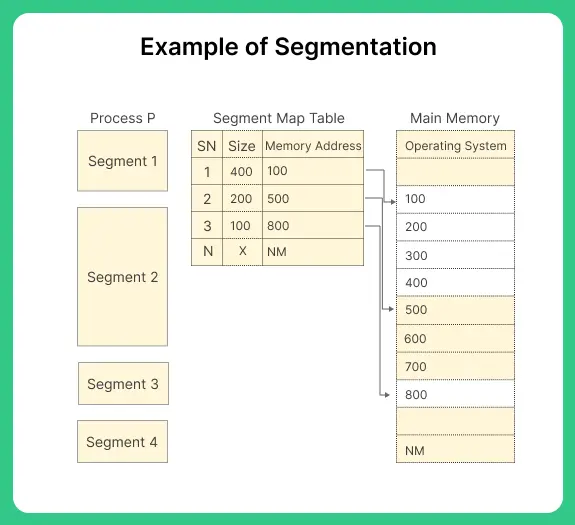
Segmentation
- Segmentation is a memory management technique which divides the computer’s primary memory into segments or sections.
- It is a scheme in which page is of the variable block size.
- In segmentation, the process is divided into two variable size segments, and these segments are loaded into logical memory address space.
- The process is segmented module by module. However, in the main memory, the only segment of the process is a store.
- The segment table is used to keep the records of the segment, its size, and its memory address.
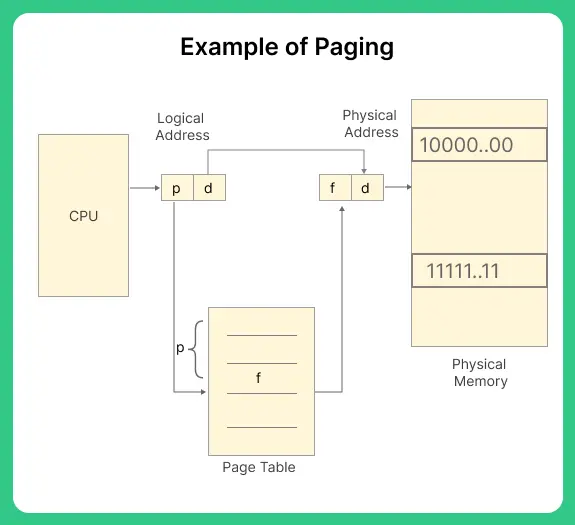
Paging
- Paging is also a memory management scheme.
- It allows a process to be stored in the memory in a non-contiguous manner.
- It resolves the issue of external fragmentation. In paging, the physical and logical memory spaces are divided into the same fixed-sized blocks.
- The blocks of physical memory are called frames, and the blocks of logical memory are called pages.
- When a process is executed the process pages from logical memory space are loaded into the frames of physical memory address space.
- Then the address generated by CPU for accessing the frame is divided into two parts:- page number and page offset. Page table maps logical address to the physical address.
Paging vs Segmentation
| Paging | Segmentation |
|---|---|
| A page is a physical unit of information. | A segment is a logical unit of information. |
| Frames on main memory are required | No frames are required |
| The page is of the fixed block size | The page is of the variable block size |
| It leads to internal fragmentation | It leads to external fragmentation |
| The page size is decided by hardware in paging | Segment size is decided by the user in segmentation |
| It does not allow logical partitioning and protection of application components | It allows logical partitioning and protection of application components |
| Paging involves a page table that contains the base address of each page | Segmentation involves the segment table that contains the segment number and offset |
Learn more about segmentation here.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others

 0
0


Login/Signup to comment