0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
Preemptive Scheduling vs Non Preemptive Scheduling
Difference between Preemptive and Non preemptive scheduling
On this page, we will learn the concepts of preemptive scheduling and non preemptive scheduling and also get to now about the difference between preemptive vs non preemptive scheduling.

Preemptive Scheduling vs Non Preemptive Scheduling
The process manager in an operating system is responsible for process scheduling. It is an operating system activity in which a running process is removed from the CPU and is replaced by another high priority process following certain set of rules. Process scheduling is an important part of a multi programming system where multiple processes need execution. The process of scheduling can be categorised into two, Pre-emptive and non-pre-emptive scheduling.
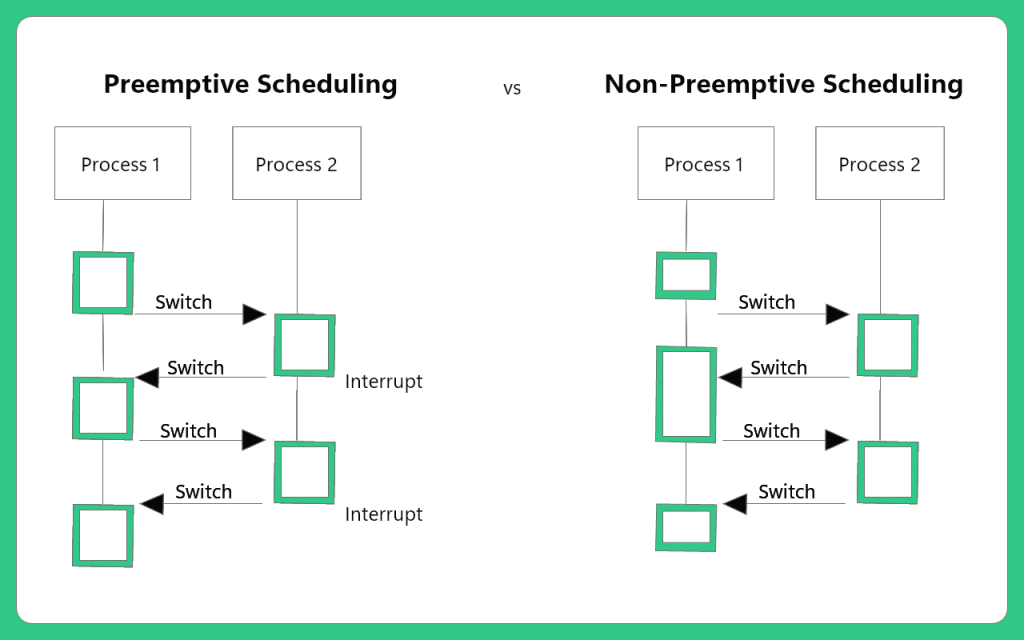
Pre-emptive Scheduling
Scheduling in which a process is switched from the running state to the ready state and from the waiting state to the ready state. In this concept, the CPU is allocated to the process for a limited time and is again taken back when its time is over. The current state of the program is saved and is resumed again when the process is assigned to the CPU.
Non Pre-emptive Scheduling
In this case, once the process is allocated the CPU, it is only released when the processing is over. The states into which a process switches are the running state to the waiting state. It is an approach in which a process is not interrupted when it is under process by the CPU.
Learn more about Non preemptive scheduling through Shortest Job First Scheduling (SJF) algorithm here.
Key Differences
[table id=632 /]
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others

 0
0


Login/Signup to comment