0
Notifications Mark All Read
No New notification
- Login
- Get Prime
Process Life Cycle in Operating System OS
Process Life Cycle in OS
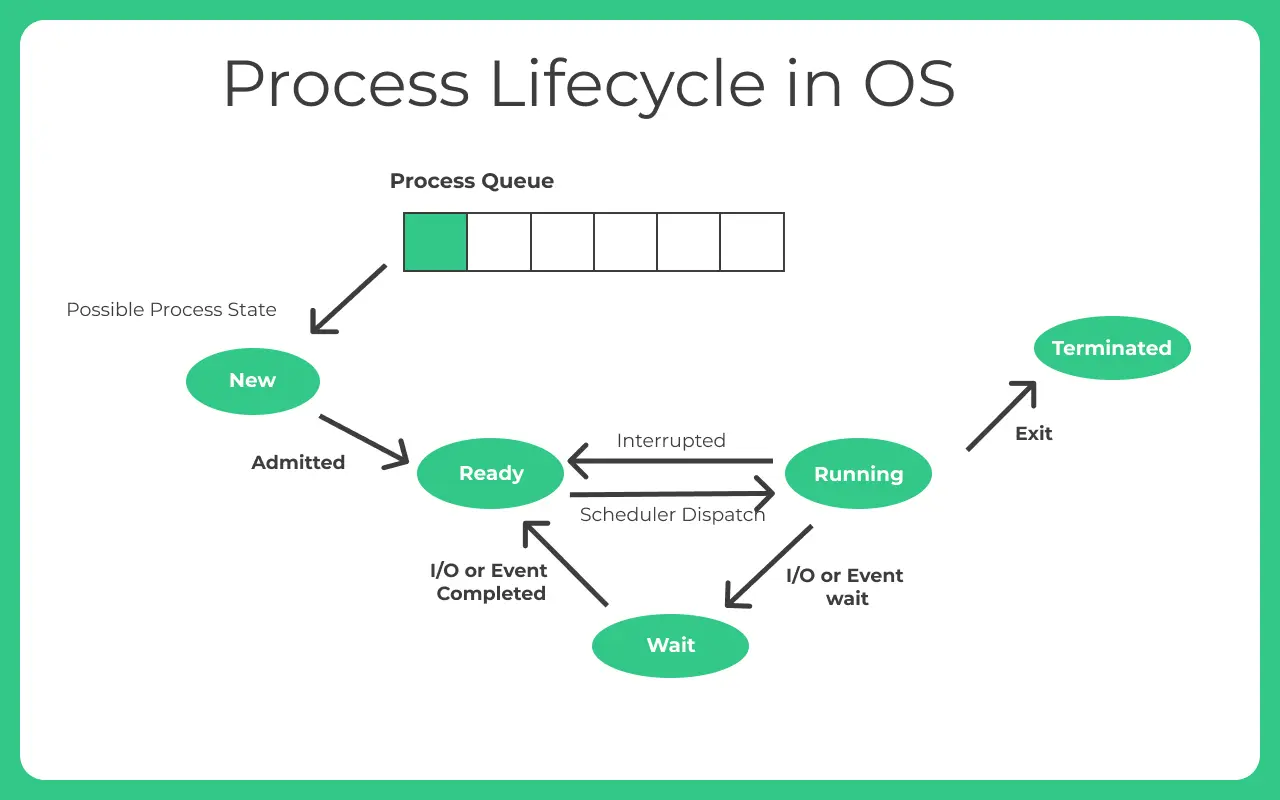
Process Life Cycle in Operating System is one of the five states in which a process can be starting from the time it has been submitted for execution, till the time when it has been executed by the system. Here we will learn detailed explanation about each states.

A process can be in any of the following states –
- New state
- Ready state
- Running state
- Waiting state
- Terminated
| Process Cycle 1 | New State |
| Process Cycle 2 | Read State |
| Process Cycle 3 | Running State |
| Process Cycle 4 | Waiting State |
| Process Cycle 4 | Terminated State |
- Imagine a unit process that executes a simple addition operation and prints it.
New State
- Process it submitted to the process queue, it in turns acknowledges submission.
- Once submission is acknowledged, the process is given new status.

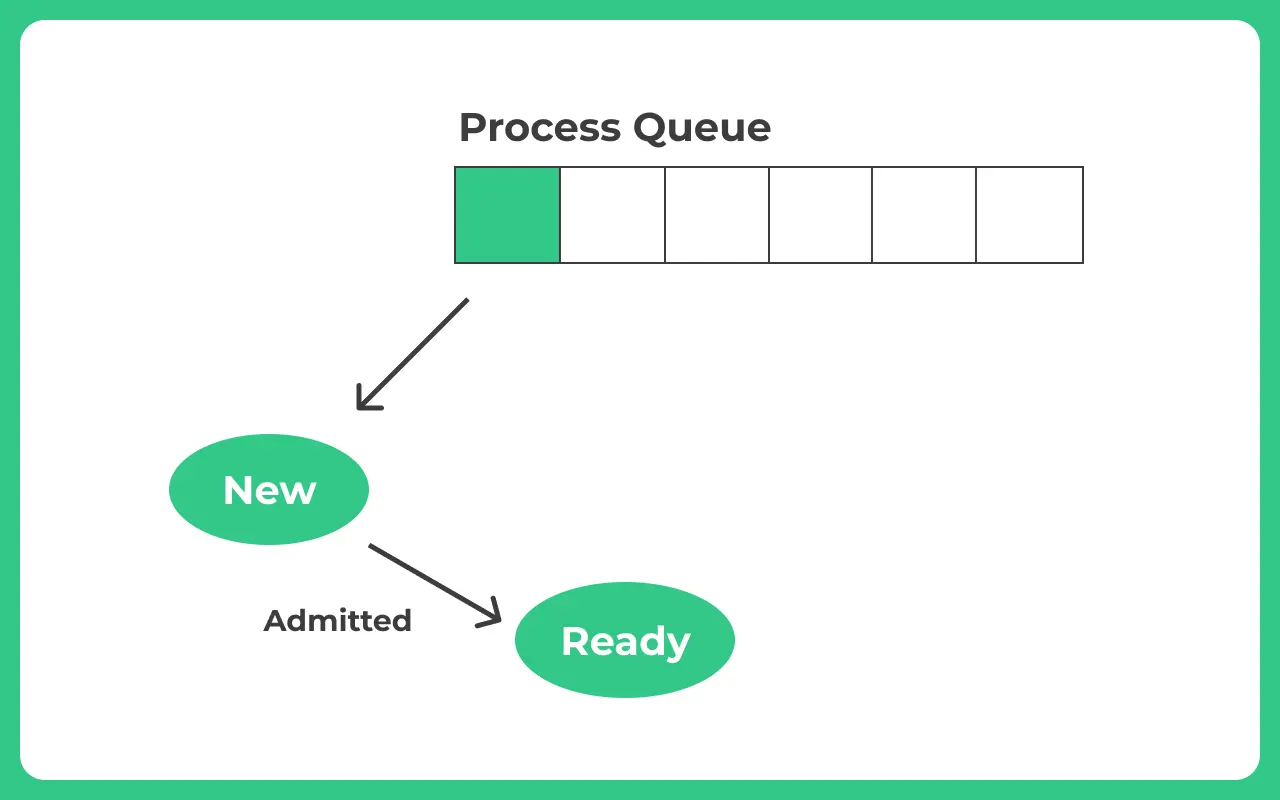
Ready State
- It then goes to Ready State, at this moment the process is waiting to be assigned a processor by the OS
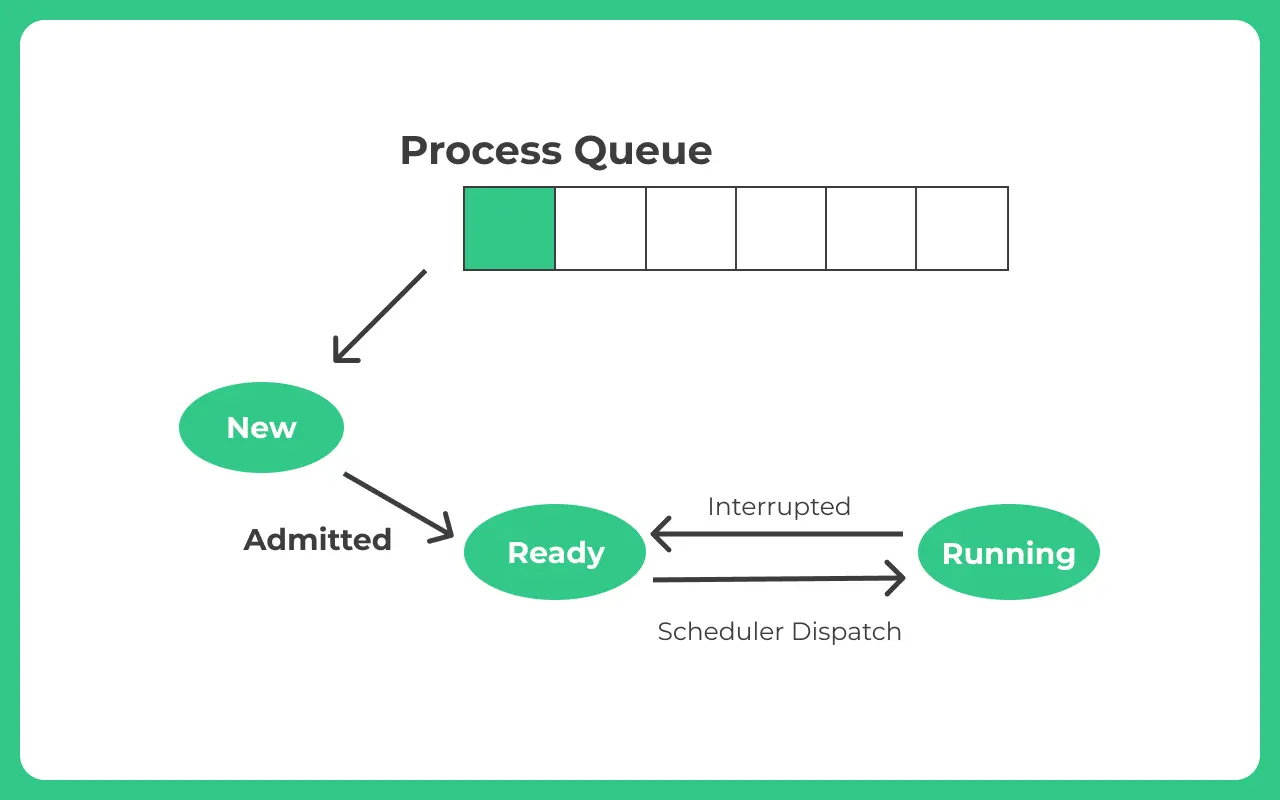
Running State
- Once the Processor is assigned, the process is being executed and turns in Running State.
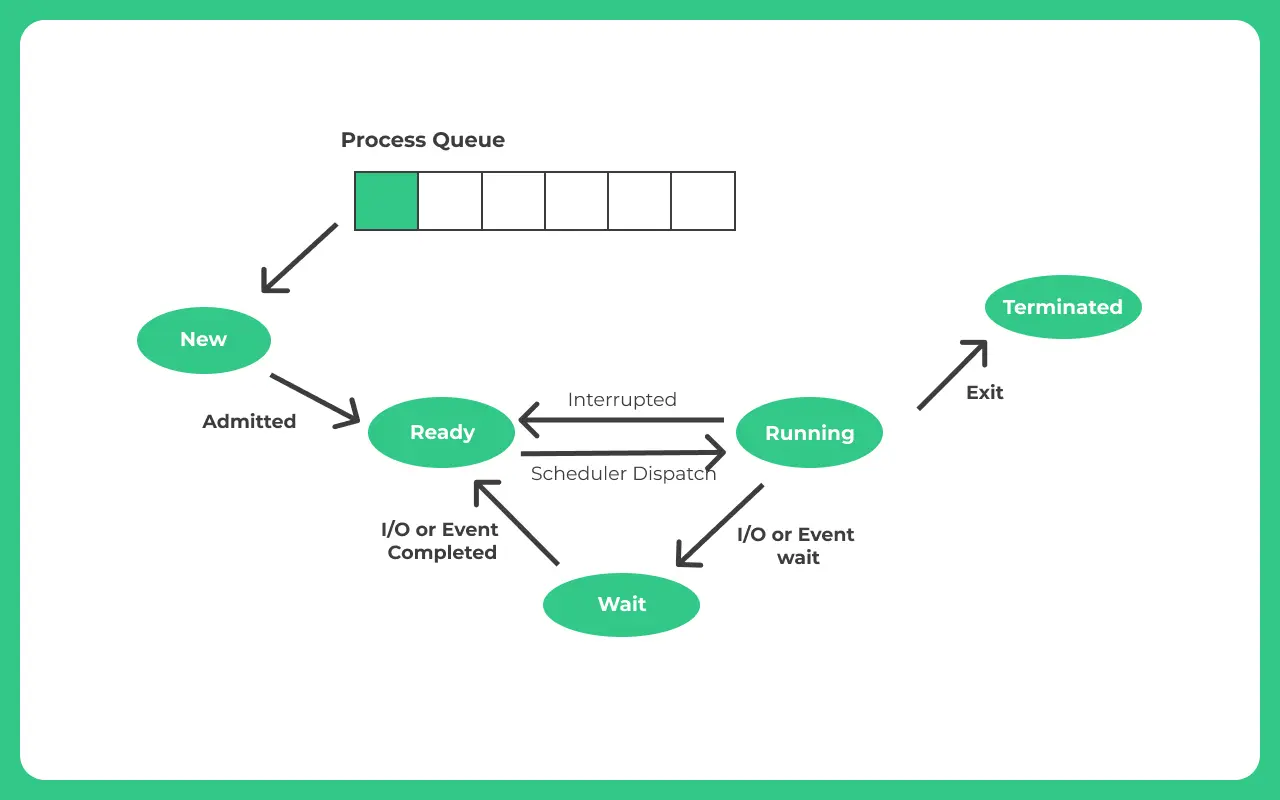
Wait and Termination State
- Now the process can follow the following transitions –
- The process may have all resources it needs and may get directly executed and goes to
Termination State. - Process may need to go to
waiting stateany of the following- Access to Input/Output device (Asking user the values that are required to be added) via console
- Process maybe intentionally interrupted by OS, as a higher priority operation maybe required, to be completed first
- A resource or memory access that maybe locked by another process, so current process goes to
waiting state and waitsfor the resource to get free.
- Once requirements are completed i.e. either it gets back the priority to executed or requested locked resources are available to use, the process will go to running state again where, it may directly go to termination state or may be required to wait again for a possible required input/resource/priority interrupt.
- The process may have all resources it needs and may get directly executed and goes to
- Termination
Summary
- New – New Process Created
- Ready – Process Ready for Processor/computing power allocation
- Running – Process getting executing
- Wait – Process waiting for signal
- Terminated – Process execution completed
Apart from the above some new systems also propose 2 more states of process which are –
- Suspended Ready – There maybe no possibility to add a new process in the queue. In such cases its can be said to be suspended ready state.
- Suspended Block – If the waiting queue is full
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Summary
Reviewer
Jatin
Review Date
Reviewed Item
Process Lifecycle
Author Rating
5










 0
0


Login/Signup to comment