Reverse an Array in C
Reverse an array in C Programming Language
On this page, we will look into a popular coding where we will learn how to reverse an array in C Programming Language. This is a fundamental problem that helps strengthen understanding of arrays and loops in C. Reversing an array means changing the order of elements so that the first becomes the last and the last becomes the first.
- It strengthens your loop and pointer logic in C.
- It is commonly asked in interviews and coding rounds.

Reverse an Array In C
In C programming language, an array is a collection of elements of the same type stored in contiguous memory locations. To reverse an array in C, you need to swap the elements of the array in a specific order.
One way to reverse an array is to use two pointers, one pointing to the first element of the array and the other pointing to the last element of the array. Then, swap the elements at the two pointers and move the pointers towards each other until they meet at the middle of the array.
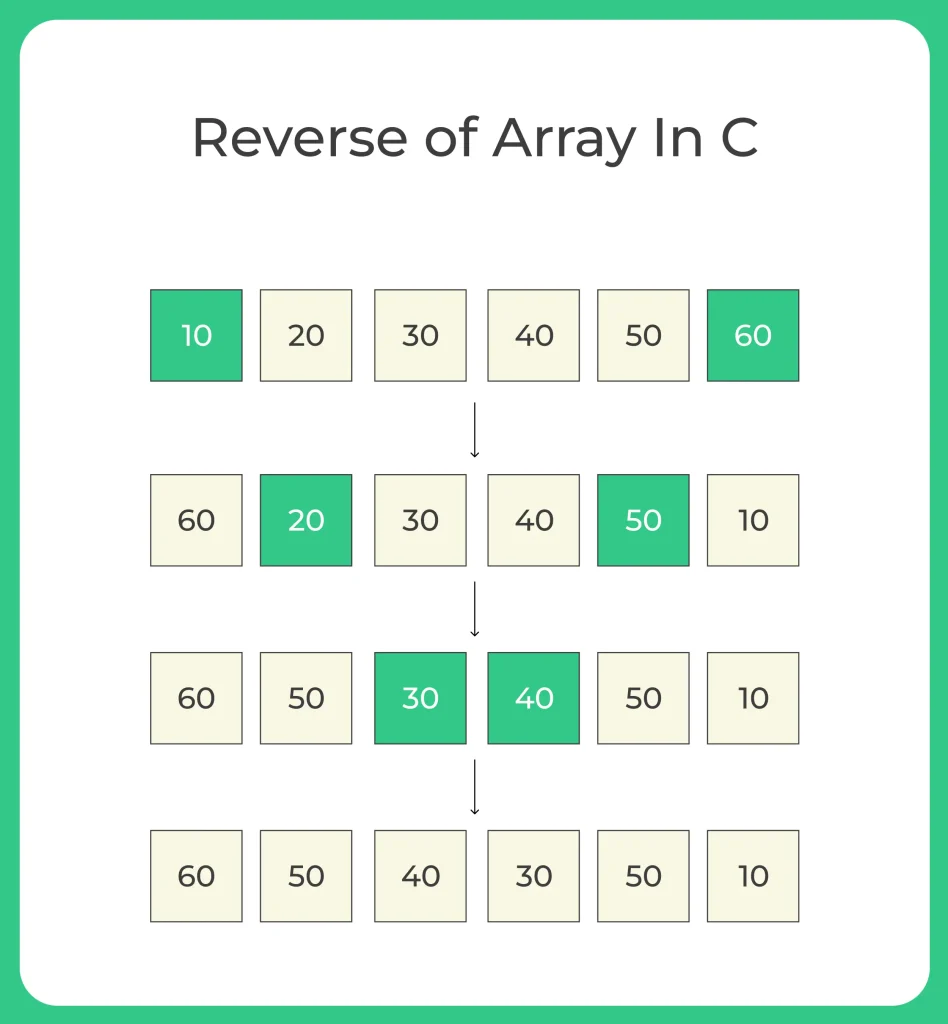

All Methods to Reverse an Array in C
- Using a Temporary Array
- Using a For Loop (Swap Method)
- Using Recursion
- Using Pointers
- Using while loop
- Using Stack (Advanced)
Method:- 1 (Using a Temporary Array)
#include
int main() {
int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int temp[n], i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
temp[i] = arr[n - i - 1];
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", temp[i]);
return 0;
}
Output:
50 40 30 20 10
Explanation:
- A new array stores the original elements in reverse order.
- Requires extra space, but it’s easy to understand and implement.
Method:- 2 (Using a For Loop (Swap Method))
#include
int main() {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, i, temp;
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
for(i = 0; i < n/2; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[n - i - 1];
arr[n - i - 1] = temp;
}
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
Output:
5 4 3 2 1
Explanation:
- Swaps the first element with the last, second with second last, and so on.
- This method is in-place and requires no extra space (space efficient).
Method:- 3 (Using Recursion)
#include
void reverse(int arr[], int start, int end) {
if (start >= end)
return;
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
reverse(arr, start + 1, end - 1);
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {5, 10, 15, 20};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
reverse(arr, 0, n - 1);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
Output:
20 15 10 5
Explanation:
Recursively swaps the start and end elements until the base condition is met.
Useful for learning recursion but not optimal for large arrays due to call stack usage.
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method:- 4 (Using Pointers)
#include
void reverse(int *start, int *end) {
while(start < end) {
int temp = *start;
*start = *end;
*end = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {9, 8, 7, 6};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
reverse(arr, arr + n - 1);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
Output:
6 7 8 9
Explanation:
Uses two pointers to swap elements directly in memory.
A flexible method especially useful for functions handling dynamic memory.
Method:- 5 (Using while loop)
#includeint main() { int arr[] = {11, 22, 33, 44}; int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); int i = 0, j = n - 1, temp; while(i < j) { temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; i++; j--; } for(i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%d ", arr[i]); return 0; }
Output:
44 33 22 11
Explanation:
Same logic as the for-loop swap method but implemented using while.
Helps in cases where the number of iterations is not known in advance.
Method:- 6 (Using Stack)
#include#define MAX 100 int main() { int arr[] = {1, 3, 5, 7}, stack[MAX]; int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); int top = -1, i; // Push elements to stack for(i = 0; i < n; i++) stack[++top] = arr[i]; // Pop back to array for(i = 0; i < n; i++) arr[i] = stack[top--]; for(i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%d ", arr[i]); return 0; }
Output:
7 5 3 1
Explanation:
Stack uses LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) to reverse the order naturally.
Needs extra space, but shows practical use of data structures.
To wrap up
Reversing an array in C is a fundamental concept that can be implemented in various ways, such as using loops, recursion, or pointers. Each method offers different benefits in terms of simplicity, efficiency, and memory usage.
Mastering how to Reverse an Array in C strengthens your core programming skills and lays the foundation for solving more complex data structure problems.
FAQs
The most efficient way is using the in-place swap method with a for or while loop, as it uses no extra space and has linear time complexity.
Yes, we can use recursion to reverse an array, although it’s not space-efficient for large arrays due to stack usage.
Pointers allow direct memory access and manipulation, making your program faster and more flexible, especially with dynamic arrays.
Using a stack is good for understanding LIFO behavior, but it requires extra space, so it’s not optimal for space-sensitive applications.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment