0
Notifications Mark All Read
No New notification
- Login
- Get Prime
Find Pairs in Array with given Sum in C
Find Pairs in Array with given Sum in C Language
On this page, we will look into a coding question where we will learn how to Find Pairs in an Array with a given sum in C Programing Language.
There might be different approaches to solve this question, one you will find here. If your approach is a bit different post it in the comment section.

Find Pairs in Array with given Sum in C
To find pairs in an array with a given sum in C, we can use two methods
- Brute Force (Time complexity: O(n^2) )
- Using Sorting (Time complexity: O(n log n) )
Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages. The brute force method is simple to implement but can be slow for large arrays. The sorting method is faster for large arrays, but requires extra space for sorting and modifying the original array.
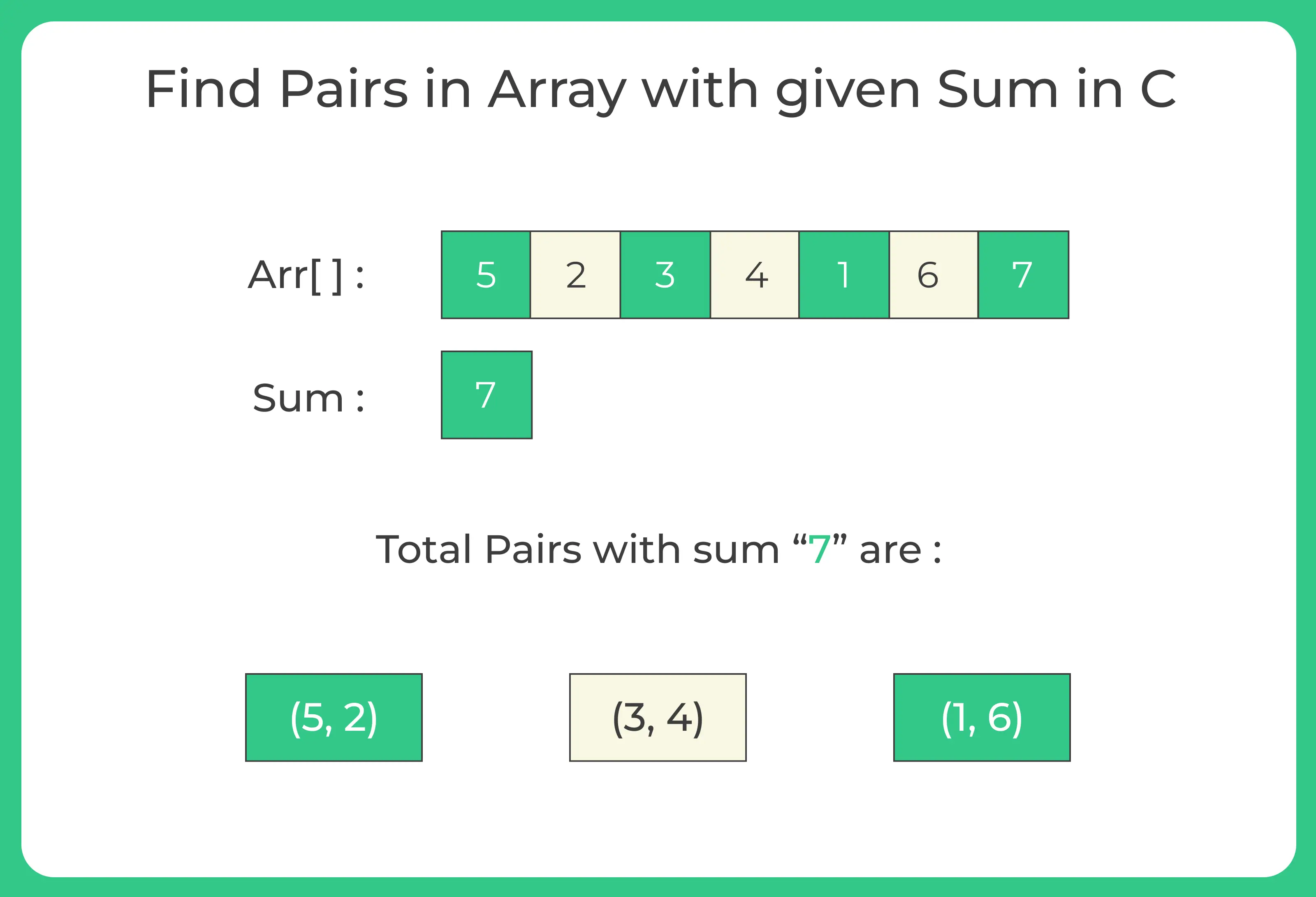
Method 1 : Brute Force Method
- In the brute force method, we compare each element in the array with all the other elements in the array to check if their sum is equal to the given sum.
- This method has a time complexity of O(n^2) as we have to compare each element with every other element
C code for brute force method
Run
#include <stdio.h>
void findPair (int nums[], int n, int target)
{
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target)
{
printf ("Pair found (%d, %d) \n", nums[i], nums[j]);
flag = 1;
}
}
}
if (flag == 0)
{
printf ("Pair not found");
}
}
int main ()
{
int nums[] = {5, 2, 3, 4, 1, 6, 7};
int target = 7;
int n = sizeof (nums) / sizeof (nums[0]);
findPair (nums, n, target);
return 0;
}
Output
Pair found (5, 2) Pair found (3, 4) Pair found (1, 6)
Method 2 : Sorting Method
- The array is first sorted in ascending order in the sorting technique.
- Then, we employ two pointers, one of which points to the first element and the other to the last element.
- These two pointers values are added, and we then check to see if the result equals the specified sum.
The left pointer is increased if the value is less than the total, and the right pointer is decreased if the value is higher. - This method has a time complexity of O(n log n) due to the sorting algorithm used.
C code for Sorting Method
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
int cmpfunc (const void *a, const void *b)
{
return (*(int *) a - *(int *) b);
}
// Function to find a pair in an array with a given sum using sorting
void findPair(int nums[], int n, int target)
{
// sort the array in ascending order
qsort (nums, n, sizeof (int), cmpfunc);
// maintain two indices pointing to endpoints of the array
int low = 0;
int high = n - 1;
int flag = 0;
// reduce the search space `nums[low…high]` at each iteration of the loop
// loop till the search space is exhausted
while (low < high)
{
// sum found
if (nums[low] + nums[high] == target)
{
printf("Pair found (%d, %d) \n",nums[low] ,nums[high]);
flag=1;
}
// increment `low` index if the total is less than the desired sum;
// decrement `high` index if the total is more than the desired sum
(nums[low] + nums[high] < target)? low++: high--;
}
if(flag==0)
{
printf("Pair not found");
}
// we reach here if the pair is not found
}
int main()
{
int nums[] = {5, 2, 3, 4, 1, 6, 7};
int target = 7;
int n = sizeof(nums)/sizeof(nums[0]);
findPair(nums, n, target);
return 0;
}
Output
Pair found (1, 6) Pair found (2, 5) Pair found (3, 4)
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java

 0
0


Login/Signup to comment