Segregate 0’s and 1’s in an array
Segregate 0’s and 1’s in an array in C
Here, in this section we will discuss the C program for segregate 0’s and 1’s in an array :
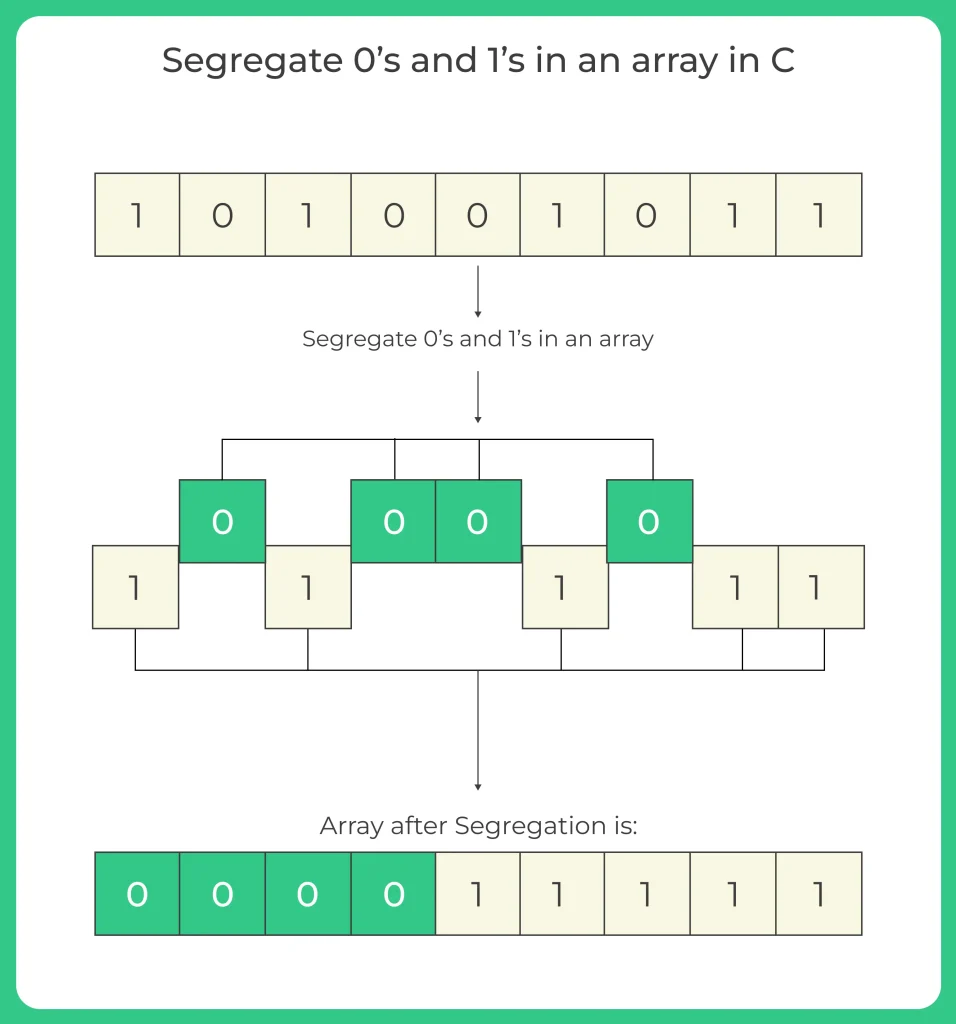
Given an array with 0’s and 1’s, we are segregating the 0’s and 1’s.
INPUT : 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1
OUTPUT : 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1

Segregate 0’s and 1’s in an array in C
- Segregating 0’s and 1’s in an array means rearranging the elements in the array such that all the 0’s appear first, followed by all the 1’s. For example,
- if we have an array [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0],segregating 0’s and 1’s would result in [0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1].
- This type of segregation is commonly used in computer science and programming when dealing with binary data or flags. It can also be used in machine learning algorithms as a preprocessing step for binary classification problems.
Algorithm
- Create two empty arrays, one for 0’s and one for 1’s.
- Loop through the original array and for each element:
a. If it is 0, append it to the array of 0’s.
b. If it is 1, append it to the array of 1’s. - Concatenate the array of 0’s and the array of 1’s to form the segregated array.
This algorithm has a time complexity of O(n), where n is the number of elements in the array, as it requires a single loop through the array to segregate the elements. However, it requires extra space to store the two arrays of 0’s and 1’s, which could be a concern for large arrays with many 0’s and 1’s.
Code for Segregate 0’s and 1’s in an array in C
#include <stdio.h>
void segregate_01(int arr[], int n)
{
int count_0 = 0, count_1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == 0)
{
count_0++;
}
else
{
count_1++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < count_0; i++)
{
printf("0 ");
}
for (int i = count_0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("1 ");
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Array: ");
for (int i=0;i < n;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
printf("\nSegregated array: ");
segregate_01(arr,n);
return 0;
}
Output
Array: 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 Segregated array: 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment