Binary Search Tree: Insertion
Insertion in a Binary Search Tree
Binary Search tree is fairly easy and we just need to know a few simple rules given below –

Rules for Insertion in a Binary Search Tree (BST)
- The left subtree for any given node will only contain nodes which are lesser than the current node
- The right subtree for any given node will only contain nodes which are greater than the current node
- Each subtree must also follow the above rules of BST
Pre Requisite to Insertion
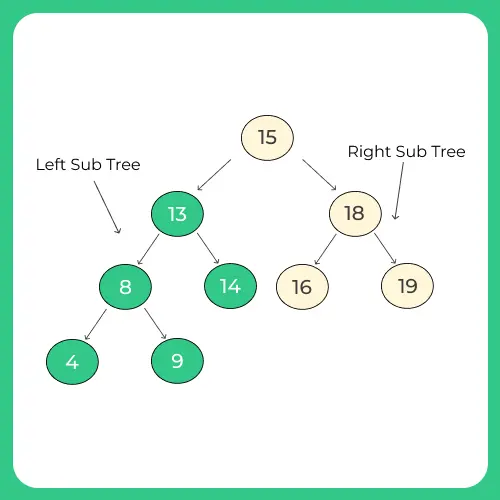
So, first, we will learn how to search a given node(value), in a binary search tree
Searching in a Binary Search Tree
Let us say we want to 9 in the binary search tree given in our example above, what approach we would follow?
Algorithm
- Start from the root node
- Compare the value with the root node, if same then found, return True
- If the value is less than the root node, recurse to the left node. Else recurse to the right node
- Do this recursively, until the value is found or not found
Example
Assuming we want to find 9 in the above example
- The root node is 15, (9 <15) thus recursing to the left node
- Now, the left node is 13, (9<14) thus again, recursing to the left node
- Now, the left node is 8, (9>8) thus, recursing to the right node
- Finally, the right node is 9, (9=9), thus value found, return true
Code to implement Search
// A sample C function to check if a given node exists in a binary search tree or not
struct node* search(struct node* root, int value)
{
// Check if the root is null or value is present at root itself
if (root == NULL || root->value == value)
return root;
// Root is smaller than value, go to right subtree's node, doing recusion here
if (root->value < value)
return search(root->right, value);
// else only one case is left
// i.e. Root is greater than value, go to left subtree's node, doing recusion here
return search(root->left, value);
}
Insertion in a Binary Search Tree
Insertion is fairly simple if you understood search perfectly
- Try to search the BST for the node to be inserted
- As the node wouldn’t exist we will hit the leaf node, with null as child node right!
- Insert the new node here
- Voila! Party, you’ve inserted
Code for Binary Search Tree Insertion
// PrepInsta's program to do insertion in a Binary Search Tree (BST)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// Basic struct of Tree
struct node
{
int val;
struct node *left, *right;
};
// Function to create a new Node
struct node* newNode(int item)
{
struct node* temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->val = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Function print the node in inorder format, when insertion is complete
void inorder(struct node* root)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
inorder(root->left);
printf("%d \n", root->val);
inorder(root->right);
}
}
// Here we are finding where to insert the new node so BST is followed
struct node* insert(struct node* node, int val)
{
/* If the tree(subtree) is empty, return a new node by calling newNode func.*/
if (node == NULL) return newNode(val);
/* Else, we will do recursion down the tree to further subtrees */
if (val < node->val)
node->left = insert(node->left, val);
else if (val > node->val)
node->right = insert(node->right, val);
/* (Safety) return the node's pointer which is unchanged */
return node;
}
int main()
{
/* Our BST will look like this
100
/ \
40 140
/ \ / \
40 80 120 160 */
struct node* root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 100);
insert(root, 60);
insert(root, 40);
insert(root, 80);
insert(root, 140);
insert(root, 120);
insert(root, 160);
// Finally printing the tree using inorder
inorder(root);
return 0;
}
Output:
40 60 80 100 120 140 160
How it works?
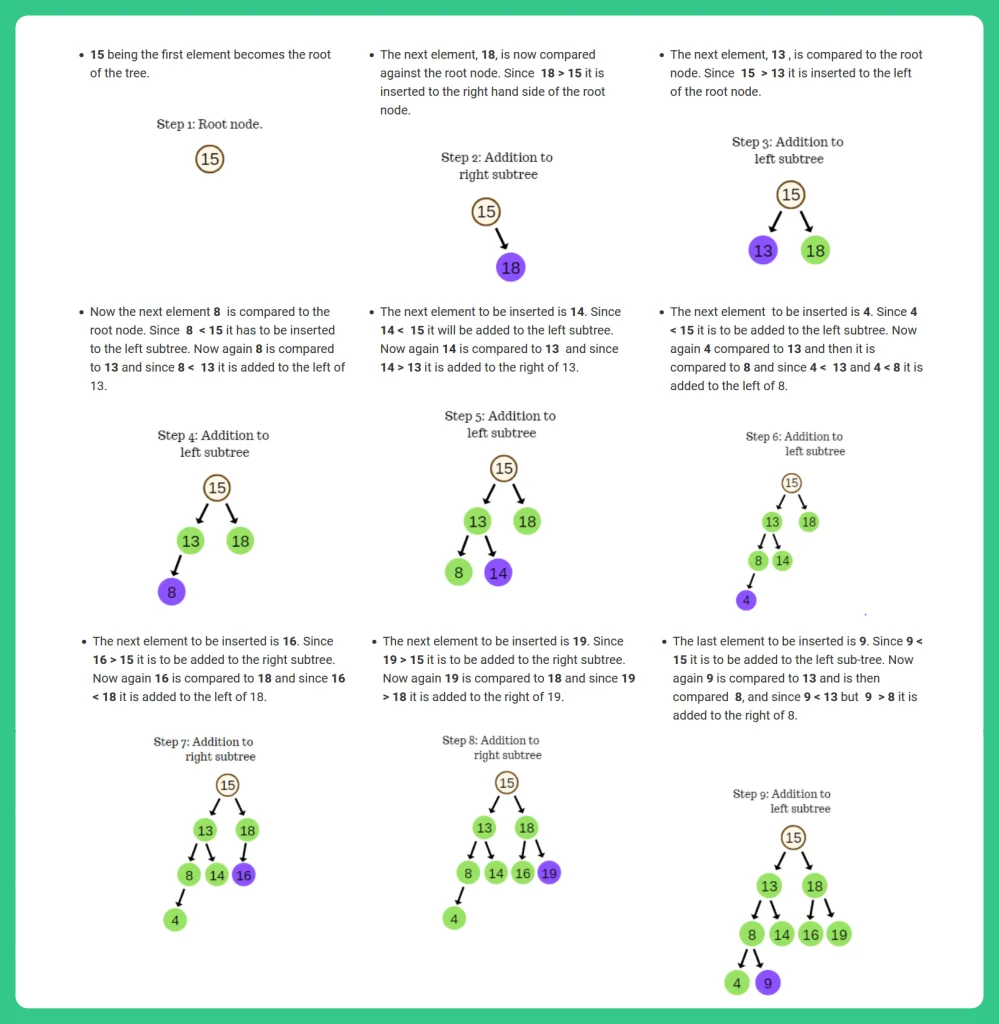
- In binary search trees, we use the INSERT function to add a new element in a tree.
- Insertion is similar to searching wherein, we first check if the element is present in the given data or not. If not, the node is entered at that position.
- If the data to be added is greater than the parent data node it is inserted towards the right of the parent; else it is inserted to the left of the parent.
- In other words,
- If root > node,
then the data node is added to the left sub-tree.
- If root < node,
then the data node is added to the right sub-tree.
For Example: [15, 18, 13, 8, 14, 4, 16, 19, 9]
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment