Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal in C
Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal
There are three types of traversals in a tree: Inorder, Preorder and Postorder Traversal. In this article we will discuss how to construct tree from given postorder and preorder traversal .
Preorder Traversal – We first print the node,then move to the left subtree and finally to the right subtree.
Postorder Traversal – Left and right subtree is visited first and then the node is printed
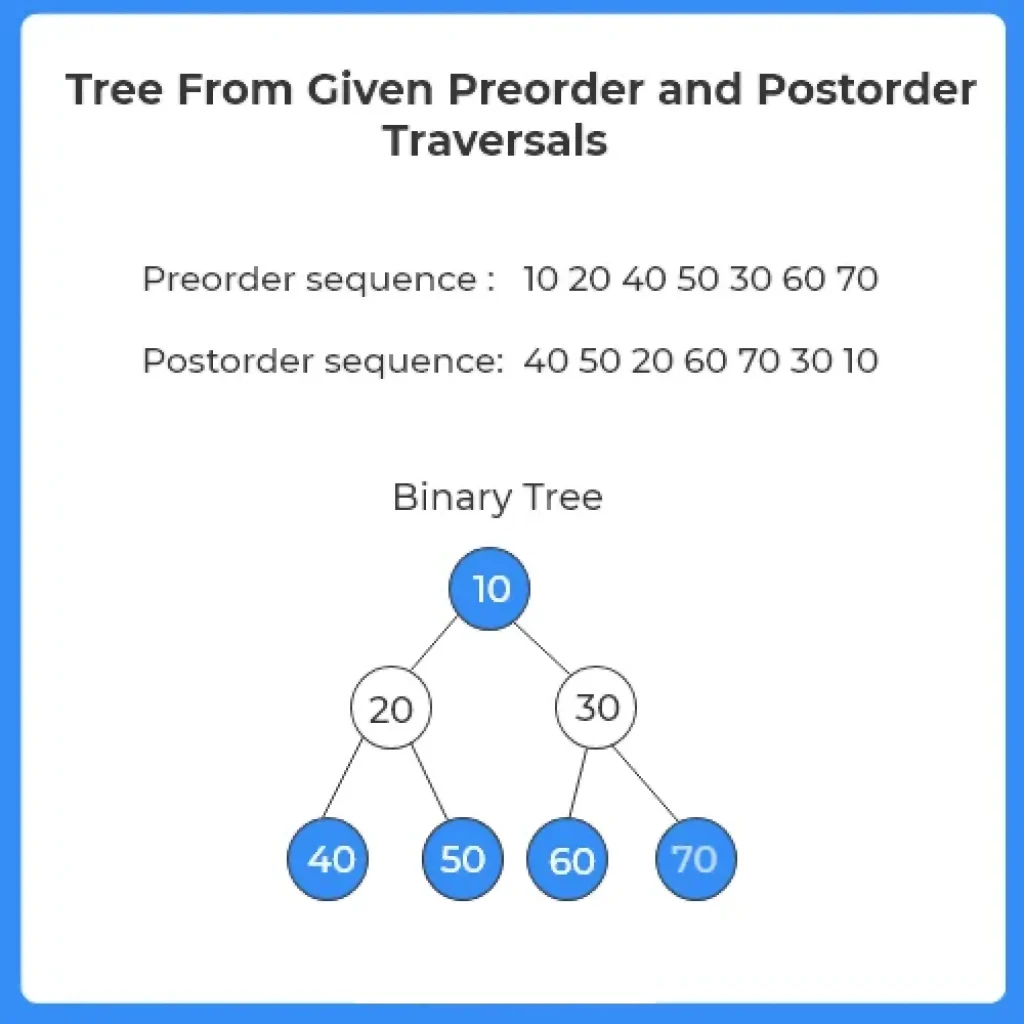
Here, we construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal

Tree From Given Postorder and Preorder Traversal
Algorithm :
- Take the first element of preorder traversal and increase the count.
- Find the index of the next element in the postorder traversal.
- All the elements to the left including this element will be in the left subtree and other elements in the right subtree.
- Recursively call for the right subtree too.
- Repeat until array is traversed.
Code in C to Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder Traversals
Run
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
};
struct node *newNode (int data)
{
struct node *temp = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
struct node *
constructTreeUtil (int pre[], int post[], int *preIndex, int l, int h,
int size)
{
if (*preIndex >= size || l > h)
return NULL;
struct node *root = newNode (pre[*preIndex]);
++*preIndex;
if (l == h)
return root;
int i;
for (i = l; i <= h; ++i)
if (pre[*preIndex] == post[i])
break;
if (i <= h)
{
root->left = constructTreeUtil (pre, post, preIndex, l, i, size);
root->right =
constructTreeUtil (pre, post, preIndex, i + 1, h - 1, size);
}
return root;
}
struct node *constructTree (int pre[], int post[], int size)
{
int preIndex = 0;
return constructTreeUtil (pre, post, &preIndex, 0, size - 1, size);
}
void printInorder (struct node *node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
printInorder (node->left);
printf ("%d ", node->data);
printInorder (node->right);
}
int main ()
{
int pre[] = { 10, 20, 40, 80, 90, 50, 30, 60, 70 };
int post[] = { 80, 90, 40, 50, 20, 60, 70, 30, 10 };
int size = sizeof (pre) / sizeof (pre[0]);
struct node *root = constructTree (pre, post, size);
printf ("Inorder traversal of the constructed tree: \n");
printInorder (root);
return 0;
}
Output:
Inorder traversal of the constructed tree: 80 40 90 20 50 10 60 30 70



Login/Signup to comment