Size of Sub Array with Max Sum in Java
Size of Sub Array with Max Sum in Java
In this article, we will explore different ways to solve Size of Sub Array with Max Sum in Java, analyze their performance in terms of time and space complexity, and walk through clean and easy to understand code examples.
Popular extension of this problem is: Along with the maximum sum, determine the size (length) of the subarray that gives that sum.

This problem not only helps you practice array manipulation but also teaches how to optimize solutions for better performance.
Finding Size of sub array with Max Sum in Java
“Size of Sub array with Maximum Sum” problem is a common algorithmic problem that involves finding the length or size of a contiguous sub array within an array of integers, such that the sum of the sub-array is maximum among all possible sub-arrays.
In other words, we need to find the sub-array with the largest sum.
Here’s an example to illustrate the problem:
Given an array of integers: [-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4]
Subarray with the maximum sum is [4,-1,2,1], and the sum of this sub-array is 6. Thus, the size of the subarray with the maximum sum is 4.
Note:
- Problem can be solved using efficient algorithms such as Kadane’s algorithm, which has a time complexity of O(N), where N is the size of the input array.
- Kadane’s algorithm iterates through the array in a single pass, keeping track of the maximum sum of sub-arrays ending at each position of the array, and updating it as necessary.
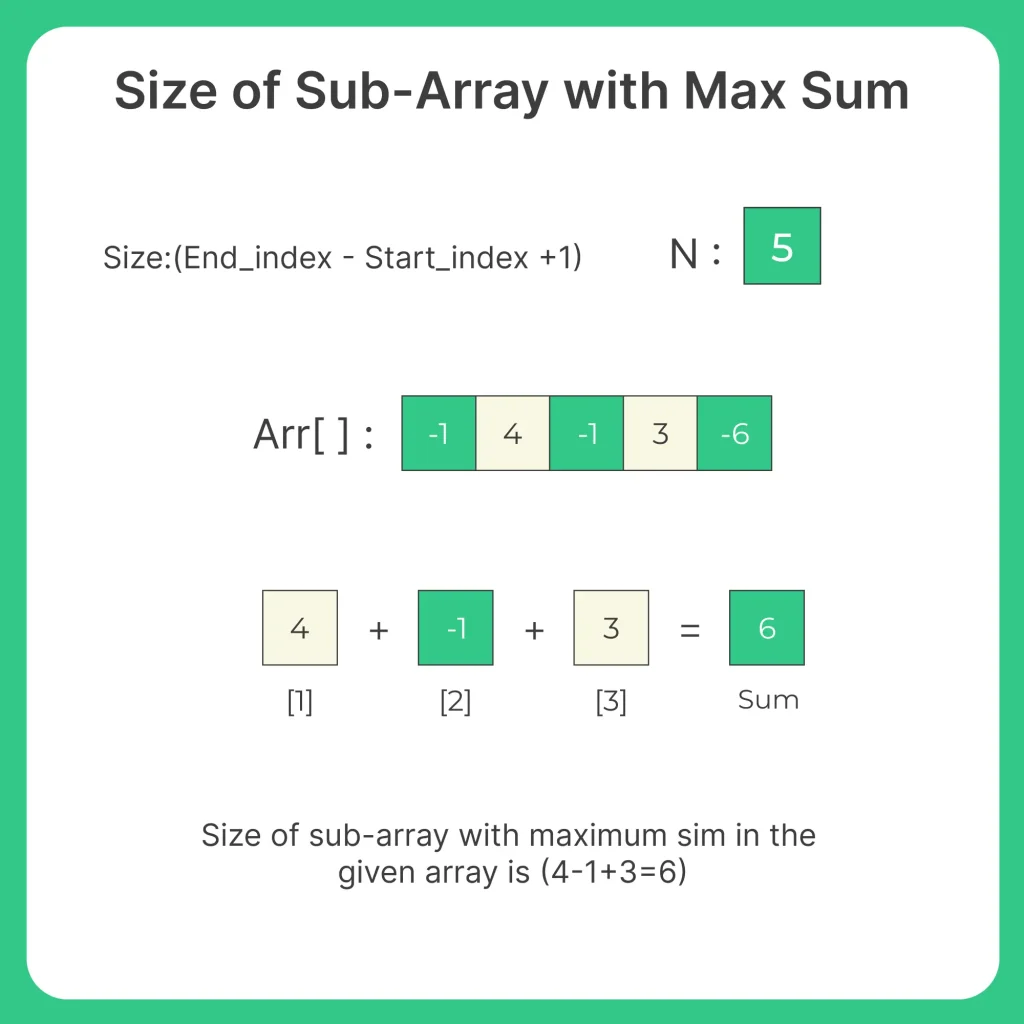

What is Size of Sub Array and Max Sum Problem?
Problem Statement: Given an array of integers, find the maximum sum of a contiguous subarray, and return the size (number of elements) of that subarray.
Input: arr = {-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4}
Output:
Maximum Sum = 6
Size = 4
Explanation: The subarray [4, -1, 2, 1] has the maximum sum of 6 and consists of 4 elements.
The key here is to find both:
- The maximum sum subarray.
- The number of elements (size) that form this subarray.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Approaches to Solve Size of Sub Array Problem
There are two main ways to solve this:
- Brute Force Approach (Check All Subarrays)
Check every possible subarray.
- Track the maximum sum and the length of the subarray.
Optimized Kadane’s Algorithm with Length Tracking
Use Kadane’s Algorithm to keep track of the running sum and length.
Update the maximum when a better sum is found.
Method 1: Brute Force Approach
In the brute force approach:
- We try all possible subarrays using two nested loops.
- For each subarray, we calculate the sum.
- We maintain the maximum sum found so far and track the size of the subarray whenever a new maximum is found.
Algorithm:
- Loop from index i = 0 to n-1.
- For each i, start another loop from j = i to n-1.
- Accumulate sum from i to j
- If the sum is greater than current maxSum, update maxSum and size = j – i + 1.
Space Complexity: O(1)
This is not efficient for large arrays but easy to understand and good for learning.
public class MaxSumSubarrayBruteForce {
public static void findMaxSumSize(int[] arr) {
int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int j = i; j < arr.length; j++) {
sum += arr[j];
if (sum > maxSum) {
maxSum = sum;
size = j - i + 1;
}
}
}
System.out.println("Maximum Sum = " + maxSum);
System.out.println("Size = " + size);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4};
findMaxSumSize(arr);
}
}
Output:
Maximum Sum = 6 Size = 4
Method 2: Kadane’s Algorithm (Optimized Approach)
Kadane’s Algorithm is an efficient way to solve the maximum sum subarray problem in O(n) time.
To also track the size of the subarray, we enhance the basic Kadane’s algorithm by keeping a counter for the number of elements in the current subarray.
Let’s define a few variables:
- currentSum: the sum of the current subarray
- currentSize: the size of the current subarray
- maxSum: stores the maximum sum found so far
- maxSize: stores the size of the subarray that has the max sum
Algorithm:
- Initialize maxSum = currentSum = arr[0], currentSize = maxSize = 1
- Loop from i = 1 to n-1:
If currentSum + arr[i] > arr[i]: Extend the subarray
currentSum += arr[i]
currentSize++
Else: Start a new subarray
currentSum = arr[i]
currentSize = 1
If currentSum > maxSum: update maxSum and maxSize
Space Complexity: O(1)
Efficient for large arrays and preferred in interviews.
public class MaxSumSubarrayKadane {
public static void findMaxSumSize(int[] arr) {
int maxSum = arr[0];
int currentSum = arr[0];
int maxSize = 1;
int currentSize = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (currentSum + arr[i] > arr[i]) {
currentSum += arr[i];
currentSize++;
} else {
currentSum = arr[i];
currentSize = 1;
}
if (currentSum > maxSum) {
maxSum = currentSum;
maxSize = currentSize;
}
}
System.out.println("Maximum Sum = " + maxSum);
System.out.println("Size = " + maxSize);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4};
findMaxSumSize(arr);
}
}
Output:
Maximum Sum = 6 Size = 4
To wrap it up….
Finding the size of the subarray with the maximum sum is a variation of the classic Kadane’s Algorithm problem. In this article, we explored both brute force and optimized approaches, analyzed their time and space complexities, and implemented them in Java.
For most practical and interview cases, Kadane’s Algorithm is the best choice due to its linear time performance and low memory usage.
FAQ's related to Size of Sub Array with Max Sum
Answer:
Kadane’s Algorithm is an efficient way to find the maximum sum of a contiguous subarray in linear time O(n). It works by tracking local and global maxima.
Answer:
You can track the number of elements (currentSize) in the current subarray and update the maximum size whenever a new maximum sum is found.
Answer:
Kadane’s Algorithm still works. The subarray with the maximum value (least negative) will be chosen, and size will be 1.
Answer:
Yes. You can store the start and end indices while updating the maximum sum, and use them to print the actual subarray.
Answer:
Brute force method checks all subarrays, leading to O(n²) time complexity. It becomes slow for large inputs and is not efficient.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment