Triplet that sum to a given value in Java
Java program for Triplet that sum to a given value
Finding a triplet that sum to a given value in Java is a common and important coding problem, frequently asked in technical interviews and online coding platforms. It helps developers understand array traversal, nested loops, sorting, and the use of two pointer techniques efficiently.
In this article, we will explore the problem in depth from understanding the concept and algorithm to implementing it using different approaches in Java.

Triplet that Sum to Given Value in Java
What is the Problem?
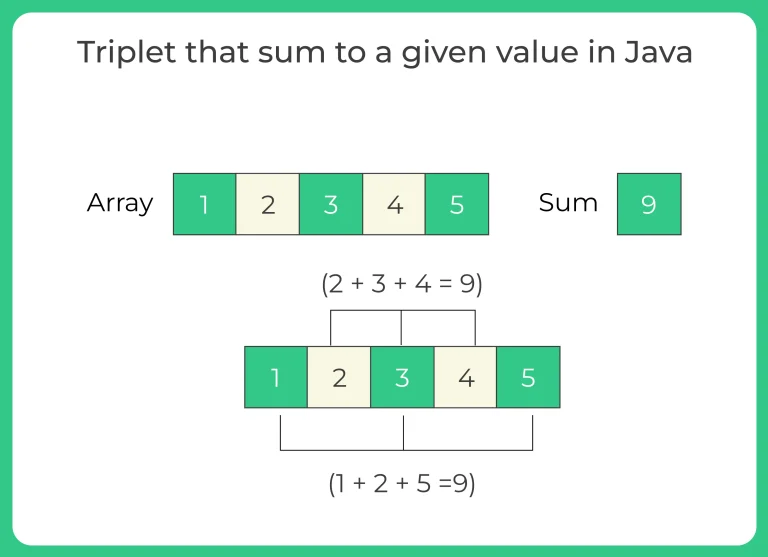
Given an array of integers and a target sum value, the goal is to find any three numbers (a triplet) in the array that add up exactly to the target value.
Example:
Input: arr = [1, 4, 6, 2, 8, 3], target = 13
Output: Triplet found: (4, 6, 3)
Explanation: 4 + 6 + 3 = 13
If no such triplet exists, we should return that no triplet is found.
For example, finding three financial transactions that sum to a given budget, or identifying three components in a system whose combined performance meets a specific threshold.
Methods to Solve the Problem:
There are two main approaches to solve the “Triplet that sum to a given value” problem in Java:
1. Brute Force Approach for Triplet that sum to a given value
In this method, we check every possible combination of three elements in the array. If the sum of any triplet equals the given target, we return that triplet.
Algorithm:
- Use three nested loops to pick all possible combinations of three elements.
- For every combination (arr[i], arr[j], arr[k]), calculate the sum.
- If the sum matches the target, print the triplet.
- If no such triplet is found, print an appropriate message.
Java Code:
public class TripletSum {
public static void findTripletBruteForce(int[] arr, int target) {
int n = arr.length;
boolean found = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n - 1; j++) {
for (int k = j + 1; k < n; k++) {
if (arr[i] + arr[j] + arr[k] == target) {
System.out.println("Triplet found: (" + arr[i] + ", " + arr[j] + ", " + arr[k] + ")");
found = true;
}
}
}
}
if (!found) {
System.out.println("No triplet found that sums to " + target);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 4, 6, 2, 8, 3};
int target = 13;
findTripletBruteForce(arr, target);
}
}
Input:
Array: [1, 4, 6, 2, 8, 3] Target Sum: 13
Output:
Triplet found: (4, 6, 3)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
2. Optimized Approach for Triplet that sum to a given value
Instead of checking every triplet, we can improve efficiency using sorting and the two pointer technique.
Algorithm:
Sort the array in ascending order.
Traverse each element arr[i] (from 0 to n−3) as the first element of the triplet.
For each i, set 2 pointers:
left = i + 1
right = n – 1
Calculate the sum:
currentSum = arr[i] + arr[left] + arr[right]If currentSum == target, print the triplet.
If currentSum < target, increment left (to increase sum).
If currentSum > target, decrement right (to decrease sum).
Continue until left < right.
Java Code:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TripletSumOptimized {
public static void findTriplet(int[] arr, int target) {
Arrays.sort(arr);
int n = arr.length;
boolean found = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++) {
int left = i + 1;
int right = n - 1;
while (left < right) {
int currentSum = arr[i] + arr[left] + arr[right];
if (currentSum == target) {
System.out.println("Triplet found: (" + arr[i] + ", " + arr[left] + ", " + arr[right] + ")");
found = true;
left++;
right--;
} else if (currentSum < target) {
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
}
if (!found) {
System.out.println("No triplet found that sums to " + target);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 4, 6, 2, 8, 3};
int target = 13;
findTriplet(arr, target);
}
}
Input:
Array: [1, 4, 6, 2, 8, 3] Target Sum: 13
Output:
Triplet found: (1, 4, 8) Triplet found: (4, 6, 3)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Comparison Between Methods to Find Triplet that sum to a given value
| Approach | Technique Used | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brute Force | 3 nested loops | O(n³) | O(1) | Slow (not practical for large inputs) |
| Optimized | Sorting + Two Pointers | O(n²) | O(1) | Efficient and widely used |
Problem of Triplet that sum to a given value in Java is a classic array based challenge that helps strengthen problem solving and algorithmic thinking.
- Starting with a brute force approach helps you understand the logic clearly, while learning the optimized two pointer method ensures you can solve such problems efficiently in coding interviews.
- Both methods are valuable to learn, the brute force for conceptual clarity and the optimized version for performance in real world scenarios.
FAQ's related to Triplet that sum to a given value
Answer:
Triplet refers to three elements in an array whose sum equals a specific target value. The problem is commonly solved using sorting and two pointer techniques for better performance.
Answer:
Brute Force (O(n³)): Check all combinations of three elements.
Optimized Two Pointer Method (O(n²)): Sort the array and use left right pointers.
Answer:
The two pointer approach after sorting is the most efficient, as it reduces time complexity from O(n³) to O(n²).
Answer:
Yes. You can fix one element and use a hash set to find if the remaining pair adds to (target – fixed element). However, the two pointer approach is simpler and faster for sorted arrays.
Answer:
It is used in problems involving financial analytics, optimization, subset sum analysis, and algorithmic reasoning in interviews and real world systems.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others





Login/Signup to comment