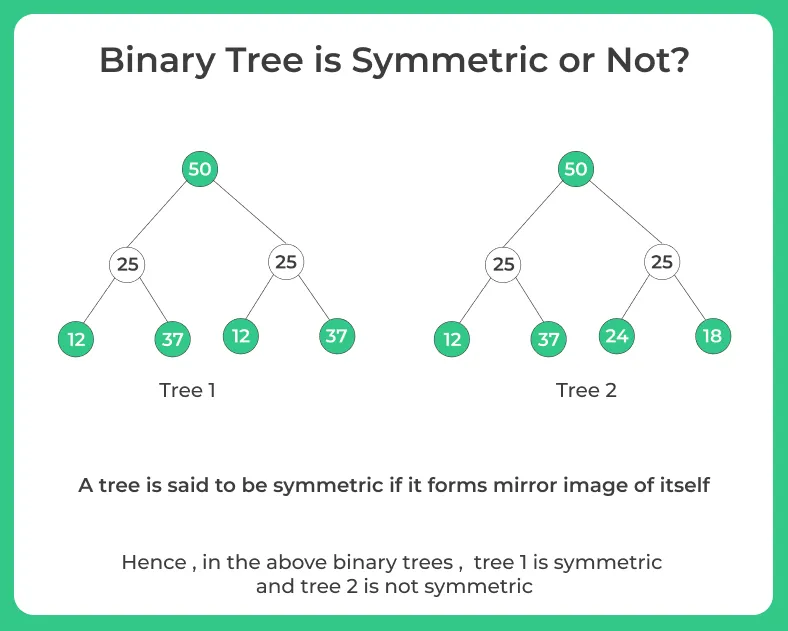
Symmetric Binary Tree
Tree is Symmetric or Not?
Here, in this page we will discuss a Java program to check whether a tree is Symmetric (mirror of itself) or not.
We need to write a recursive function isSymmetrical() that takes two trees as argument and returns true if trees are Symmetrical and false if trees are not Symmetrical.

Check Whether Tree is Symmetric in C Language
Define a recursive function called
isMirror()that takes in two binary trees as arguments and returnstrueif the trees are mirrored andfalseotherwise.Within
isMirror(), compare the left and right subtrees of each tree by recursively callingisMirror()with their corresponding subtrees.The base case of
isMirror()is when both subtrees arenull, in which case they are considered mirrored andtrueis returned.Define another function called
isSymmetric()that takes in the root of a binary tree as an argument and returnstrueif the tree is symmetric, andfalseotherwise.Within
isSymmetric(), callisMirror()with the left and right subtrees of the root and return the result.If
isMirror()returnstrue, the tree is symmetric, so returntrue. Otherwise, returnfalse.Use
isSymmetric()to determine whether a binary tree is symmetric or not. IfisSymmetric()returnstrue, the tree is symmetric, otherwise it is not.
Code in Java to check Symmetry of Binary Tree
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item) {
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
public Node() {
data = 0;
left = right = null;
}
}
// Binary tree Class
class BTree {
static Node root;
static boolean isSymmetryTree(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return true;
}
return isSymmetry(node.left, node.right);
}
static boolean isSymmetry(Node nodeLeft, Node nodeRight) {
//Check both left and right node is null, if yes then that is fine, return true.
if (nodeLeft == null && nodeRight == null) {
return true;
}
//If one is present and other is null, return false.
if (nodeLeft == null || nodeRight == null) {
return false;
}
if (nodeLeft.data != nodeRight.data)
return false;
// The most Important step is -> when you are Checking if it is symmetric ,
// Send the left child of left subtree and right child of right subtree together. Similarly,
// send the right child of left subtree and left child of right subtree.
boolean left = isSymmetry(nodeLeft.left, nodeRight.right);
boolean right = isSymmetry(nodeLeft.right, nodeRight.left);
return (left && right);
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
BTree tree = new BTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(5);
tree.root.right = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(9);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(10);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(13);
System.out.println(" The Symmetry of tree is " + tree.isSymmetryTree(tree.root));
}
}
Output:
The Symmetry of tree is false
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java





