Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing
JAVA Program to Print reverse of a linked list
In this page we’ll take a look at a JAVA program in which we’ll print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing it .We’ll simply have to traverse to last node and print node data and traverse back.
Algorithm
In this program we are not actually reversing a Linked List, but just printing the Linked List backwards, for doing so we will be following the below steps -:
- Step 1 – Take a pointer ptr.
- Step 2 – Check whether the Linked List has nodes or not.
- Step 3 – If the linked list is empty, return 0.
- Step 4 – If the linked list has nodes, move the pointer ahead till it reaches NULL.
- Step 5 – Backtrack and print the data of the nodes
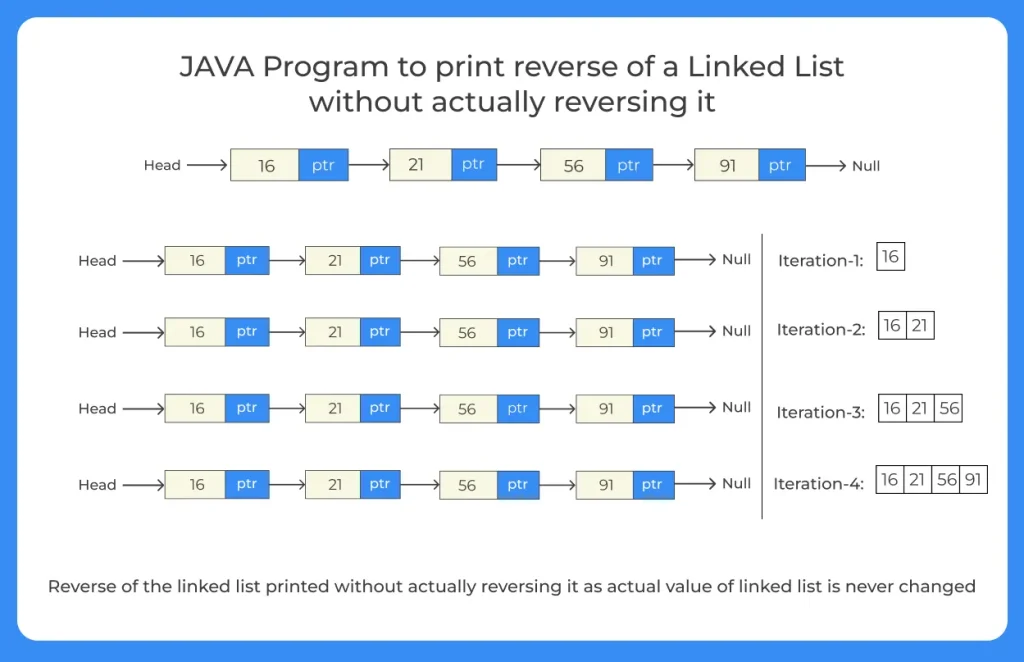
JAVA code to print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing it
import java.util.*;
class LinkedList { // Head of list Node head; // Linked list Node class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int d) { data = d; next = null; } } // Function to print reverse of // linked list void printReverse(Node head) { if (head == null) return; // Print list of head node printReverse(head.next); // After everything else is printed, // Print head System.out.print(head.data + " "); } // Function to traverse and print the linked list public void display () { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { System.out.print (temp.data + " "); // Set temp to point to the next node temp = temp.next; } System.out.println(" "); } public void addFirst(int new_data) { Node new_node = new Node(new_data); new_node.next = head; head = new_node; } } public class Main{ public static void main(String args[]) { // Create linked LinkedList llist = new LinkedList(); llist.addFirst(42); llist.addFirst(13); llist.addFirst(25); llist.addFirst(10); System.out.println("Linked List before reversing"); llist.display(); System.out.println("Linked List after reversing"); llist.printReverse(llist.head); }
Linked List before reversing 10 25 13 42 Linked List after reversing 42 13 25 10
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java





