Singly Linked List in C (All Methods)
Singly Linked List in C
Singly Linked List in C is one of the simplest linear data structures, that we use for storing our data in an easy and efficient way. Linked List in C comprises nodes like structures, which can further be divided into 2 parts in the case of a singly linked list. These two parts are-:
- Node – for storing the data.
- Pointer – for storing the address of the next node

Singly Linked List Program in Data Structure Implementation
Singly Linked List Program in Data Structure Implementation
We implement Linked List using user-defined data type, with the help of structure or struct.
Since the Singly linked list has only 1 pointer type value, which means it can store the address of only one node, which will be the next to it.
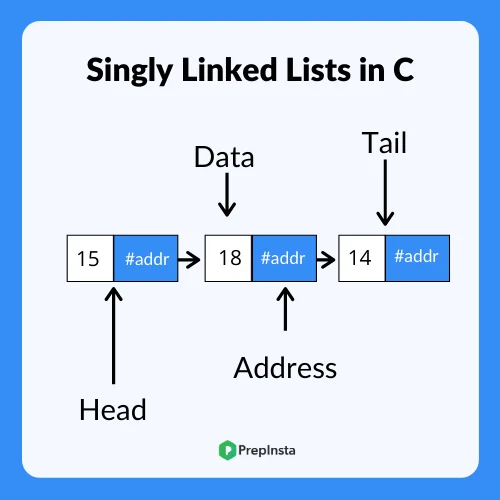

How to Construct a Singly Linked List in C ?
For constructing a singly linked list in C we make use of the structure keyword(struct), for creating user-defined data types, which can store various different types of data in the nodes of the singly linked list.
Each linked list has two parts –
- One for storing the desired data
- The other is a pointer type variable, which stores the address of the next node.
The syntax for creating a node
struct Node
{
int Data;
Struct Node *next;
};
This code will create a data type Node, which will be able to store two values-:
- int value – data
- pointer value – address of the next node
Prime Course Trailer
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
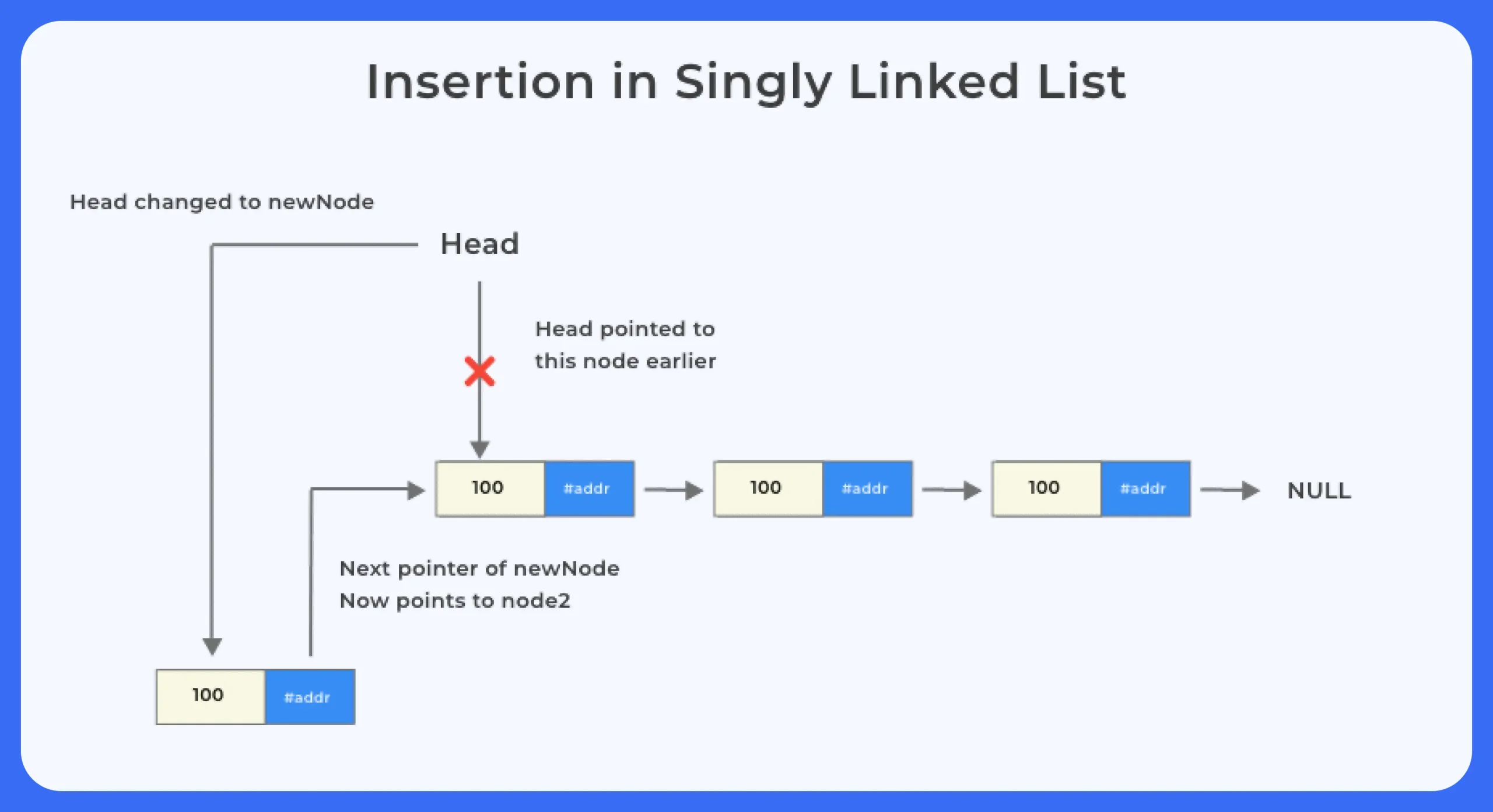
Insertion of a node
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode - >
data = data;
newNode - >
next = *head;
//changing the new head to this freshly entered node
*head = newNode;
}
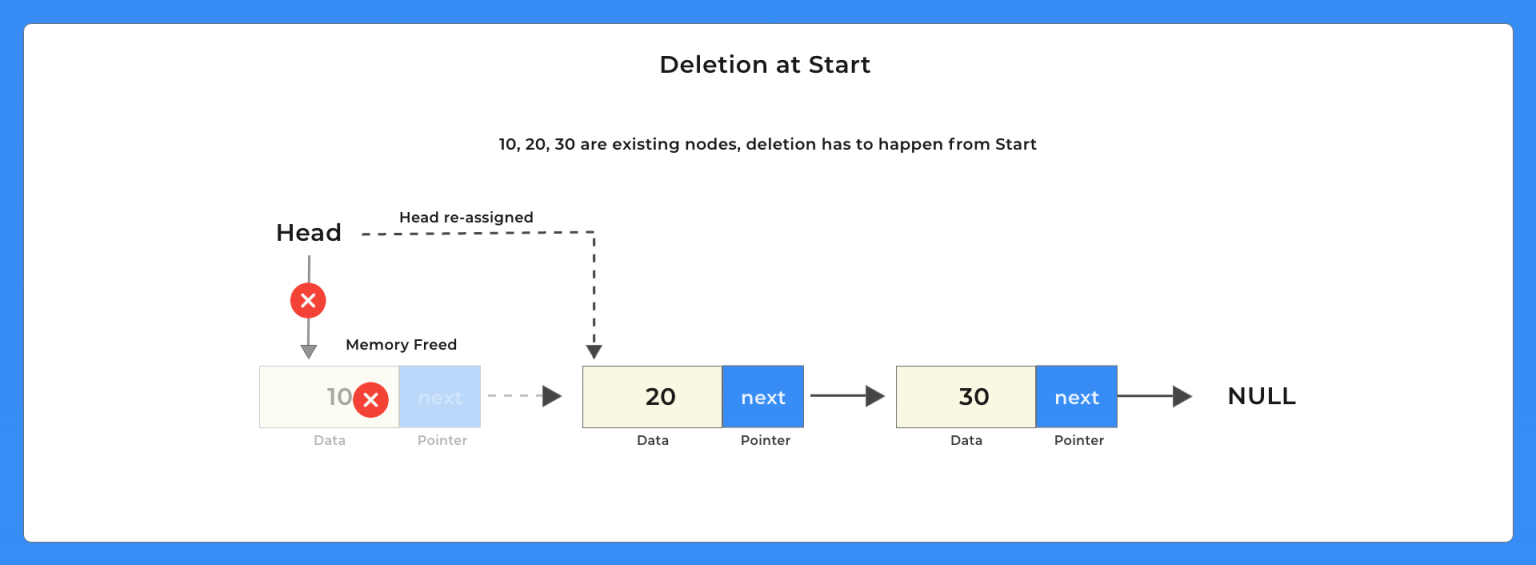
Deletion of a node
void deleteStart(struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
free (temp);
} 
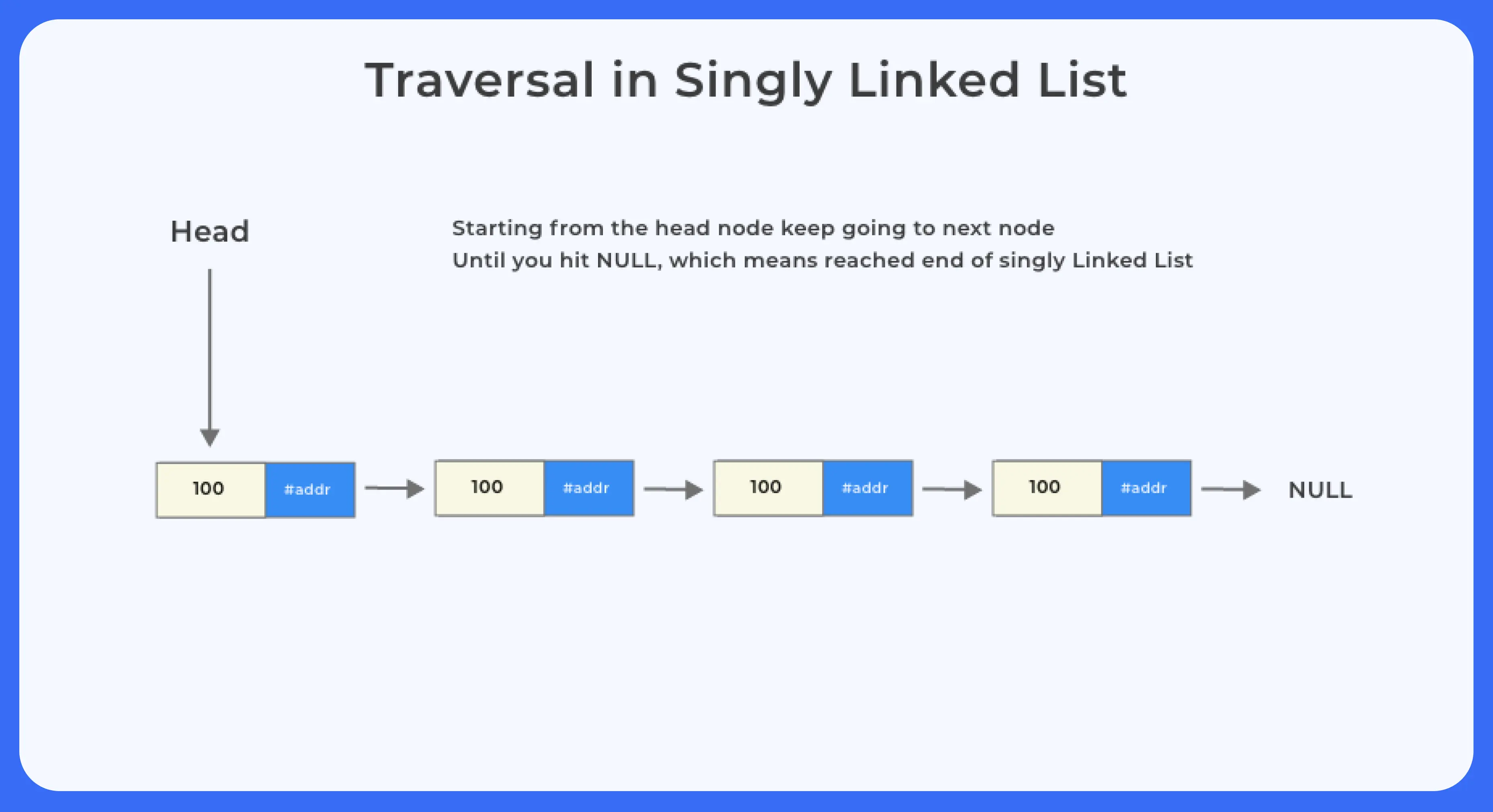
Traversal in a Singly Linked List
void display(struct Node* node)
{
printf("Linked List: ");
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL){
printf("%d ",node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
} 
Code for Implementing Single Linked List in C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void deleteStart (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
printf ("\n%d deleted\n", temp->data);
free (temp);
}
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assign data value
newNode->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
newNode->next = *head;
//re-assign head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
printf ("\n%d Inserted\n", newNode->data);
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
printf ("\nLinked List: ");
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
insertStart (&head, 100);
insertStart (&head, 80);
insertStart (&head, 60);
insertStart (&head, 40);
insertStart (&head, 20);
// No Need for '&' as not changing head in display operation
display (head);
deleteStart (&head);
deleteStart (&head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
100 Inserted 80 Inserted 60 Inserted 40 Inserted 20 Inserted Linked List: 20 40 60 80 100 20 deleted 40 deleted Linked List: 60 80 100

Time Complexity
For Singly Linked List
Best
O(1)
Average
O(n)
Worst
O(n)
Average Comparisons
(n+1)/2
Time Complexity
For Singly Linked List
Best
O(1)
Average
O(n)
Worst
O(n)
Average Comparisons
(n+1)/2
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others



Login/Signup to comment