C Program for Reverse a linked list by changing links between node
Reverse a linked list by changing links between node
Here we will learn how to code a C program for Reverse a linked list by changing links between node. Reversing a linked list is one of the most common problems asked in coding interviews and exams. But instead of just reversing the data inside the nodes, what if we reverse the actual connections between them?
In this blog, we’ll learn how to reverse a singly linked list by changing the links between the nodes, not by swapping the data. This means, if the list is like 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> NULL, we’ll make it 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL by changing the direction of the arrows (pointers).

How to Reverse a Linked List by changing the links between the nodes
- Step 1 – We will take three pointers ptr1, ptr2 and ptr3. Initially the first and the third pointer will point NULL, and the second pointer will point the head.
- Step 2 – We will iterate through the linked list, swapping the value of these 3 pointers.
- Step 3 – ptr3 will now point the second node of the linked, and ptr2 will be removed from the linked list.
- Step 4 – Now ptr1 will point the removed node.
- Step 5 – ptr2 node will point ptr1 node.
- Step 6 – All the three pointers will be moved by +1.
- Step 7 – The above steps will be repeated until ptr3 points the NULL.
- Step 8 – Than in the last step, the last node will become the HEAD of the linked list
Algorithm for Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes
- START WHILE
- NEXT=CURRENT->NEXTPTR
- CURRENT->NEXTPTR=PREV
- PREV=CURRENT
- CURRENT=NEXT
- END WHEN CURRENT=NULL
- HEAD_ADDR=PREV
Prime Course Trailer
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C Program for Reverse a linked list by changing links between node(Iterative)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Function to reverse the linked list iteratively
struct Node* reverseIterative(struct Node* head) {
struct Node *prev = NULL, *curr = head, *next = NULL;
while (curr != NULL) {
next = curr->next; // Store next node
curr->next = prev; // Reverse current node's link
prev = curr; // Move prev one step forward
curr = next; // Move curr one step forward
}
return prev; // New head of reversed list
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(struct Node* head) {
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// Function to create a new node
struct Node* createNode(int data) {
struct Node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
int main() {
// Creating list: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4
struct Node* head = createNode(1);
head->next = createNode(2);
head->next->next = createNode(3);
head->next->next->next = createNode(4);
printf("Original List:\n");
printList(head);
head = reverseIterative(head);
printf("Reversed List (Iterative):\n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Output
Original List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> NULL Reversed List (Iterative): 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL
Explanation:
- We use 3 pointers: prev, curr, and next.
At each step, we:
- Save the next node.
- Reverse the curr->next to point to prev.
- Move prev and curr forward.
Time and Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Space Complexity: O(1)
C Program for Reverse a linked list by changing links between node(Recursive)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Recursive function to reverse the linked list
struct Node* reverseRecursive(struct Node* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
struct Node* rest = reverseRecursive(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return rest;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(struct Node* head) {
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// Function to create a new node
struct Node* createNode(int data) {
struct Node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
int main() {
// Creating list: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4
struct Node* head = createNode(1);
head->next = createNode(2);
head->next->next = createNode(3);
head->next->next->next = createNode(4);
printf("Original List:\n");
printList(head);
head = reverseRecursive(head);
printf("Reversed List (Recursive):\n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Output
Original List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> NULL
Reversed List (Recursive): 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL
Explanation:
- The function keeps calling itself for the next node until it reaches the end.
As it returns back up the call stack, it:
- Makes the next node point back to the current node.
- Breaks the original forward link by setting head->next = NULL.
Time and Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Space Complexity: O(n) (due to recursion stack)
Conclusion
Reversing a linked list by changing the links between nodes is a fundamental concept in data structures. It helps you understand how pointers work and how linked lists are connected internally. Instead of moving the data around, we simply change the direction of the pointers, which makes the process more efficient and memory-friendly.
In this blog, we explored two main approaches—iterative and recursive. The iterative method is commonly used in real-world coding because it’s simple and uses constant memory. The recursive method, on the other hand, offers a cleaner and more elegant solution but uses extra space due to function calls.

Fun Fact

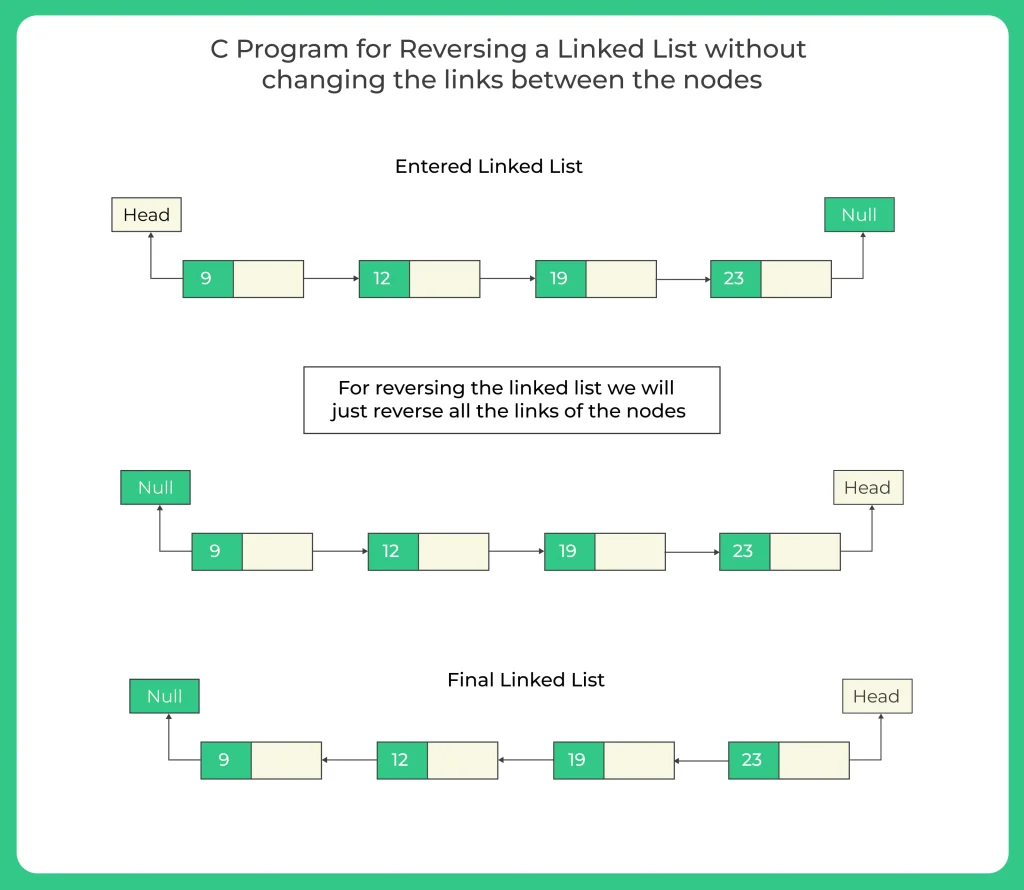
Problems for performing different operations on Linked List are asked in various coding competitions, either directly or in the form of a logical problem. Here we have described one of the manner of reversing a Linked list, but there are few more ways of reversing a linked list according to your needs, like Reversing it without changing the links, or just reverse printing the data.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others



Login/Signup to comment