C Program for Insertion at the End of the Singly Linked List
Insertion in singly linked list at the end
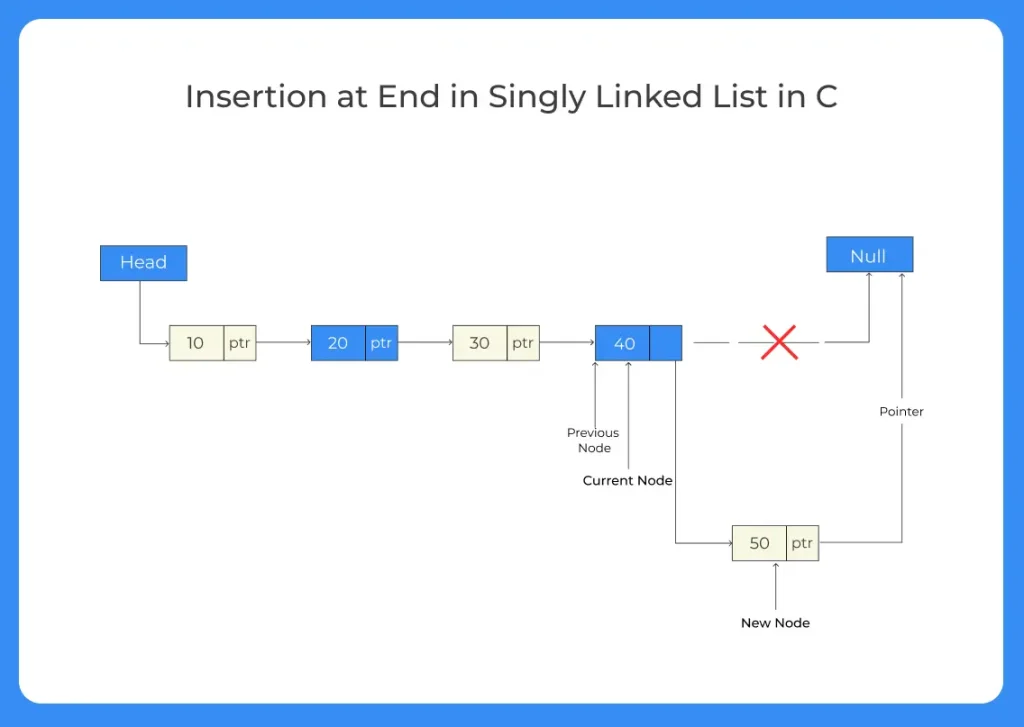
Below we are going to look at the C Program for Insertion at the End of the Singly Linked List. Follow the detailed steps and code below to do the same 0

Implementation:-
- Create a new node, assign its data value
- Since this new node will be the last node its next will be NULL
- Traverse to the current last node of the linked list
- Set the current last node’s next to this new node
If the linked list was initially empty and we were entering the first node, change the head from NULL to this new Node.
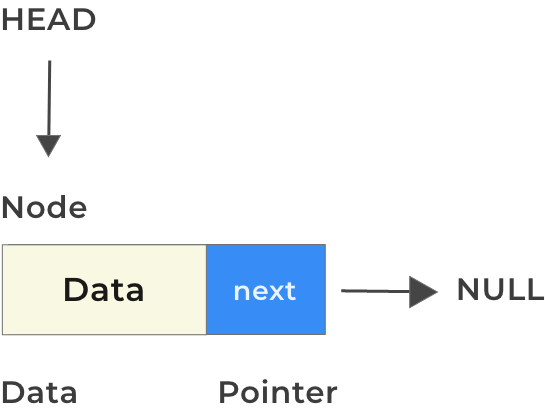
Declare Head & mark it NULL
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Node* head = NULL;

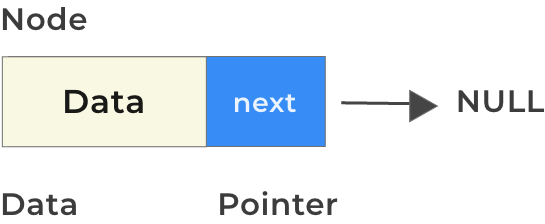
Create a Node
void insertEnd(struct Node** head, int data){
// since this will be the last node so it will point to NULL
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
} 
If its the first node being entered
void insertEnd(struct Node** head, int data){
// since this will be the last node so it will point to NULL
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
// if Linked List is empty its is first node being entered
if(*head == NULL){
*head = newNode;
return;
}
} 
Otherwise Traverse to the current last node
void insertEnd(struct Node** head, int data){
// since this will be the last node so it will point to NULL
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
// if Linked List is empty its is first node being entered
if(*head == NULL){
*head = newNode;
return;
}
// otherwise find the current last node
// create another variable to traverse the LL
// *head should not be used as we do not want to change head
struct Node* temp = *head;
// traverse to the last node of Linked List
while(temp->next!=NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// assign last node's next to this newNode
temp->next = newNode;
} Full Program for Insertion at the End of the Singly Linked List:-
Let us look at the full program for it below –
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void insertEnd (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// since this will be the last node so it will point to NULL
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
// if Linked List is empty its is first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
return;
}
// otherwise find the current last node
// create another variable to traverse the LL
// *head should not be used as we do not want to change head
struct Node *temp = *head;
// traverse to the last node of Linked List
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// assign last node's next to this newNode
temp->next = newNode;
printf ("%d inserted at the end\n", data);
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int
main ()
{
//creating 4 pointers of type struct Node
//So these can point to address of struct type variable
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *node2 = NULL;
struct Node *node3 = NULL;
struct Node *node4 = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node2 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node3 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node4 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
head->data = 22; // data set for head node
head->next = node2; // next pointer assigned to address of node2
node2->data = 30;
node2->next = node3;
node3->data = 24;
node3->next = node4;
node4->data = 20;
node4->next = NULL;
/*No need for & i.e. address as we do not
need to change head address
*/
printf ("Linked List Before Operations : ");
display (head);
insertEnd (&head, 5);
insertEnd (&head, 6);
insertEnd (&head, 7);
insertEnd (&head, 8);
printf ("Linked List After Operations : ");
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List Before Operations: 22 30 24 20
5 inserted at the end
6 inserted at the end
7 inserted at the end
8 inserted at the end
Linked List After Operations : 22 30 24 20 5 6 7 8



Login/Signup to comment