Insertion at end in Singly Linked List in Java
Singly Linked List insertion at end Program in Java
Insertion at end in Singly Linked List in Java is one of the fundamental operations you must understand while learning about linked list data structures. Unlike arrays, where appending elements is relatively straightforward, linked lists require you to manage node references manually.
This article explains what this operation is, how to implement it in Java, and includes clear examples, algorithms, complexities, and common FAQs.

Insertion at end in Singly Linked List in Java
1. Data:The actual value stored.
2. Next:Reference (link) to the next node in the list.
The first node is called the head, and the last node's next reference points to null.
What is Insertion at End in a Singly Linked List?
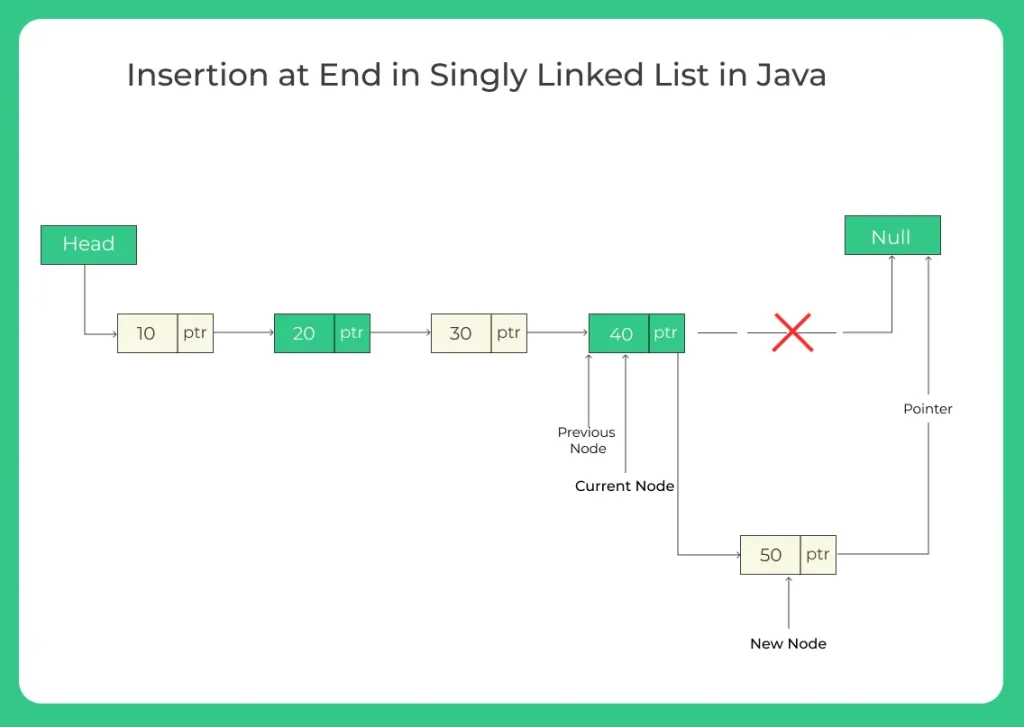
Insertion at the end means adding a new node after the current last node (also known as the tail). It involves:
- Creating a new node.
- Traversing the list to reach the last node.
- Pointing the last node’s next reference to the new node.
Insertion at the end is commonly used in:
- Implementing queues (FIFO).
- Building lists from streaming or batch input.
- Dynamically adding data during traversal.
Methods to Insertion at End in singly linked list

Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method 1: Basic Approach for Insertion at end in singly linked list
Space Complexity: O(1)
Java Code:
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class SinglyLinkedList {
Node head;
// Method to insert at end
public void insertAtEnd(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
}
// Method to print list
public void printList() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " -> ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SinglyLinkedList list = new SinglyLinkedList();
list.insertAtEnd(10);
list.insertAtEnd(20);
list.insertAtEnd(30);
System.out.println("Linked List after insertion at end:");
list.printList();
}
}
Output:
Linked List after insertion at end: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> null
Method 2: Optimized Approach for Insertion at end in singly linked list
Space Complexity: O(1)
Java Code:
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class OptimizedSinglyLinkedList {
Node head;
Node tail;
public void insertAtEnd(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
} else {
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
}
public void printList() {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " -> ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
}
public class MainOptimized {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OptimizedSinglyLinkedList list = new OptimizedSinglyLinkedList();
list.insertAtEnd(5);
list.insertAtEnd(15);
list.insertAtEnd(25);
System.out.println("Optimized Linked List after insertion at end:");
list.printList();
}
}
Output:
Optimized Linked List after insertion at end: 5 -> 15 -> 25 -> null
Comparison of Both Methods:
Approach | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Without Tail Reference | O(n) | O(1) | Simple one-time insertion |
| With Tail Reference | O(1) | O(1) | Frequent insertions at the end |
Conclusion:
Understanding insertion at end in Singly Linked List in Java is crucial for working with dynamic data structures. This article covered both naive and optimized methods with clear Java code, making it easy for beginners to grasp.
Efficient manipulation of linked lists forms the backbone of more advanced algorithms and system design, so mastering these basics will take you a long way in your programming journey.
FAQ's related to Insertion at end in singly linked list
Answer:
If the list is empty (head == null), the new node becomes the head (and optionally the tail, if using tail reference).
Answer:
Yes, but it’s not recommended for large lists due to potential StackOverflowError. Iterative approaches are preferred.
Answer:
If you perform frequent insertions at the end, then yes. It reduces time complexity from O(n) to O(1).
Answer:
It is useful in scenarios like task scheduling, queue implementations, and stream processing where order matters.
Answer:
Use a loop and a tail reference to insert multiple elements efficiently in O(1) time per operation.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment