0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
Singly Linked List in C++
What is a singly linked list in C++ programming?
Singly linked list in C++ is one of the simplest data structure. Since, we can dynamically add or delete items as per requirement, while in Arrays the size of the array once defined can not be altered.
Let us learn more about the singly linked lists in C++ programming in this article.

What is Singly Linked List in C++
A Singly linked List a Sequence of nodes connected to one another using pointers. Following are components of Singly Linked List –
- Data – The value held
- Next Pointer – Contains the address of the next node in the sequence
Unlike an array that is contiguous each node in a Singly Linked List is scattered all over memory and are connected to one another using pointers.
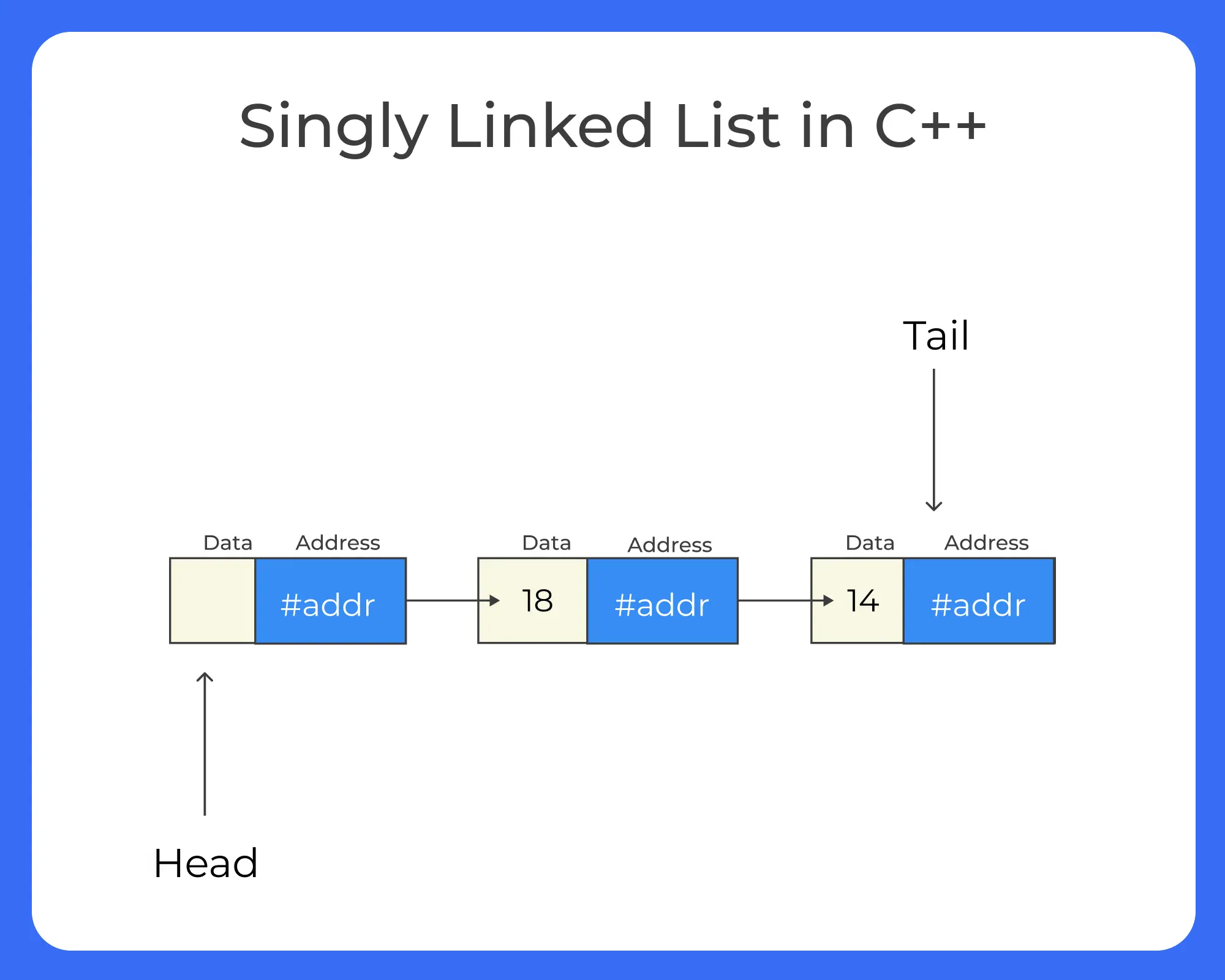
Structure of the singly linked list
The following set of code is used to struct the nodes of a singly linked list. Here we have defined a singly linked list that will store integer type data in it.
class node
{
int data;
node *next;
};
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
This code will create a data type Node, which will be able to store two values-:
- int value – data
- pointer value – address of the next node
Operations on singly linked list
Following operations can be performed over a singly linked list
Insertion of a node
void insertStart(int data)
{
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
cout << data << " Inserted" << endl;
}
void insertStart(Node** head, int data)
{
Node* newNode = new Node;
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
cout << "\n" << newNode->data << " Inserted" << endl;
}

Deletion of a node
void deleteStart()
{
if (head == nullptr)
{
cout << "Linked List Empty, nothing to delete" << endl;
return;
}
Node* temp = head;
head = head->next;
cout << temp->data << " deleted" << endl;
delete temp;
}
void deleteStart(Node** head)
{
Node* temp = *head;
if (*head == nullptr)
{
cout << "Linked List Empty, nothing to delete" << endl;
return;
}
*head = (*head)->next;
cout << "\n" << temp->data << " deleted" << endl;
delete temp;
}

Traversal in a Singly Linked List
void display()
{
cout << "Linked List: ";
Node* current = head;
while (current != nullptr)
{
cout << current->data << " ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
void display(Node* node)
{
cout << "\nLinked List: ";
while (node != nullptr)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}

Code for Implementing Single Linked List in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int value) : data(value), next(nullptr) {}
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
LinkedList() : head(nullptr) {}
void insertStart(int data)
{
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
cout << data << " Inserted" << endl;
}
void deleteStart()
{
if (head == nullptr)
{
cout << "Linked List Empty, nothing to delete" << endl;
return;
}
Node* temp = head;
head = head->next;
cout << temp->data << " deleted" << endl;
delete temp;
}
void display()
{
cout << "Linked List: ";
Node* current = head;
while (current != nullptr)
{
cout << current->data << " ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
LinkedList list;
list.insertStart(100);
list.insertStart(80);
list.insertStart(60);
list.insertStart(40);
list.insertStart(20);
list.display();
list.deleteStart();
list.deleteStart();
list.display();
return 0;
}
Output
100 Inserted 80 Inserted 60 Inserted 40 Inserted 20 Inserted Linked List: 20 40 60 80 100 20 deleted 40 deleted Linked List: 60 80 100
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* next;
};
void insertStart(Node** head, int data)
{
Node* newNode = new Node;
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
cout << "\n" << newNode->data << " Inserted" << endl;
}
void deleteStart(Node** head)
{
Node* temp = *head;
if (*head == nullptr)
{
cout << "Linked List Empty, nothing to delete" << endl;
return;
}
*head = (*head)->next;
cout << "\n" << temp->data << " deleted" << endl;
delete temp;
}
void display(Node* node)
{
cout << "\nLinked List: ";
while (node != nullptr)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = nullptr;
insertStart(&head, 100);
insertStart(&head, 80);
insertStart(&head, 60);
insertStart(&head, 40);
insertStart(&head, 20);
display(head);
deleteStart(&head);
deleteStart(&head);
display(head);
return 0;
}
Output
100 Inserted 80 Inserted 60 Inserted 40 Inserted 20 Inserted Linked List: 20 40 60 80 100 20 deleted 40 deleted Linked List: 60 80 100
Disadvantages of singly linked list in CPP programming
- Members could be assigned anywhere in the memory.
- Each member shall include an address size member, hence it utilizes poor memory.
- Some operations like reversing a list is complicated when compared with arrays,

Why Singly Linked List?
Performing operations on a list becomes easy
Singly linked list give us the flexibility to perform various operations such as insertion, deletion in an efficient manner as compared to arrays.
Efficient memory allocation
We need not tho allocate memory in advance to the singly linked list, dynamic memory is allocated in singly linked list hence it saves extra memory .
Implentation of advance data structure
Many advance data structures are implemented with the help of singly linked list hence they become very useful there.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Time Complexity
For Singly Linked List
Best
O(1)
Average
O(n)
Worst
O(n)
Average Comparisons
(n+1)/2
Time Complexity
For Singly Linked List
Best
O(1)
Average
O(n)
Worst
O(n)
Average Comparisons
(n+1)/2

Question 1. Which of the following operations has a time complexity of O(1) in a singly linked list?
- Insertion at the beginning
- Deletion at the end
- Traversal
- Searching for an element
The correct answer is a)
Insertion at the beginning. In a singly linked list, insertion at the beginning involves updating only a few pointers, irrespective of the size of the list.
Therefore, the time complexity of this operation is constant, O(1). The other options require traversing the list, which takes linear time, O(n).

Question 2. What is the time complexity for searching an element in a singly linked list, assuming the element is present in the list?
- O(1)
- O(log n)
- O(n)
- O(n^2)
The correct answer is c) O(n).
Searching for an element in a singly linked list requires traversing through each node until the desired element is found or the end of the list is reached.
In the worst case, when the element is at the end of the list or not present at all, the algorithm needs to visit every node, resulting in a linear time complexity, O(n).

Question 3. What is the main disadvantage of a singly linked list compared to an array?
- Dynamic memory allocation
- Random access
- Insertion and deletion at the end
- Efficient memory utilization
The correct answer is b) Random access.
In a singly linked list, accessing an element at a specific index requires traversing the list from the beginning. This makes random access inefficient as compared to an array, where elements can be accessed directly using their indices.
Singly linked lists are better suited for operations that involve sequential access, such as traversal, insertion, and deletion.

Question 4. Which of the following operations can be performed efficiently in both singly linked lists and doubly linked lists?
- Insertion at the beginning
- Insertion at the end
- Deletion at the beginning
- Deletion at the end
The correct answer is a) Insertion at the beginning.
Both singly linked lists and doubly linked lists support efficient insertion at the beginning. In both cases, updating a few pointers is sufficient to insert a new node at the front, regardless of the size of the list.
The other options require additional traversal or pointer manipulation, resulting in slower operations.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –

 0
0




Login/Signup to comment