0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
Linked List in C++
What is linked list in C++?
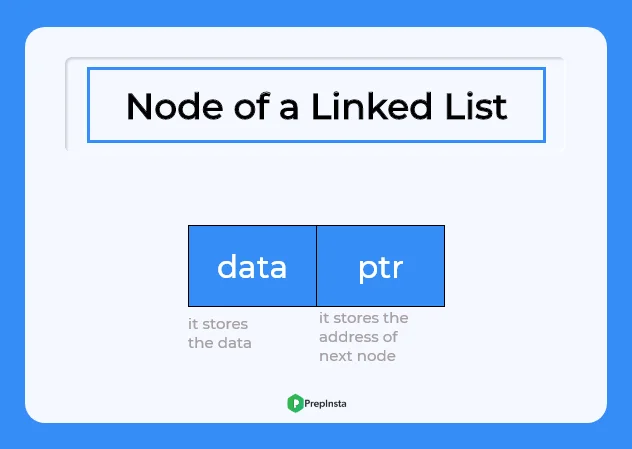
Linked List in C++ is data structures and alternative to arrays, where every node of the linked list is made up of two parts data and pointer.
- Data: It stores the data of the node.
- Pointer: It stores the address of the next node.

What is a Linked List ?
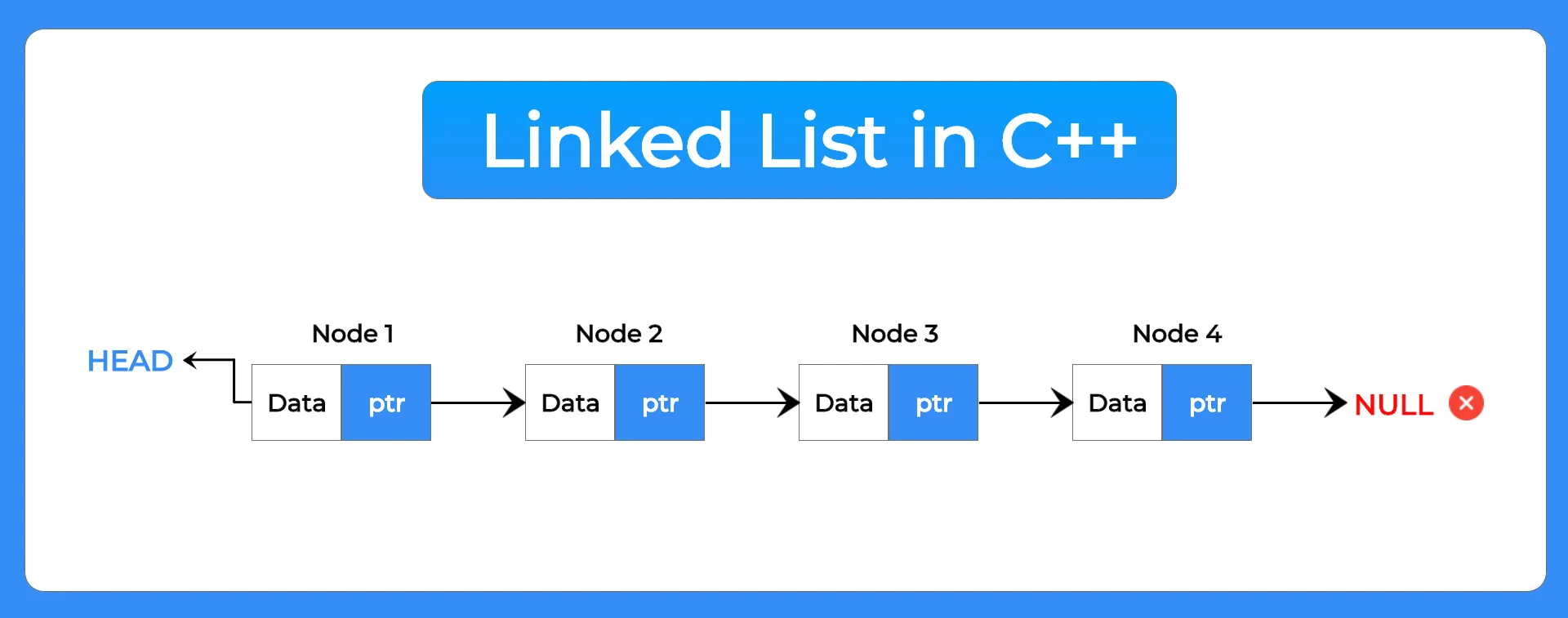
A linked list is a chain of nodes that are connected to one another using pointers. Each node in a linked list has the following two things –
- Data: Value stored in Linked List Data Structure
- Next Pointer: Contains the address to the next node
Comparison with Arrays
Arrays are sequential and contiguous structures. Linked lists are non-contiguous structures i.e. each node in the linked list is scattered all over memory and need not be contiguous.
This has a significant advantage as in the case of arrays we need to pre-declare the size of the array
- We can not increase the size of the array on requirement once the size is defined
- If the declared size of the array is too large and the requirement later is lesser, the size of the array can not be reduced, thus waste of memory.
However, in the case of Linked List, we can increase/decrease the size or number of nodes in real-time.
Types of Linked List
There are three types of Linked lists majorly –
Singly Linked List
In C++ Singly Linked List is a simple data structure that has a sequence of nodes connected to each other with pointers.
- Data:- Value held
- Next Pointer:- Contains the address of the next node in sequence
Syntax of a singly linked list:-
class node { int data; node *next; };
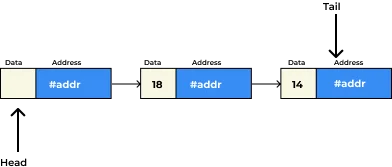
Doubly Linked List in C++
Doubly Linked Lists allows users to navigate through both the ends of a linked list, i.e., from head to tail and from tail to head. The beginning of the linked list is called header and the last node is the tail.

struct Node
{
int Data;
Struct Node* next;
Struct Node* prev;
}; Circular Linked List in C++
In a circular linked list, each node has the link to the next node, and the last node does not points to null rather points to the head of the list.

Syntax for a singly circular linked list:-
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
}Construction of a Linked List
This set of code will create a new empty node in a linked list which will be storing integer type of data.
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};class Node{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};C++ : Operations on Linked List
Insertion operations on linked list
- Insertion at beginning
- Insertion at end
- Insertion in between of nodes.
Deletion operations on linked list
- Deletion at beginning
- Deletion at end
- Deletion of a specific node.
Other operations on linked list
- Reverse a linked list
- Search an element in linked list
- Find middle of the linked list
- Fold a linked list
C++ Code for Creating/Deleting from a Linked List
We will cover the following methods –
- Method 1: Using struct
- Method 2: Using class but with external functions
- Method 3: Using class and member functions
#include< bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
// Pointer pointing towards next node
};
void insertFront (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assign data value
newNode->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
newNode->next = *head;
//re-assign head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
}
void deleteFront (struct Node *&head)
{
struct Node *temp = head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << "Linked List Empty, nothing to delete";
return;
}
// move head to next node *head = (*head)->next;
cout << "Value deleted: " << temp->data << endl;
// Node *temp = head;
head = head->next;
delete temp;
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
cout << "\n\n";
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << "\n" << endl;
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
insertFront (&head, 6);
insertFront (&head, 12);
insertFront (&head, 18);
insertFront (&head, 24);
insertFront (&head, 30);
// No '&' as head is not changed
display (head);
deleteFront (head);
deleteFront (head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
30 24 18 12 6 Value deleted: 30 Value deleted: 24 18 12 6
#include< iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
void insertFront(Node** head, int data){
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
Node* newNode = (Node*) malloc(sizeof(Node));
// assign data value
newNode->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
newNode->next = *head;
//re-assign head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
}
void deleteFront(Node *&head){
Node* temp = head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if(head == NULL)
{
cout << "Linked List Empty, nothing to delete" ;
return;
}
// move head to next node *head = (*head)->next;
cout << "Value deleted: " << temp->data << endl;
head = head->next;
delete temp;
}
void display(Node* node){
cout << "\n\n";
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << "\n" << endl;
}
int main() {
Node* head = NULL;
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
insertFront(&head,6);
insertFront(&head,12);
insertFront(&head,18);
insertFront(&head,24);
insertFront(&head,30);
// No '&' as head is not changed
display(head);
deleteFront(head);
deleteFront(head);
display(head);
return 0;
}
Output
30 24 18 12 6 Value deleted: 30 Value deleted: 24 18 12 6
#include< iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
LinkedList() { // constructor
head = NULL;
}
void insertFront(int data);
void deleteFront();
void display();
};
void LinkedList::insertFront(int data){
Node* newNode = new Node();
// assign data value
newNode->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
newNode->next = head;
//re-assign head to this newNode
head = newNode;
}
void LinkedList::deleteFront(){
Node* temp = head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if(head == NULL)
{
cout << "Linked List Empty, nothing to delete" ;
return;
} // move head to next node head = head->next;
cout << "Value deleted: " << temp->data << endl;
head = head->next;
delete temp;
}
void LinkedList::display(){
cout << "\n\n";
// temporary variable to traverse
Node* node = head;
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while(node!=NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << "\n" << endl;
}
int main() {
LinkedList* linked_list = new LinkedList();
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
linked_list->insertFront(6);
linked_list->insertFront(12);
linked_list->insertFront(18);
linked_list->insertFront(24);
linked_list->insertFront(30);
// No '&' as head is not changed
linked_list->display();
linked_list->deleteFront();
linked_list->deleteFront();
linked_list->display();
return 0;
}
Output
30 24 18 12 6 Value deleted: 30 Value deleted: 24 18 12 6
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java

 0
0



Login/Signup to comment