C++ program to delete alternate nodes of a Linked List

How to delete alternate nodes of a Singly Linked List in C++?
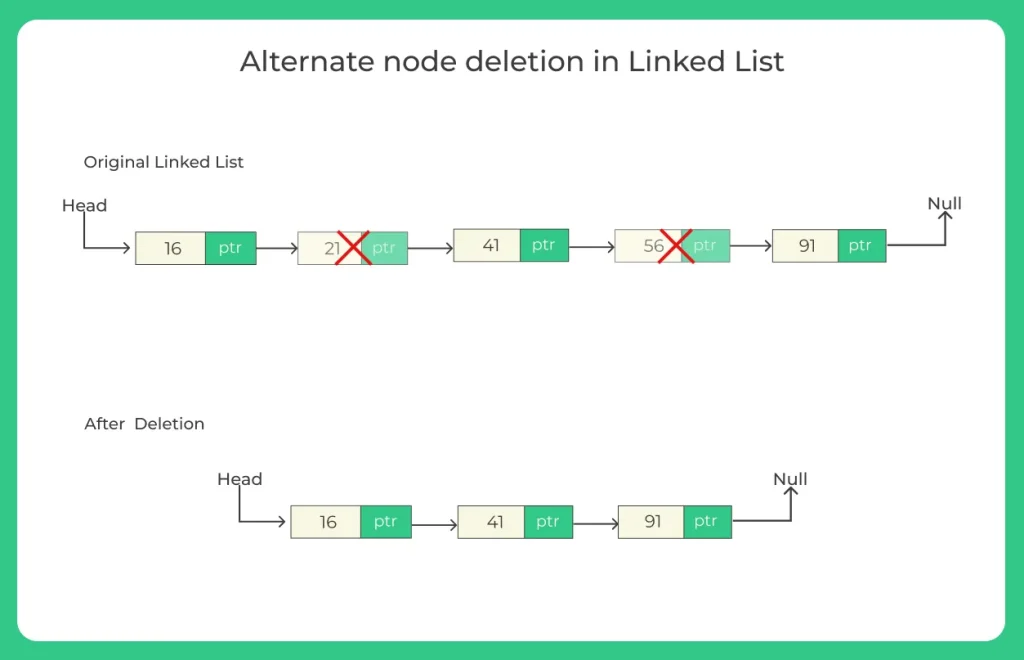
Deleting alternate nodes of the linked list means to keep one node and delete another for example if the data in the list is 14,7,6,20 and 56 it should return 14,6 and 56 after deleting alternate node 7 and 20. In this article, we will learn how to code a C++ program to delete alternate nodes of a linked list.
Steps to write a C++ program to delete alternate nodes of a linked list
To delete alternate nodes of a linked list in C++, you first traverse the list while keeping track of the current node and its next node. By adjusting the next pointers, you can remove every second node and free its memory, ensuring the list remains properly linked. This method efficiently modifies the list without creating a new one.
If we want to delete alternate nodes of a linked list, following steps are followed.
- Create linked list using the set of code defined below.
- Initialize the variables.
- Create a function named make() to create all the nodes of linked list.
- Now we need a display function that will be help us to show list before and after deletion.
- Create that display function.
- Create a function to delete alternate nodes named alternateDel().
- Take two pointers prev and alt_node
- Initially prev will points to head and alt_node will points to second node .
- Make the link of prev to point to link of alt_node and free alt_node.
- Traverse prev to next node.
- Traverse alt_node to next node of prev.
- Repeat step 9,10, and 11 until prev and alt_node becomes null.
- Print list after deleting alternate nodes.
Syntax
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
};
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Algorithm to delete alternate nodes of a linked list
Following algorithm is used to delete alternate nodes of a linked list.
- IF STNODE==NULL
- EXIT
- WHILE (PREV!=NULL&&ALT_NODE!=NULL)
- PREV->NEXTPTR=ALT_NODE->NEXTPTR
- FREE(ALT_NODE)
- PREV=PREV->NEXTPTR
- IF(PREV!=nULL)
- ALT_NODE=PREV->NEXTPTR
Program to delete alternate nodes of a linked list in C++
This C++ program efficiently removes every alternate node from a linked list, updating links to maintain the list’s structure while freeing memory of the deleted nodes. It helps simplify the list by eliminating unnecessary elements.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int num;
node *nextptr;
} *stnode; //node declared
void make (int n);
void alternateDel (node * stnode);
void display ();
int main () //main method
{
int n, num;
cout << "Enter the number of nodes: "; cin >> n;
make (n);
cout << "\nLinked list data: \n";
display ();
cout << "\nAfter deleting alternate node:\n";
alternateDel (stnode);
display ();
return 0;
}
void make (int n) //function to create linked list.
{
struct node *frntNode, *tmp;
int num, i;
stnode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (stnode == NULL)
{
cout << " Memory can not be allocated";
}
else
{
cout << "Enter the data for node 1: "; cin >> num;
stnode->num = num;
stnode->nextptr = NULL; //Links the address field to NULL
tmp = stnode;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
frntNode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (frntNode == NULL) //If frntnode is null no memory cannot be alloted
{
cout << "Memory can not be allocated";
break;
}
else
{
cout << "Enter the data for node " << i << ": "; // Entering data in nodes. cin >> num;
frntNode->num = num;
frntNode->nextptr = NULL;
tmp->nextptr = frntNode;
tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
}
}
}
void display () //function to display linked list
{
struct node *tmp;
if (stnode == NULL)
{
cout << "List is empty";
}
else
{
tmp = stnode;
cout << "Linked List\t";
while (tmp != NULL)
{
cout << tmp->num << "\t"; tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
}
}
void alternateDel (node * stnode) //function to delete alternate nodes.
{
if (stnode == NULL)
return;
node *prev = stnode;
node *alt_node = stnode->nextptr;
while (prev != NULL && alt_node != NULL)
{
prev->nextptr = alt_node->nextptr;
free (alt_node);
prev = prev->nextptr;
if (prev != NULL)
alt_node = prev->nextptr;
}
}
Output:
Enter the number of nodes: 5 Enter the data for node 1: 14 Enter the data for node 2: 7 Enter the data for node 3: 6 Enter the data for node 4: 20 Enter the data for node 5: 56 Linked list data: Linked List 14 7 6 20 56 After deleting alternate node: Linked List 14 6 56
Explanation:
- The program creates a singly linked list, displays it, and then deletes every alternate node using dynamic memory allocation (malloc).
- The make() function constructs the linked list by creating n nodes and linking them sequentially.
- The display() function traverses the list from the start node (stnode) and prints all node values until it reaches NULL.
- The alternateDel() function removes every second node by adjusting the nextptr of previous nodes and freeing memory of deleted nodes.
- In the example, input 14 → 7 → 6 → 20 → 56 becomes 14 → 6 → 56 after deleting alternate nodes.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
Create List (make()) |
O(n) | O(n) | Creates and links all nodes once. |
Display List (display()) |
O(n) | O(1) | Traverses list to print data. |
Delete Alternate Nodes (alternateDel()) |
O(n) | O(1) | Deletes every second node. |
| Overall | O(n) | O(n) | Linear time and space complexity. |
To wrap it up:
In summary, the article clearly outlines the logic and steps to remove alternate nodes from a singly linked list using C++. It explains the use of two pointers (prev and alt_node) to traverse the list and rewire pointers while freeing memory of the nodes to be deleted.
This approach ensures that every second node is removed cleanly with O(n) time complexity and without needing extra space. It’s a practical method to understand pointer manipulation and memory handling in linked list operations.
FAQs
Yes, after skipping a node, it should be deleted using delete to free memory and avoid memory leaks.
It works for singly linked lists; for doubly linked lists, both next and prev pointers need adjustment while deleting.
Nothing is deleted since there’s either no node or no alternate node to remove, and the program safely handles these cases.
Yes, recursion can be used by deleting the second node and then recursively calling the function for the rest of the list.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment