Deletion from end in singly linked list in C++
How to delete element from end in Singly Linked List in C++?
In this article, let’s see how to code a C++ Program for deleting the last/end node of a singly linked list.
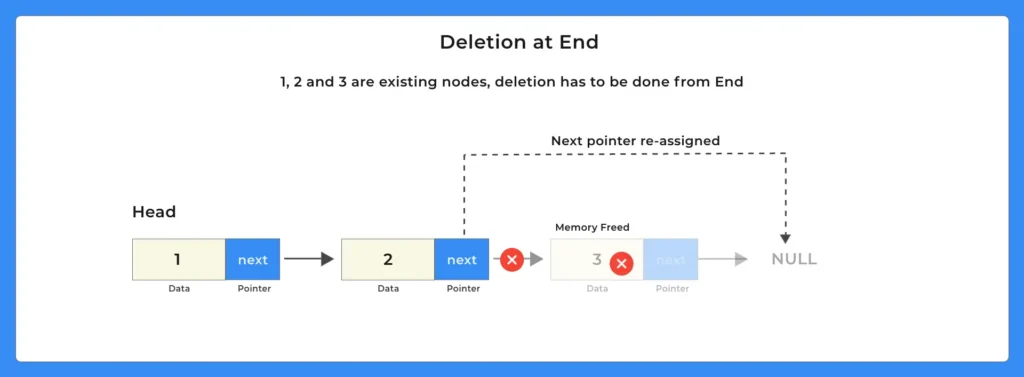
In a Singly Linked List, deleting an element from the end involves traversing the list to find the second last node and updating its pointer to NULL. This effectively removes the last node from the list, freeing up its memory and maintaining the linked structure.

Steps to delete an element from end in singly linked list
Following steps are followed for deletion of an element from the end in a singly linked list.
- Check if the Linked List is empty as we can not delete from an empty Linked List
- Check if the Linked List has only one Node
- In this case, just point the head to NULL and free memory for the existing node
- Otherwise, if the linked list has more than one node, traverse to the end of the Linked List
- Point next of 2nd Last node to NULL
- Free the memory for the last node.
Defining a singly linked list in C++
Nodes of singly linked list is created by using the code mentioned besides.
This set of code will construct linked list by creating each node of the list.
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
}; 
Program for deletion from end in singly linked list in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
void deleteEnd (Node ** head)
{
Node *tempNode = *head;
Node *previous;
// Can't delete from empty Linked List
if (*head == NULL)
{
cout << ("\nEmpty List, can't delete");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (tempNode->next == NULL)
{
cout << "\nValue Deleted: " << (*head)->data;
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// else traverse to the last node
while (tempNode->next != NULL)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode->next;
}
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to Null
previous->next = NULL;
cout << "\nValue Deleted: " << tempNode->data;
// delete the last node
free (tempNode);
// 2nd last now becomes the last node
}
void insert (Node ** head, int data)
{
Node *newNode = new Node ();
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
// assigned head to newNode
*head = newNode;
}
void display (Node * temp)
{
cout << "\nLinked List: ";
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (temp != NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main ()
{
Node *head = NULL;
insert (&head, 4);
insert (&head, 5);
insert (&head, 6);
insert (&head, 7);
insert (&head, 8);
insert (&head, 9);
insert (&head, 10);
display (head);
deleteEnd (&head);
deleteEnd (&head);
deleteEnd (&head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 Value Deleted: 4 Value Deleted: 5 Value Deleted: 6 Linked List: 10 9 8 7
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node * head;
public:
LinkedList ()
{ // constructor
head = NULL;
}
int calcSize ();
void deleteEnd ();
void display ();
void insert (int data);
};
void LinkedList::deleteEnd ()
{
Node *temp = head;
Node *previous;
// Can't delete from empty Linked List
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << ("\nEmpty List, can't delete");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (temp->next == NULL)
{
cout << "\nValue Deleted: " << head->data;
head = NULL;
return;
}
// else traverse to the last node
while (temp->next != NULL)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to Null
previous->next = NULL;
cout << "\nValue Deleted: " << temp->data;
// delete the last node
free (temp);
// 2nd last now becomes the last node
}
void LinkedList::insert (int data)
{
Node *newNode = new Node ();
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = head;
// assigned head to newNode
head = newNode;
}
void LinkedList::display ()
{
Node *node = new Node ();
node = head;
cout << "\nLinked List: ";
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main ()
{
LinkedList *list = new LinkedList ();
list->insert (4);
list->insert (5);
list->insert (6);
list->insert (7);
list->insert (8);
list->insert (9);
list->insert (10);
list->display ();
list->deleteEnd ();
list->deleteEnd ();
list->deleteEnd ();
list->display ();
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 Value Deleted: 4 Value Deleted: 5 Value Deleted: 6 Linked List: 10 9 8 7
Time and Space Complexity table :
| Operation | Code Function | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insertion at Beginning | insert() | O(1) — Constant time as insertion happens at the head | O(1) — Only one new node is created |
| Deletion from End | deleteEnd() | O(n) — Traverses the entire list to find the last node | O(1) — Uses a few temporary pointers only |
| Display Linked List | display() | O(n) — Iterates through all nodes once | O(1) — No extra space apart from traversal pointer |
| Overall Program | main() | O(n) — Dominated by traversal and deletion operations | O(1) — No additional dynamic memory used beyond linked list nodes |
To wrap it up:
Deleting the last node in a singly linked list in C++ requires careful handling of different scenarios, such as an empty list or a list with a single node. The article explains the step-by-step approach, including traversing to the second-last node and updating pointers correctly. The code example reinforces these concepts practically.
Understanding this deletion process strengthens your grasp of linked list operations in C++. The explanations and examples make it easier for learners to implement and debug similar operations in their programs. The hands-on approach ensures clarity and practical knowledge.
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
FAQs
In a singly linked list, it’s not possible to directly access the previous node, so you must traverse the list to find the second-last node before deletion.
After updating the second-last node’s next pointer to NULL, the last node must be explicitly deleted using delete in C++ to free memory and avoid leaks.
Yes, but you should pass the head pointer by reference (or as Node**) to update the list correctly, especially when the list has only one node.
Deleting the last node reduces the list size by one, and care must be taken to update the head if it was the only node, ensuring the list doesn’t become invalid.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment