Singly Linked List Insertion at beginning in C
Insertion in singly linked list at the beginning
C Program for insertion at the beginning of the Singly Linked List. A Singly linked list is made up of many nodes which are connected. Every node is mainly divided into two parts, one part holds the data and the other part is the link that connects to the next node
Singly Linked List allow insertion at the following places:
- Insertion at the start of the singly Linked List
- Insertion at the end of the singly linked list.
- Insertion at the nth node of the singly linked list.
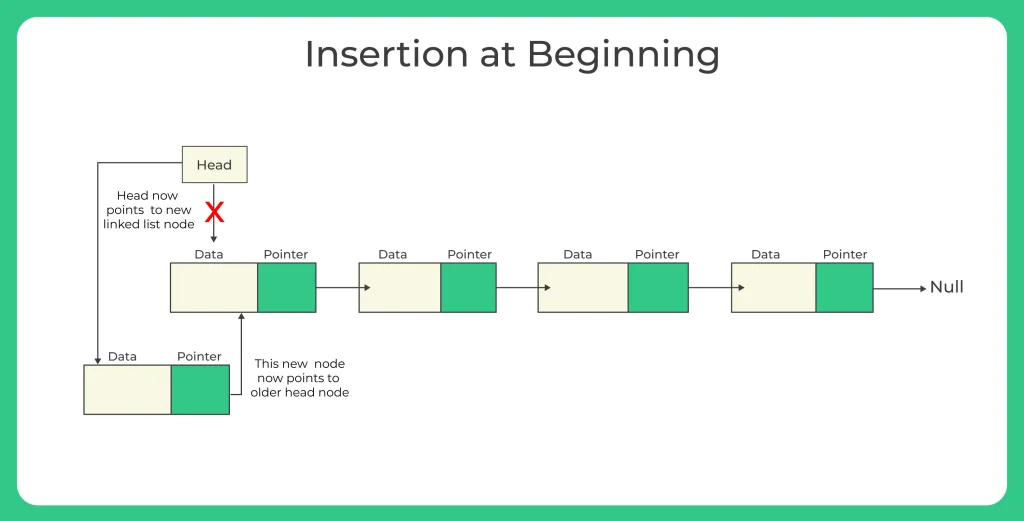
Singly Linked List Definition
struct Node
{
int Data;
Struct Node *next;
};
C Program for Insertion at the Beginning of the Singly Linked List
C Program for Insertion at the Beginning of the Singly Linked List
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assign data value
newNode->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
newNode->next = *head;
//re-assign head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
printf ("%d Insertion Successful\n", newNode->data);
}
void printLinkedList (struct Node *node)
{
printf ("\nLinked List: ");
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
// Use '&' i.e. address as we need to change head address
insertStart (&head, 100);
insertStart (&head, 80);
insertStart (&head, 60);
insertStart (&head, 40);
insertStart (&head, 20);
// Don't use '&' as not changing head in printLinkedList operation
printLinkedList (head);
return 0;
}
Output
100 Insertion Successful 80 Insertion Successful 60 Insertion Successful 40 Insertion Successful 20 Insertion Successful Linked List: 20 40 60 80 100
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assign data value
newNode->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
newNode->next = *head;
//re-assign head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
printf ("%d Insertion Successful\n", newNode->data);
}
void printLinkedList (struct Node *node)
{
printf ("\nLinked List: ");
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
int input, item;
do
{
printf ("\nEnter the item to insert?\n");
scanf ("%d", &item);
// Use '&' i.e. address as we need to change head address
insertStart (&head, item);
printf ("\nPress 0: To Exit\n");
printf ("Press 1: To insert more items\n");
scanf ("%d", &input);
}
while (input == 1);
// Don't use '&' as not changing head in printLinkedList operation
printLinkedList (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the item to insert? 10 10 Insertion Successful Press 0: To Exit Press 1: To insert more items 1 Enter the item to insert? 20 20 Insertion Successful Press 0: To Exit Press 1: To insert more items 1 Enter the item to insert? 30 30 Insertion Successful Press 0: To Exit Press 1: To insert more items 0 Linked List: 30 20 10
To wrap it up
Adding a node at the beginning of a singly linked list is one of the easiest and most useful operations you’ll come across. It simply means creating a new node, linking it to the current first node, and then making it the new head of the list.
The best part? It takes constant time, no matter how long the list is. This makes it super handy when you need to insert data quickly.
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others



Login/Signup to comment