0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
Java program for Insertion in a Sorted Linked List
Insertion in a sorted linked list in java
What is insertion in a sorted linked list in java? It is a process of inserting data in between of the linked list, for that first we have to create a linked list which is already in a sorted form or we can say it is ascending/descending order, if it is not then we have to sort the linked list after that we will insert a node according to the data given to us in a node.
Algorithm
Step 1 :- Create a new node first with data equal to data to be inserted and next equal to null.
Step 2 :- If the linked list is empty or data to be inserted is less than the head node data then we need not do much. Simply change the next of new node such that it points to the head and update the head.
Step 2 :- Else, find the first node whose data is greater than the data to be inserted.
Step 3 :- Change the next of new node such that it points to next of node found in step 3.
Step 4 :- Change the next of node found in step 3 such that it points to new node.
Step 5 :- The data is inserted now and the linked list is still sorted.
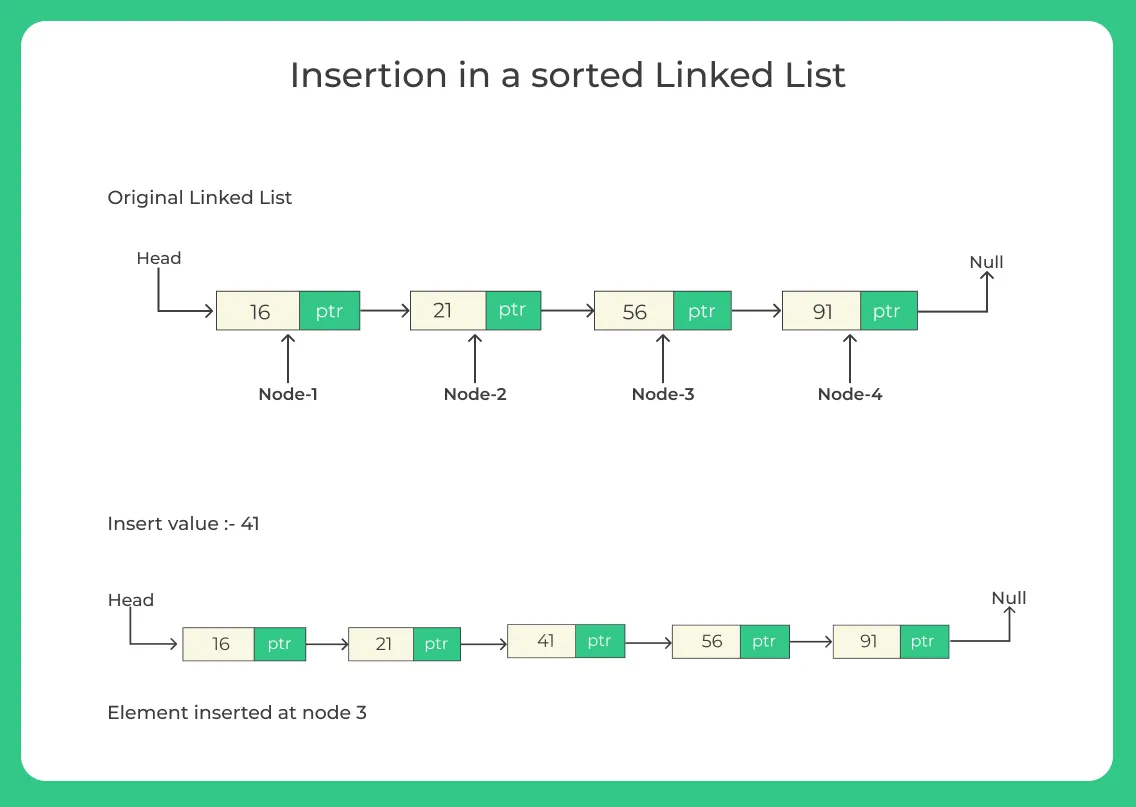
Example
For Insertion in a sorted linked list in java. Suppose we have a linked list like ( 16–>21–>53–>97) and we have to insert a node which have the data (40). After insertion linked list would look like or the output will be
Output -: (16–>21–>40–>53–>97)
Java Program for insertion in a sorted Linked List
import java.util.*;
class LinkedList
{
Node head;
// Node Class
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node (int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
private Node tail;
private int size;
// Linked list constructor
//
// Function to find the size of linked list
public int size ()
{
return this.size;
}
// Function to check whether linked list is empty or not
public boolean isEmpty ()
{
return this.size () == 0;
}
// Function to add a node in beginning of linked list
public Node insert (int data)
{
Node newNode = new Node (data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
public void display ()
{
Node node = head;
//as linked list will end when Node reaches Null
while (node != null)
{
System.out.print (node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println ("\n");
}
public void sortedInsert (int data)
{
this.sortedInsert (this.head, data);
}
// Function to insert a node sch that the linked list remains sorted
private void sortedInsert (Node node, int data)
{
// Create a new node first
Node newNode = new Node (data);
// If the linked list is empty or data to be inserted is less than the head node data
// then change the next of newNode such that it points to the head and update head
if (node == null || data <= node.data)
{
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
}
else
{
// Move till we find the lastnode whose data is lesser than the data to be inserted
while (node.next != null && node.next.data < data)
{
node = node.next;
}
// Now make changes to next pointers accordingly
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
}
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args) throws Exception
{
LinkedList ll = new LinkedList ();
ll.insert (97);
ll.insert (53);
ll.insert (21);
ll.insert (16);
System.out.println ("Linked List before Insertion");
ll.display ();
ll.sortedInsert (7);
System.out.println ("Linked List after Insertion");
ll.display ();
}
}
Output: Linked List before Insertion 16 21 53 97 Linked List after Insertion 7 16 21 53 97
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java

 0
0



Login/Signup to comment