Insertion at nth position in Singly Linked List in Java
Java Program for Insertion at nth position in Singly Linked List
In this article, we will explore how to insertion at nth position in a singly linked list in Java. We will walk through the logic step by step, share the complete Java code, and answer common FAQs to ensure clarity and understanding.

Insertion at nth position in Singly Linked List in Java
What is the Problem?
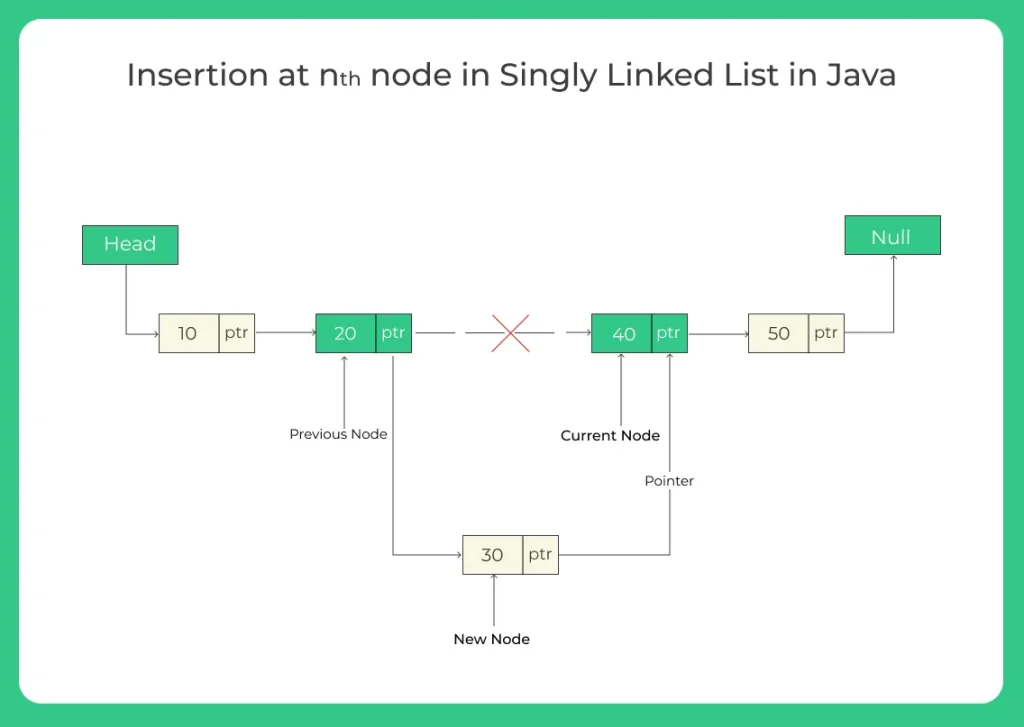
We are given a singly linked list and a position n. We are to insert a new node with a given value at that nth position.
Example:
Original List: 10 → 20 → 30 → 40 Insert 25 at position 3 Resulting List: 10 → 20 → 25 → 30 → 40
Note: Positions are 1-based (i.e., position 1 is the head of the list).
Understanding the Singly Linked List Structure
A singly linked list is made up of nodes. Each node contains:
- Data: The actual value
- Next: Reference to the next node in the list
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Algorithm for Insertion at nth Position in Singly Linked List
There are 2 main scenarios to consider when inserting at position n:
- Insert at the head (n = 1)
- Insert at a position > 1
Step by Step Logic:
- If position = 1:
Create a new node
Point its next to the current head
Update head to the new node
Else:
Traverse to the (n-1)th node (let’s call it prev)
Store prev.next in a temporary variable
Point prev.next to the new node
Point the new node’s next to the temporary node.
Time and Space Complexity for Insertion at nth position in singly linked list
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insert at head | O(1) | O(1) |
| Insert at position n | O(n) | O(1) |
- Time increases linearly with position since we need to traverse the list.
- Space remains constant because we’re using only a few extra pointers.
Java Code for Insertion at nth Position in Singly Linked List
public class SinglyLinkedList {
// Node class
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
Node head;
// Insert at nth position
public void insertAtPosition(int data, int position) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (position < 1) {
System.out.println("Invalid position. Position should be >= 1.");
return;
}
// Insertion at the head
if (position == 1) {
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node current = head;
// Traverse to (position - 1)th node
for (int i = 1; i < position - 1; i++) {
if (current == null) {
System.out.println("Position out of bounds.");
return;
}
current = current.next;
}
if (current == null) {
System.out.println("Position out of bounds.");
return;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
}
// Print the linked list
public void printList() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " → ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
// Main method for testing
public static void main(String[] args) {
SinglyLinkedList list = new SinglyLinkedList();
list.insertAtPosition(10, 1);
list.insertAtPosition(20, 2);
list.insertAtPosition(30, 3);
list.insertAtPosition(40, 4);
System.out.println("Initial List:");
list.printList();
System.out.println("\nInserting 25 at position 3:");
list.insertAtPosition(25, 3);
list.printList();
System.out.println("\nInserting 5 at position 1:");
list.insertAtPosition(5, 1);
list.printList();
System.out.println("\nTrying to insert at position 10 (out of bounds):");
list.insertAtPosition(100, 10);
}
}
Output:
Initial List: 10 → 20 → 30 → 40 → null Inserting 25 at position 3: 10 → 20 → 25 → 30 → 40 → null Inserting 5 at position 1: 5 → 10 → 20 → 25 → 30 → 40 → null Trying to insert at position 10 (out of bounds): Position out of bounds.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Conclusion
Insertion at the nth position in a singly linked list is a foundational concept that teaches pointer manipulation and list traversal. By mastering this, you build a strong base in data structures.
- This operation is commonly used in building more complex systems like stacks, queues, and even custom memory managers.
- Understanding the logic and practicing variations (like insertion at the end, insertion after value X, etc.) will make you confident in linked list manipulations.
FAQ's related to Insertion at nth position in a singly linked list
Answer:
To insert at the nth position:
- Traverse to the (n-1)th node
- Set the new node’s next to point to the current node’s next
- Update the (n-1)th node’s next to the new node
Answer:
The time complexity is O(n) because we may need to traverse up to n nodes to reach the target position.
Answer:
No, insertion is only valid at position 1 in an empty list. Any position beyond that will be considered out of bounds.
Answer:
Before inserting:
- Check if the position is less than 1 (invalid)
- Traverse carefully, and stop with a message if the list ends before reaching the desired point
Answer:
Inserting at position 1 makes the new node the new head of the list. Its next will point to the previous head node.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




public class SinglyLinkedListPractice {
Node head;
//creating of Node in Singly linked list
class Node
{
String data;
Node next;
Node(String data)
{
this.data=data;
this.next=null;
}
}
//Add fist operation
public void addFirst(String data){
Node newNode=new Node(data);
if (head==null){
head=newNode;
return;
}
newNode.next=head; // set the newNode.next as a head
head=newNode; // Now the head is point to the newNode
}
//Add Last operation
public void addLast(String data){
Node newNode=new Node(data);
if (head==null)
{
head=newNode;
return;
}
Node currNode=head;
while (currNode.next != null)
{
currNode=currNode.next; //upadate the current node as a next node till currNode.next == null
}
currNode.next=newNode;
}
//Print operation of sll
public void printList()
{
if (head==null)
{
System.out.println(“The linked list is empty”);
return;
}
Node currNode=head;
while (currNode != null)
{
System.out.print(currNode.data+” -> “);
currNode=currNode.next;
}
System.out.println(“NULL”);
}
//Check the size of Linked list
public int checkSize()
{
if (head==null)
{
System.out.println(“The linked list empty”);
}
Node currNode=head;
int count=0;
while (currNode.next != null)
{
count++;
currNode=currNode.next;
}
return count;
}
//insertion at specific position
public void insertSpecific(String data,int position)
{
Node newNode=new Node(data);
if (position checkSize())
{
System.out.println(“Invalid position”);
}
Node currNode=head;
int i=0;
while (i<position)
{
currNode=currNode.next;
i++;
}
if (i==position)
{
newNode.next=currNode.next;
currNode.next=newNode;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SinglyLinkedListPractice sll=new SinglyLinkedListPractice();
sll.addFirst("10");
sll.addFirst("20");
sll.printList();
sll.addLast("30");
sll.printList();
sll.addFirst("40");
sll.printList();
sll.insertSpecific("50",1);
sll.printList();
}
}