Minimum number of Merge Operations to make an Array Palindrome in Java
Minimum Number of Merge Operations
In this article, we will solve a specific problem: Find the minimum number of merge operations needed to make an array a palindrome.
We will explain the concept, walk through multiple methods, understand their time and space complexity, and provide a complete Java solution with input/output examples.

Minimum Merge Operations To Make Array Palindrome
For example, [1, 2, 3, 2, 1] is a palindrome.
2. In real world applications such as data cleanup, symmetric structure generation, and bioinformatics, you may need to convert a sequence into a palindrome.
What is Minimum Merge Operation Problem?
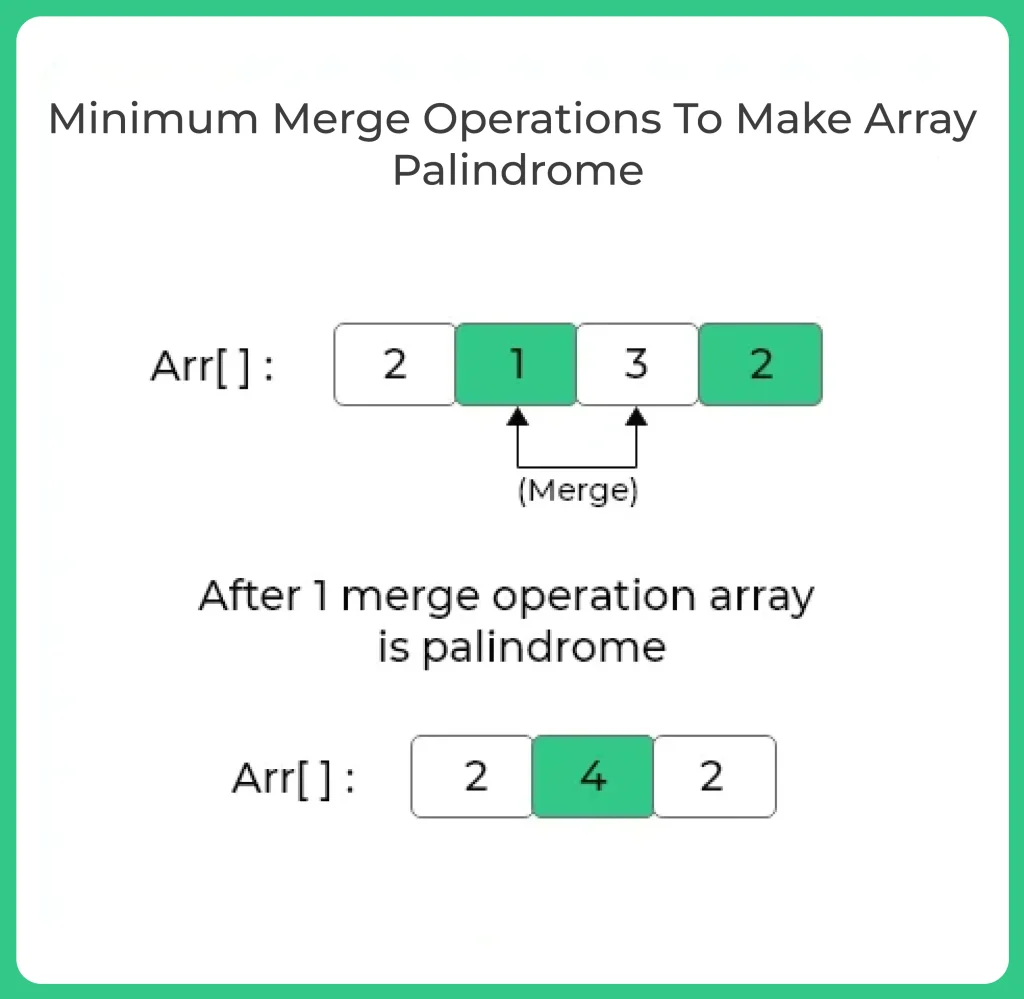
Given an array of integers, you are allowed to merge two adjacent elements into one (by summing them). The goal is to make the array a palindrome using the minimum number of such merge operations.
Example:
- Input: [1, 4, 5, 9, 1]
- Output: 1
Explanation: Merge 4 and 5 to get [1, 9, 9, 1], which is a palindrome.
Allowed Operation:
- You can merge only adjacent elements.
- After merging, the new element becomes the sum of the two merged elements.
- The number of such operations should be minimized.
To perform Minimum Merge Operations to Make Array Palindrome there is only 1 efficient methods, apart from it we have mentioned the details about one more methods that is not used but, you need to be aware about it, why it is not used:

Methods for Minimum Merge Operations to Make Array Palindrome
Method 1: Two Pointer Approach
Approach:
- Use two pointers, one at the start (i) and one at the end (j) of the array.
- If arr[i] == arr[j], move both pointers inward.
- If arr[i] < arr[j], merge arr[i] with arr[i+1] and count the operation.
- If arr[i] > arr[j], merge arr[j] with arr[j-1] and count the operation.
Space Complexity = O(1)
Algorithm for Minimum Number of Merge Operations
Let’s break it down step by step using simple variables:
- i = 0 → Start of the array
- j = n – 1 → End of the array
While i < j:
If arr[i] == arr[j], move both inward → i++, j–
If arr[i] < arr[j], merge arr[i] with arr[i+1], replace arr[i+1] with the sum, increase operation count, and move i forward.
If arr[i] > arr[j], merge arr[j] with arr[j-1], replace arr[j-1] with the sum, increase operation count, and move j backward.
This way we try to balance the values on both ends of the array to become equal.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Code in Java based on above algorithm
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MinMergeToPalindrome {
public static int minMergeOperations(int[] arr) {
int i = 0;
int j = arr.length - 1;
int operations = 0;
while (i < j) {
if (arr[i] == arr[j]) {
i++;
j--;
} else if (arr[i] < arr[j]) {
arr[i + 1] += arr[i]; // Merge arr[i] with arr[i+1]
i++;
operations++;
} else {
arr[j - 1] += arr[j]; // Merge arr[j] with arr[j-1]
j--;
operations++;
}
}
return operations;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] input = {1, 4, 5, 9, 1};
System.out.println("Input Array: " + Arrays.toString(input));
int[] copy = Arrays.copyOf(input, input.length);
int result = minMergeOperations(copy);
System.out.println("Minimum merge operations to make it palindrome: " + result);
}
}
Sample Input:
int[] input = {1, 4, 5, 9, 1}; Sample Output:
Input Array: [1, 4, 5, 9, 1]
Minimum merge operations to make it palindrome: 1
Method 2: Recursion (Inefficient but Conceptual)
You can use recursion to explore all combinations, but this approach is not efficient.
Space Complexity: O(n) stack memory
Hence, not suitable for large arrays.
Idea:
We use recursion to explore all possible merges and choose the path with the minimum number of operations to convert the array into a palindrome.
Why Inefficient?
“This approach checks multiple combinations and doesn’t use memoization (DP), which leads to redundant calls.”
FAQ's related to Minimum Number of Merge Operations
Answer:
It is the smallest number of adjacent merges required to convert the array into a palindrome. This can be done using a two-pointer technique.
Answer:
No. Only adjacent elements are allowed to be merged in this problem.
Answer:
Optimal two pointer method works in O(n) time and O(1) space.
Answer:
Yes, the solution modifies the array during merging. You can copy it if you want to preserve the original.
Answer:
Yes, any array can be turned into a palindrome through a series of adjacent merges.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment