Level Order Traversal
Level Order Traversal in Java
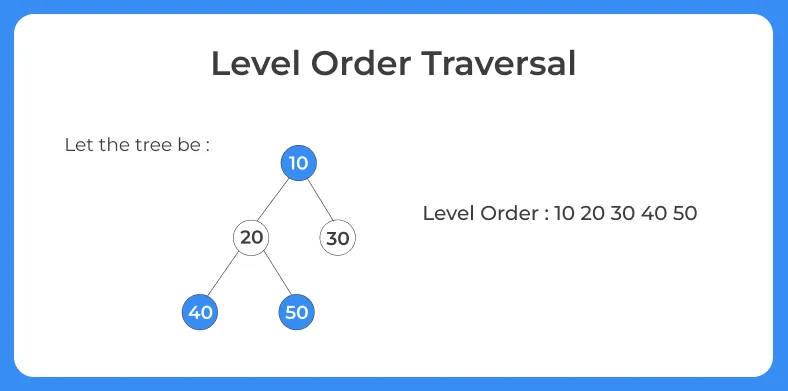
On his page we will discuss about level order traversal in C language . In level order traversal, we move level by level. Before moving to the next level, we first visit all the elements of present level.

Level Order Traversal
Steps for Level Order Traversal
- Step 1 : Push the root i.e. 10 to the queue.
- Step 2 : Pop the element 10 from the queue and print it.
- Step 3 : Now, Add it’s left and right child i.e. add 20 and 30 to queue.
- Step 4 : Again pop the front element i.e. 20 from queue and print it .
- Step 5 : Add it’s left and right child i.e. 40 and 50 in the queue.
- Step 6 : Pop the element 30 from the queue and print it.
- Step 7 : Now pop all the elements from the queue and print them as there is no child of these elements.
Therefore the printing sequence will be 10 20 30 40 50.
Example for Searching in a Binary Search Tree
Algorithm:
- We will use queue here. In implementation we have used linked list as queue. A linked list with addLast and removeFirst function acts like a queue.
- First enqueue the root node
- While the queue is not empty, dequeue from the queue, print the node data and enqueue its left and right child if they are present.
Code For Binary Search Tree
Run
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
// Node class
public static class Node
{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node (int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// Binary tree class to create a binary tree
public static class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
public BinaryTree ()
{
this.root = null;
}
}
// Level Order traversal
public static void levelOrder (Node root)
{
// We are using linked list as queue
LinkedList < Node > queue = new LinkedList <> ();
// Enqueue the root node
queue.addLast (root);
while (!queue.isEmpty ())
{
// Remove the first node from queue
Node temp = queue.removeFirst ();
//Print the node data
System.out.print (temp.data + ", ");
//Enqueue the left child
if (temp.left != null)
{
queue.addLast (temp.left);
}
//Enqueue the right child
if (temp.right != null)
{
queue.addLast (temp.right);
}
}
System.out.println ("END");
}
public static void main (String[]args) throws Exception
{
// Construct binary tree
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree ();
bt.root = new Node (10);
bt.root.left = new Node (20);
bt.root.right = new Node (30);
bt.root.left.left = new Node (40);
bt.root.left.right = new Node (50);
levelOrder (bt.root);
}
}
Output :
10, 20, 30, 40, 50, END
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java





