0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
Insertion at nth position in Singly Linked List in Java
Insertion at nth Position in JAVA
Let’s have a look at the program of Insertion at nth position in Singly linked list in Java.

Implementation
For Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List in Java we’ll have to follow these steps:
- First, Traverse the list from head to n-1 position
- After traversing the list add the new node and allocate memory space to it.
- Point the next pointer of the new node to the next of current node.
- Point the next pointer of current node to the new node.
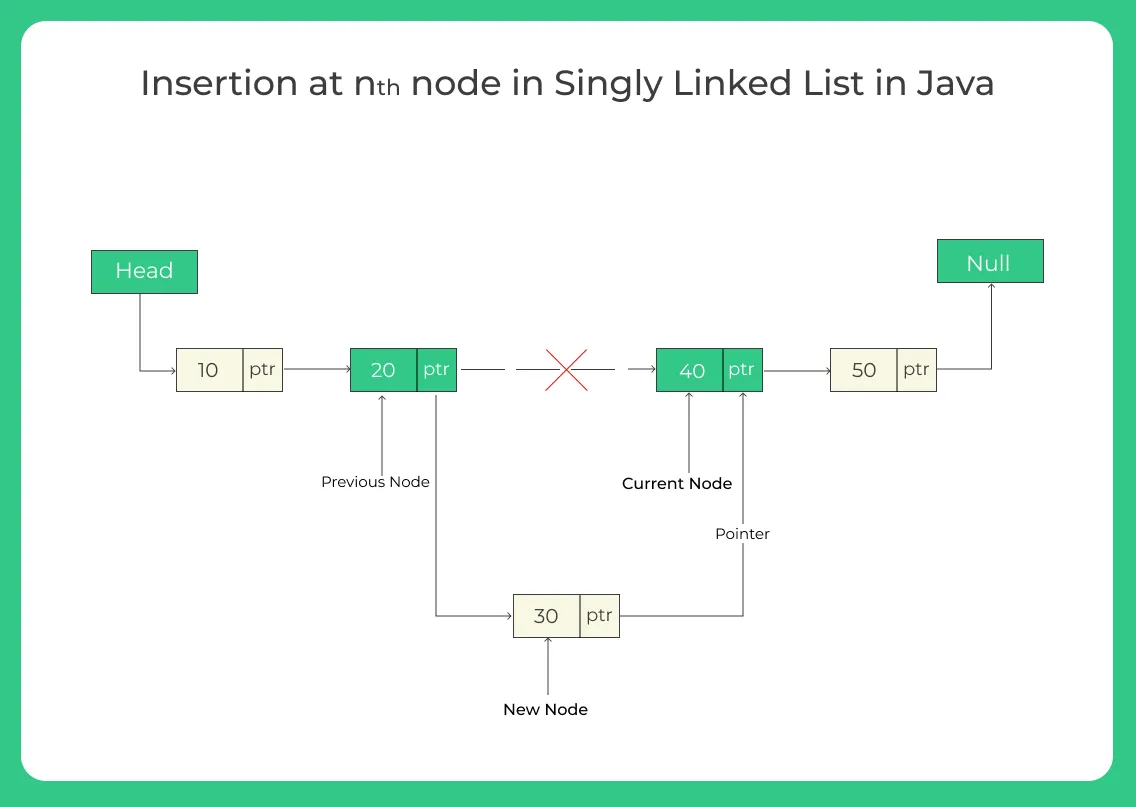
Algorithm for Insertion at nth Position in Singly Linked List
- IF HEAD == NULL
EXIT - ELSE
- NEW_NODE = ADDNODE()
- NEW_NODE -> DATA = ITEM
- SET TEMP = HEAD
- SET I = 0
- REPEAT
- TEMP = TEMP → NEXT
- IF TEMP = NULL
- EXIT
- PTR → NEXT = TEMP → NEXT
- TEMP → NEXT = PTR
- SET PTR = NEW_NODE
- EXIT
Code for Insertion in a Linked List in Java at a Given Node
Method 1
Method 2
Method 1
Uses Objects to call functions
Run
import java.lang.*;
class LinkedList {
Node head;
// Node Class
class Node{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
public Node insertBeginning(int data)
{
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
public void insertAfter(int n,int data)
{
int size = calcSize(head);
// Can only insert after 1st position
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if(n < 1 || n > size)
{
System.out.println("Can't insert\n");
}
else
{
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// required to traverse
Node temp = head;
// traverse to the nth node
while(--n > 0)
temp=temp.next;
newNode.next= temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
}
}
public void display()
{
Node node = head;
//as linked list will end when Node reaches Null
while(node!=null)
{
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public int calcSize(Node node){
int size = 0;
while(node!=null){
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList listObj = new LinkedList();
listObj.insertBeginning(15);
listObj.insertBeginning(10);
listObj.display();
listObj.insertAfter(1,100);
listObj.insertAfter(2,200);
listObj.display();
}
}
Output
10 15 10 100 200 15
Method 2
Uses Static functions that are called from static main
Run
import java.lang.*;
// Node Class
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class Main
{
static Node insertBeginning(Node head, int data)
{
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
static Node insertAfter(int pos, int data, Node head) {
int size = calcSize(head);
// Can only insert after 1st position
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if(pos < 1 || size < pos) { System.out.println("Can't insert," + pos + " is not a valid position\n"); }
else { Node newNode = new Node(data);
// required to traverse Node
Node temp = head;
// traverse to the nth node while (--pos > 0)
temp = temp.next;
newNode.next= temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
}
return head;
}
static void display(Node node) {
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
static int calcSize(Node node){
int size=0;
while(node!=null)
{
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = null;
head = insertBeginning(head,15);
head = insertBeginning(head,10);
head = insertBeginning(head,5);
display(head);
//Inserts after 3rd position
head = insertAfter(3,100,head);
head = insertAfter(2,200,head);
display(head);
}
}
Output
5 10 15 5 10 200 100 15
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
Click Here - Linked List in –
- Singly Linked List in –
- Insertion in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at beginning in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at nth position in singly Linked List –
- Insertion at end in singly Linked List –
- Deletion in singly Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in singly linked list :
- Deletion from nth position in singly linked list :
- Deletion from end in singly linked list :
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing –
- Insertion in the middle Singly Linked List –
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List –
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List –
- Find middle of the linked list –
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size –
- Find kth node from end of the linked list –
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list –
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not –
- Fold a Linked List –
- Insert at given Position –
- Deletion at given Position –
Singly Linked List
- Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
- Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Singly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in singly Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only) – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List Insertion and Deletion – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list by changing links between nodes – C | C++ | Java
- Linked List insertion in the middle – C | C++ | Java
- Print reverse of a linked list without actually reversing – C |C++ | Java
- Search an element in a linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in a Sorted Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Find middle of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a linked list in groups of given size – C | C++ | Java
- Find kth node from end of the linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Append the last n nodes of a linked list to the beginning of the list – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether linked list is palindrome or not – C | C++ | Java
- Fold a Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insert at a given position – C | C++ | Java
- Delete at a given position – C | C++ | Java

 0
0
public class SinglyLinkedListPractice {
Node head;
//creating of Node in Singly linked list
class Node
{
String data;
Node next;
Node(String data)
{
this.data=data;
this.next=null;
}
}
//Add fist operation
public void addFirst(String data){
Node newNode=new Node(data);
if (head==null){
head=newNode;
return;
}
newNode.next=head; // set the newNode.next as a head
head=newNode; // Now the head is point to the newNode
}
//Add Last operation
public void addLast(String data){
Node newNode=new Node(data);
if (head==null)
{
head=newNode;
return;
}
Node currNode=head;
while (currNode.next != null)
{
currNode=currNode.next; //upadate the current node as a next node till currNode.next == null
}
currNode.next=newNode;
}
//Print operation of sll
public void printList()
{
if (head==null)
{
System.out.println(“The linked list is empty”);
return;
}
Node currNode=head;
while (currNode != null)
{
System.out.print(currNode.data+” -> “);
currNode=currNode.next;
}
System.out.println(“NULL”);
}
//Check the size of Linked list
public int checkSize()
{
if (head==null)
{
System.out.println(“The linked list empty”);
}
Node currNode=head;
int count=0;
while (currNode.next != null)
{
count++;
currNode=currNode.next;
}
return count;
}
//insertion at specific position
public void insertSpecific(String data,int position)
{
Node newNode=new Node(data);
if (position checkSize())
{
System.out.println(“Invalid position”);
}
Node currNode=head;
int i=0;
while (i<position)
{
currNode=currNode.next;
i++;
}
if (i==position)
{
newNode.next=currNode.next;
currNode.next=newNode;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SinglyLinkedListPractice sll=new SinglyLinkedListPractice();
sll.addFirst("10");
sll.addFirst("20");
sll.printList();
sll.addLast("30");
sll.printList();
sll.addFirst("40");
sll.printList();
sll.insertSpecific("50",1);
sll.printList();
}
}