Find Maximum in Binary Tree
Maximum in Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, we need to find the maximum element in the binary tree. As we need to visit each node present in the tree, we can use any tree traversal or recursion. In this page, Recursion is used

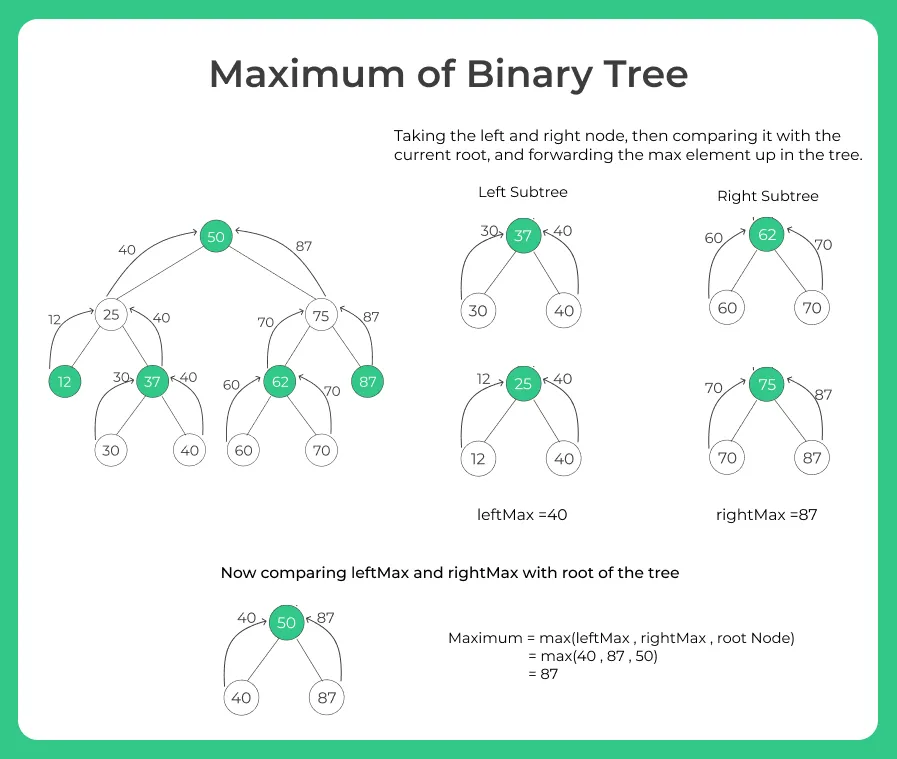
The maximum in this tree is 87. It is obtained with the help of recursion. Each subtree gives its maximum and at last we get the maximum in the complete tree. It is explained as:
- max(50) is called initially. It calls max(25) and max(75)
- max(25) calls max(12) and max(37)
- max(12) returns 12 and max(37) calls max(30) (returns 30) and max(40) (returns 40). So max(37) returns maximum among 30,40,37 i.e. 40.
- Now max(25) returns 40. This is max of left subtree of 50
- In the similar way, we get max of right subtree of 50. The max would be 87.
- Now max of tree would be max of three values – left max (40), right max(87), node value(50). So the max of the tree is 87.
For better understanding see the diagram:
Java Program to Find Maximum in Binary Tree
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
// Binary tree class
public static class BinaryTree
{
// Node class
public class Node
{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node (int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
private Node root;
public BinaryTree (int[]pre, int[]post)
{
this.root =
this.construct (pre, 0, pre.length - 1, post, 0, post.length - 1);
}
private Node construct (int[]pre, int presi, int preei, int[]post,
int postsi, int postei)
{
// this case occurs when a node has only one child
if (presi > preei)
{
return null;
}
Node node = new Node (pre[presi]);
node.left = null;
node.right = null;
if (presi == preei)
{
return node;
}
//Searching pre[presi + 1] in postorder array
int pos = -1;
for (int i = postsi; i <= postei; i++)
{
if (post[i] == pre[presi + 1])
{
pos = i;
break;
}
}
//Number of elements in left subtree
int clc = pos - postsi + 1;
//Left subtree
node.left =
this.construct (pre, presi + 1, presi + clc, post, postsi, pos);
//Right subtree
node.right =
this.construct (pre, presi + clc + 1, preei, post, pos + 1,
postei - 1);
return node;
}
public int max ()
{
return this.max (this.root);
}
//Function to find max in binary tree
private int max (Node node)
{
//Base case
if (node == null)
{
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
//Find max of left subtree
int lmax = this.max (node.left);
//Find max of right subtree
int rmax = this.max (node.right);
//Max of tree is max of left max, right max and the node data itsef.
int rv = Math.max (node.data, Math.max (lmax, rmax));
return rv;
}
}
public static void main (String[]args) throws Exception
{
// Construct binary tree
int[] pre = { 50, 25, 12, 37, 30, 40, 75, 62, 60, 70, 87 };
int[] post = { 12, 30, 40, 37, 25, 60, 70, 62, 87, 75, 50 };
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree (pre, post);
System.out.println ("Maximum of the tree is : " + bt.max ());
}
}
Output:
Maximum of the tree is : 87
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java