Deletion In Binary Search Tree In Java
Deletion In Binary Search Tree
A Binary Search Tree is a rooted binary tree whose internal nodes each a key greater than all the keys in the node’s left subtree and less than those in it’s right subtree. Delete function is used to delete the specified node from binary search tree. In this article we will perform deletion in binary search tree.

There are three possible cases in deletion :-
Deleting a node with no children .
Deleting a node with two children.
Deleting a node with no child.
Case 1: Deleting a node with no children :-
If the node to be deleted from the tree has no child nodes, the node is simple deleted from the tree since it is a leaf node.
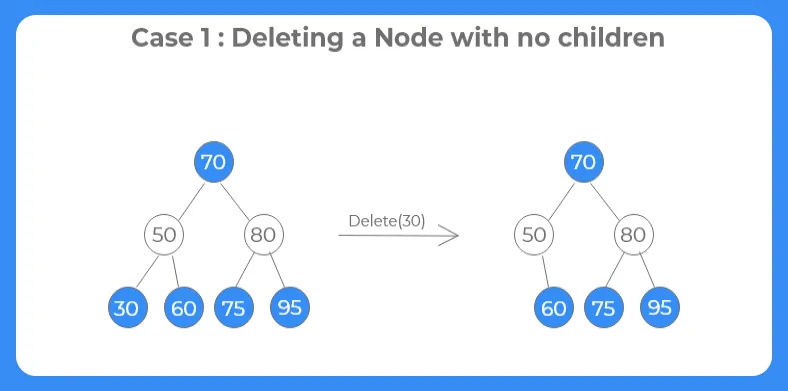
Case 2: Deleting a node with two children :-
we first find the inorder predecessor of the node and replace the target node with the inorder predecessor.
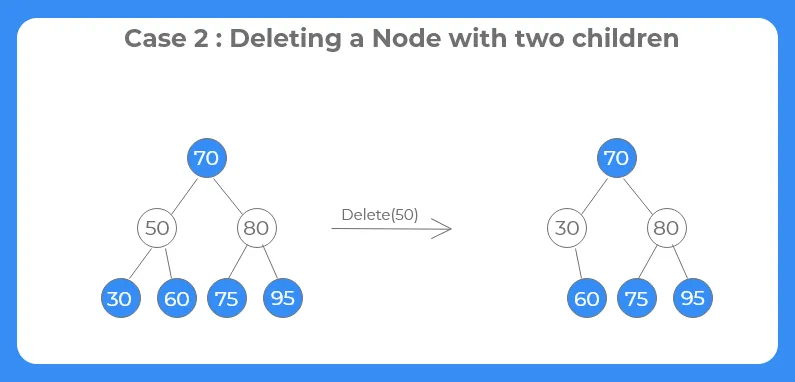
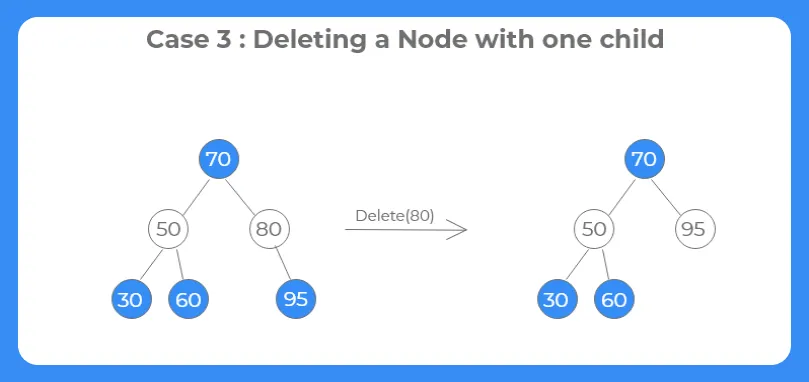
Case 3: Deleting a node with one child :-
If the node to be deleted has a single child node, the target node is replaced from its child node and then the target node is simply deleted.
Code for Deletion in BST
//Deletion in BinarySearch Tree
import java.util.*;
/*Representing a Node of a Binary Search Tree*/
class Node
{
int value;
Node left,right;
//constructor
Node(int value)
{
this.value=value;
left=null;
right=null;
}
}
class BSTDeletion
{
Node root; //Root of a Binary Search Tree
public BSTDeletion()
{
root=null;
}
/*Inorder Traversal of a Binary Tree */
public void inorder(Node ptr)
{
if(ptr==null)
return;
inorder(ptr.left);
System.out.print(ptr.value+" ");
inorder(ptr.right);
}
public void delete(int value)
{
root=deleteNode(root,value); //calling deleteNode() method
}
public Node deleteNode(Node ptr,int value)
{
if(ptr==null)
return ptr;
if(valueptr.value) //if value if greater than current value
ptr.right=deleteNode(ptr.right,value);
else
{
//if node having max one child
if(ptr.left==null)
return ptr.right;
else if(ptr.right==null)
return ptr.left;
// if node having two children then get the inorder predecessor of node
ptr.value=minimumValue(ptr.left);
//delete the inorder predecessor
ptr.left=deleteNode(ptr.left,ptr.value);
}
return ptr;
}
//get minimum element in binary search tree
public int minimumValue(Node ptr)
{
int min;
for(min=ptr.value;ptr.right!=null;ptr=ptr.right)
min=ptr.right.value;
return min;
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//Creating Binary Search Tree
BSTDeletion tree=new BSTDeletion();
tree.root=new Node(70);
tree.root.left=new Node(50);
tree.root.right=new Node(80);
tree.root.left.left=new Node(30);
tree.root.left.right=new Node(60);
tree.root.right.left=new Node(75);
tree.root.right.right=new Node(95);
System.out.println("Inorder Traversal of a Binary Search Tree");
tree.inorder(tree.root);
tree.delete(60);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Inorder Traversal After deleting a Node 60");
tree.inorder(tree.root);
tree.delete(50);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Inorder Traversal After deleting a Node 50");
tree.inorder(tree.root);
tree.delete(80);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Inorder Traversal After deleting a Node 80");
tree.inorder(tree.root);
}
}
Output
Inorder Traversal of a Binary Search Tree 30 50 60 70 75 80 95 Inorder Traversal After deleting a Node 60 30 50 70 75 80 95 Inorder Traversal After deleting a Node 50 30 70 75 80 95 Inorder Traversal After deleting a Node 80 30 70 75 95
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment