Preorder Traversal Without Recursion in C++
Preorder Traversal Without Recursion
Preorder traversal is one of the fundamental depth-first tree traversal techniques used to visit nodes in the order: root, left subtree, and then right subtree. While recursion is commonly used to implement it, an iterative approach using a stack offers better control over memory usage and avoids function call overhead.
In this method, the stack stores nodes temporarily, allowing us to process each element systematically without relying on recursive calls. This approach is especially useful in environments where recursion depth is limited or when handling large trees efficiently.

More About Preorder Traversal
- Preorder traversal is a depth first algorithm.
- We first print the value of the node,them move to the left subtree and finally to the right subtree.
- If we need to explore more about the node itself before inspecting its leaves, we use preorder traversal.
- Preorder traversal is used to find the prefix expression of an expression tree.
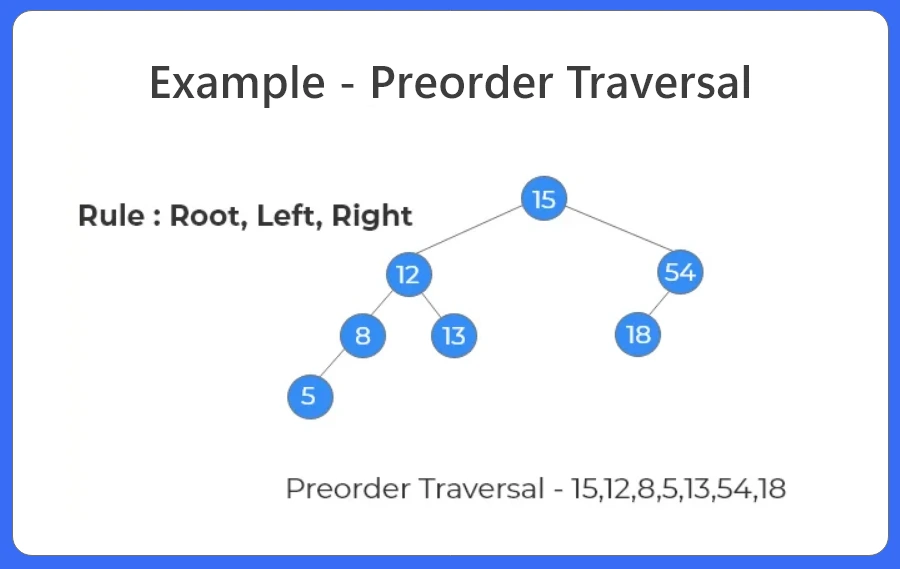
Algorithm:
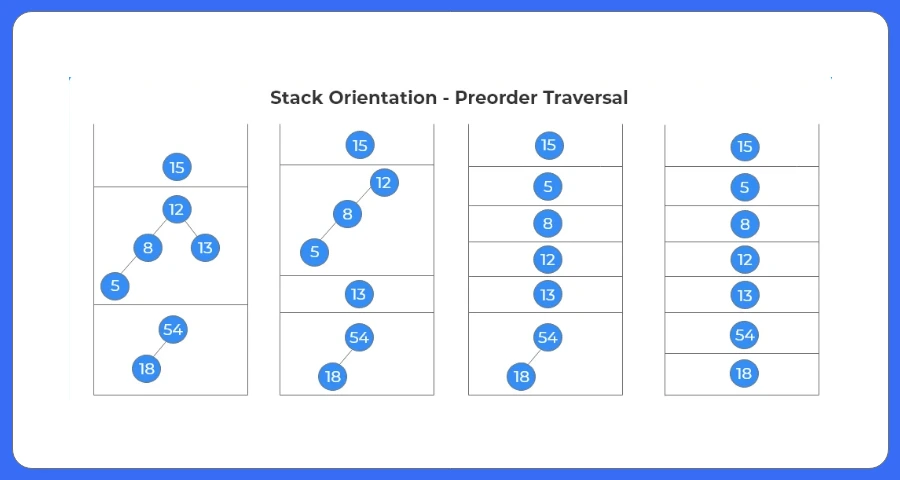
- If root is empty, return.
- Push root to stack.
- Continue until stack is not empty.
- Print the top element of stack.
- Add the right and the left child of the top element.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Code Implementation for Preorder Tree traversal without recursion
Preorder tree traversal without recursion uses an explicit stack to process nodes in the correct root-left-right sequence. This approach removes the overhead of recursive calls while still ensuring that each node is visited efficiently. It is especially useful in environments where stack memory is limited or recursion is not preferred.
- It uses a stack to simulate the recursive process and ensures nodes are visited in Root → Left → Right order.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Tree
{
public:
int data;
Tree *left = NULL, *right = NULL;
// Constructor initialised
Tree (int x)
{
data = x;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
void preorder (Tree * root)
{
// If empty return;
if (root == NULL)
return;
stack < Tree * >s;
s.push (root);
// Continue till stack is empty
while (!s.empty ())
{
Tree *temp = s.top ();
// Print data
cout << temp->data << " "; // Remove Data s.pop (); // Add right child if (temp->right != NULL)
s.push (temp->right);
// Add Left child
if (temp->left != NULL)
s.push (temp->left);
}
}
int main ()
{
Tree *root = new Tree (10);
root->left = new Tree (20);
root->right = new Tree (30);
root->left->left = new Tree (40);
root->left->right = new Tree (50);
cout << "Preorder Traversal" << endl;
preorder (root);
return 0;
}
Output:
Preorder Traversal 10 20 40 50 30
Explanation:
- The code uses a stack to perform preorder traversal (Root → Left → Right) without using recursion.
- It first pushes the root node into the stack and repeatedly processes nodes until the stack becomes empty.
- At each step, the node on the top of the stack is printed and then popped, ensuring preorder order is maintained.
- The code pushes the right child first, then the left child, so that the left child is processed before the right child (stack is LIFO).
- Memory for the tree structure is created dynamically, and all nodes are processed exactly once.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation / Traversal | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Preorder Traversal (Iterative) | O(N) | O(N) |
To Wrap It Up:
The concept of preorder traversal without recursion shows how easily a stack can replace the function call stack, allowing the algorithm to run smoothly even in environments where recursion is limited. This method ensures the same visiting order as traditional recursion while giving developers more control over the flow.
By understanding the iterative approach, it becomes simpler to handle larger trees and avoid stack overflow issues. It also makes the traversal process more transparent, as each step can be monitored and debugged, making it a practical technique for real-world applications.
FAQs
Preorder traversal visits nodes in the order: first the root, then the left subtree, and finally the right subtree, ensuring the root is processed before all other nodes.
A stack helps simulate the function call stack used in recursion, allowing the algorithm to maintain the same visiting sequence without needing recursive calls.
Since a stack works on LIFO, pushing the right child first ensures the left child is processed next, preserving the correct preorder order.
Yes, the iterative stack-based method produces the exact same traversal sequence as recursion, only differing in how the process is executed internally.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment