Insertion in a Binary Tree (Level Order)
Insertion In A Binary Tree
Given a tree and a key, add a node in the first available node in the tree. After adding the node, print the level order traversal. In this article, Queue data structure is used to add a node. In this article, we will learn about the process of insertion in a binary tree (Level Order) in C++.
This approach ensures that the tree remains as compact as possible and follows the properties of a binary tree. Level order insertion is commonly used when the structure of the tree matters more than the ordering of elements.

Prerequisite Knowledge:
- A Binary Tree is a data structure with maximum of two children for each parent.
- Level Order Traversal is an example Of Breadth First Search algorithm.
- Level order is a traversal in which each node is visited in the level before we move to a lower level.
- Queues are used to find the level order traversal.
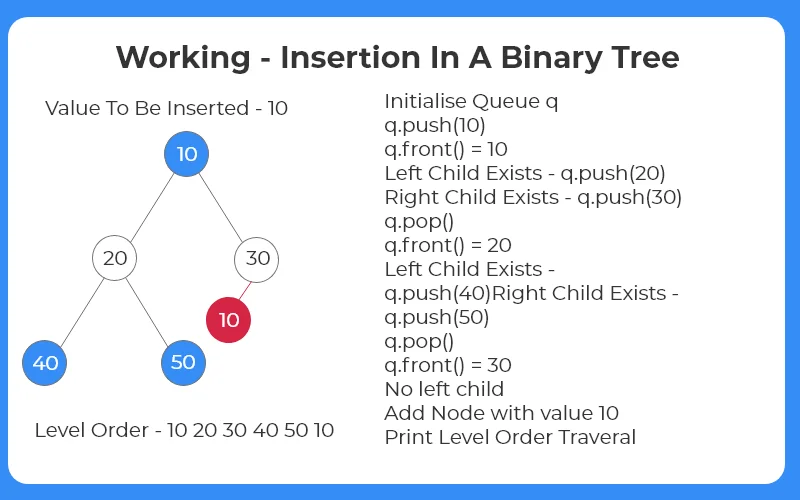
Algorithm:
- Create a queue q.
- If root is NULL, add node and return.
- Else continue until q is not empty.
- If a child does not exists, add the node there.
- Otherwise add the node to the leftmost node.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Code Implementation for Insertion in a Binary Tree in C++
This section demonstrates how to insert a new node into a binary tree using C++. It explains the logic step by step, showing how the tree structure is maintained while adding elements efficiently.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode (int x):val (x), left (NULL), right (NULL)
{ }
};
void insert (TreeNode * &root, int val)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
root = new TreeNode (val);
return;
}
if (val < root->val)
{
insert (root->left, val);
}
else
{
insert (root->right, val);
}
}
void inorder_traversal (TreeNode * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Visit Left subtree
inorder_traversal (root->left);
// Print the data
cout << root->val << " "; inorder_traversal (root->right);
// Visit right subtree inorder_traversal (root->right);
}
int main ()
{
TreeNode *root = NULL;
insert (root, 50);
insert (root, 20);
insert (root, 70);
insert (root, 10);
insert (root, 30);
insert (root, 60);
insert (root, 80);
cout << "The binary tree is : ";
inorder_traversal (root);
return 0;
}
Output:
The binary tree is : 10 20 30 50 60 70 80
Explanation:
- The TreeNode structure defines a node of the Binary Search Tree (BST) with a value and pointers to left and right children.
- The insert() function adds a new value to the BST by comparing it with the current node and recursively moving left or right.
- If the root is NULL, a new node is created and assigned as the root of the tree.
- The inorder_traversal() function visits the left subtree, prints the root value, and then visits the right subtree recursively.
- In the main() function, multiple values are inserted into the BST, and inorder traversal prints the values in sorted order.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion | O(h) | O(h) |
| Inorder Traversal | O(n) | O(h) |
| Tree Creation | O(n) | O(n) |
Conclusion:
Insertion in a binary tree using level order is a structured approach that ensures nodes are added in the first available position, keeping the tree complete and well-organized. By using a queue, the process efficiently traverses the tree level by level until the correct insertion point is found. This method is simple to implement and plays an important role in understanding how binary trees grow dynamically.
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment