Inorder Tree Traversal Without Recursion In C++
Inorder Tree Traversal Without Recursion
Inorder Tree Traversal Without Recursion In C++ – Inorder traversal means visiting the left part of the tree first, then the root, and finally the right part. It’s a common way to go through all the nodes of a binary tree. Usually, we do this using recursion, but sometimes using recursion can cause issues if the tree is too big. So instead, we can do it without recursion by using a stack. In this method, we manually manage the steps that recursion would handle.
There are three types of traversals in trees: Preorder, Inorder and Postorder. The traversals can be performed using recursion or stack. In this article, inorder traversal is performed using stacks.

More About Inorder Traversal
- Inorder Traversal is a depth first algorithm.
- In Inorder Traversal, we first move to the left subtree, then print the node and finally move to the right subtree.
- If you want the orginal sequence or how the tree was made, we use the inorder sequence.
- Inorder Traversal of a binary search tree gives the sequence in non decreasing order.
Algorithm for Inorder Tree Traversal Without Recursion In C++:
- Return if root is empty.
- Store temp as root.
- Continue the while loop until temp is not null or stack is not empty.
- Keep adding the left child of temp until NULL is encountered.
- Print the temp node.
- Since all the left children are visited, change temp to its right child.
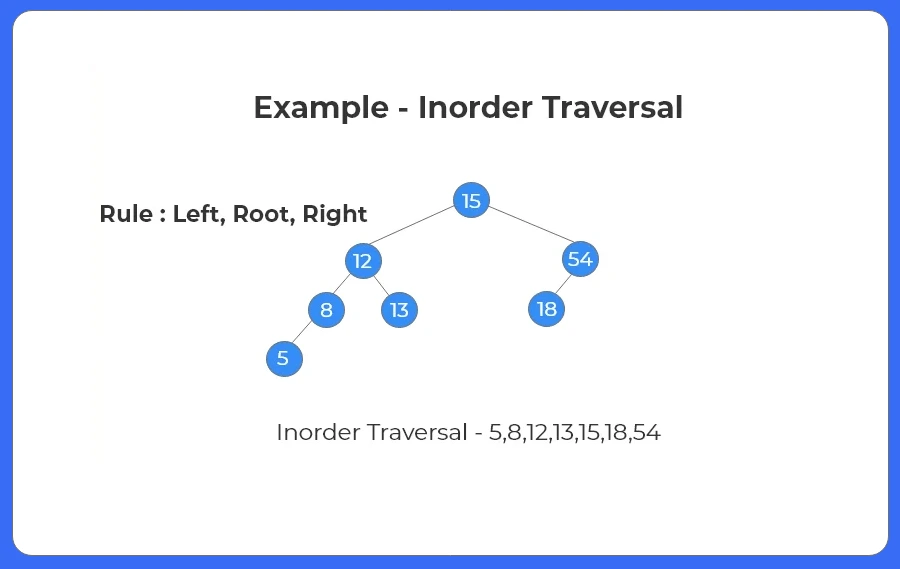
What is Inorder generally used for?
We generally use Inorder traversal technique on Binary Tress , as it fetches the values from the underlying set in order. Using Post-order traversal is also an option, but during post order traversal while delete or freeing nodes it can even delete or free an entire binary tree, which is not a favorable condition.
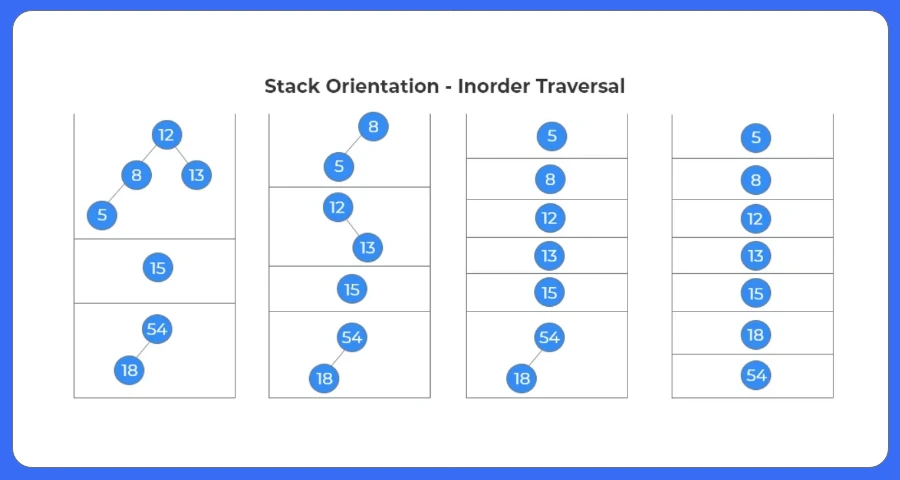
Algorithm To Find Inorder Traversal:
- If root is NULL, return NULL.
- Visit the left subtree.
- Print the node.
- Visit the right subtree.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Code Implementation for Inorder Tree traversal
A well-structured code implementation for Inorder Tree Traversal helps you understand how nodes are visited in a left-root-right sequence, making it ideal for sorted output in binary search trees. It also provides a clear step-by-step flow that strengthens your grasp of recursive tree operations.
- Inorder traversal is widely used because it naturally returns nodes in ascending order for BSTs.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
Node (int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
void inOrder(struct Node *root)
{
stack s;
Node *curr = root;
while (curr != NULL || s.empty() == false)
{
while (curr != NULL)
{
s.push(curr);
curr = curr->left;
}
curr = s.top();
s.pop();
cout << curr->data << " "; curr = curr->right;
}
}
int main()
{
struct Node *root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
inOrder(root);
return 0;
}
Output:
4 2 5 1 3
Explanation
- The code uses an iterative method to perform inorder traversal, which helps avoid the overhead of recursive function calls.
- A stack is used to remember the path while moving down the left subtree, ensuring nodes are processed in the correct left-root-right order.
- After reaching a null left child, the algorithm retrieves the last stored node from the stack, prints its value, and shifts focus to its right child.
- The traversal continues until both the current pointer becomes NULL and the stack becomes empty, ensuring all nodes are visited exactly once.
- The tree in main() is manually constructed with five nodes, and running the traversal prints the nodes in sorted inorder form for this specific structure.
Time & Space Complexity
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Inorder Traversal (Iterative) | O(N) | O(N) |
| Pushing all left nodes | O(N) | O(H) |
| Visiting each node once | O(N) | O(1) |
| Complete Tree Traversal | O(N) | O(H) |
| Overall Complexity | O(N) | O(N) |
To Wrap It Up:
Inorder traversal without using recursion is a smart way to go through a binary tree when you want to avoid the limitations of recursive calls. By using a stack, we can keep track of nodes ourselves and visit them in the correct Left–Root–Right order. It might seem tricky at first, but once you understand how the stack helps in the process, it becomes much easier.
FAQs - Inorder Tree Traversal Without Recursion in C++
FAQs - Inorder Tree Traversal Without Recursion in C++
In the recursive method, the system stack automatically tracks function calls for the left and right subtrees. In the iterative method, we manually use a stack to mimic this behavior. We first go deep into the leftmost node, pushing nodes onto the stack. Once we reach the end, we process the top node (root), then move to its right child—just like the recursive Left–Root–Right order.
Some common edge cases include:
- The tree is completely empty (root == NULL)
- The tree has only one node (no left or right child)
- The tree is skewed (all left or all right nodes)
You should make sure the code works for all these cases and does not throw null pointer or segmentation errors.
- Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes. Every node is visited once.
- Space Complexity: O(h), where h is the height of the tree. The stack stores at most h nodes at a time in the worst case.
Yes, this can be done using Morris Traversal, which uses the concept of threaded binary trees. It avoids both stack and recursion by temporarily modifying the tree structure during traversal. However, it’s more complex and requires restoring the tree afterward.
Instead of printing each node’s value, you can store it in a vector:
vector<int> result;
result.push_back(curr->data);
This is useful when you need to return the traversal result from a function or compare it with another tree.
In large trees, recursion may cause stack overflow due to deep recursive calls. Iterative traversal avoids this risk by using heap memory for the stack. It also gives more control over the flow, better error handling, and is generally safer and more efficient in memory-constrained environments.
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment