Construct Tree From Given Inorder and Preorder traversals in C++
Construct Tree From Given Inorder and Preorder traversals in C++
There are three types of traversals in a tree: Inorder, Preorder and Postorder traversal. A tree can be formed with any two tree traversals in which one of them being the inorder traversal. In this article, we will learn how to construct a tree from given inorder and preorder traversals in C++.
The preorder traversal helps in identifying the root node at each step, while the inorder traversal helps in determining the left and right subtrees. By recursively dividing the traversals into smaller parts, we can efficiently rebuild the original binary tree structure.

Algorithm For InOrder Traversal:
- Traverse The Left subtree.
- Print the node.
- Traverse the right subtree.
Algorithm For PreOrder Traversal:
- Print the node.
- Traverse the left subtree.
- Traverse the right subtree.
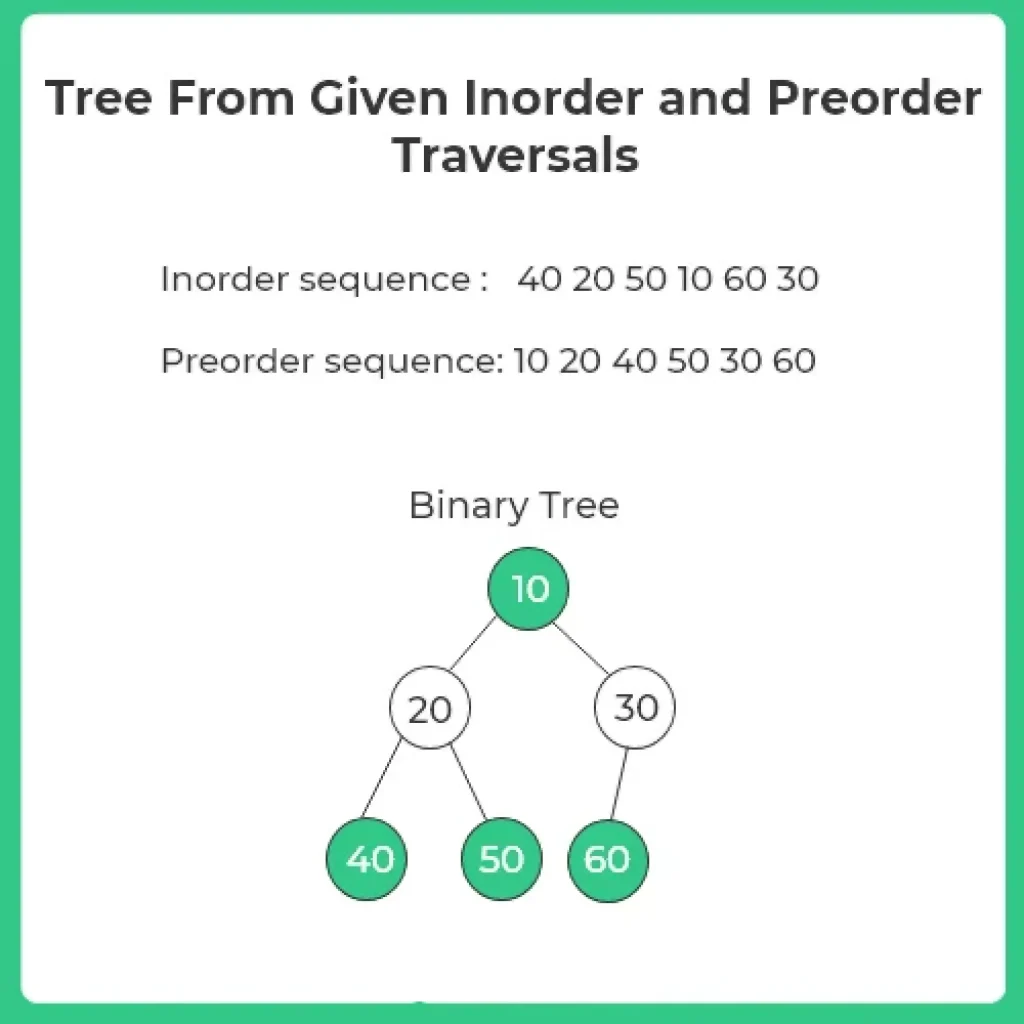
Algorithm To Create Tree:
- Pick the first element and increment the count.
- Find the position of the element in inorder traversal.
- Call recursively for the left subtree and make it as the left child of the current node.
- Call recursively for the right subtree and make it as the right child of the current node.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Code Implementation for constructing tree from preorder and inorder traversals in C++
This implementation demonstrates how to build a binary tree using preorder and inorder traversal arrays. By identifying the root from preorder and dividing the inorder array into left and right subtrees, the tree is constructed recursively in an efficient and structured manner.
Run
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Tree
{
public:
int data;
Tree *left = NULL, *right = NULL;
Tree (int x)
{
data = x;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
int search (int inorder[], int start, int end, int element)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = start; i < end; i++) { if (inorder[i] == element) { break; } } return i; } void printInorder (Tree * node) { if (node == NULL) return; printInorder (node->left);
cout << node->data << " "; printInorder (node->right);
}
Tree * build_tree (int inorder[], int preorder[], int start, int end)
{
static int index = 0;
if (start > end)
return NULL;
Tree *curr_node = new Tree (preorder[index++]);
int x = curr_node->data;
if (start == end)
return curr_node;
int search_index = search (inorder, start, end, x);
curr_node->left = build_tree (inorder, preorder, start, search_index - 1);
curr_node->right = build_tree (inorder, preorder, search_index + 1, end);
return curr_node;
}
int main ()
{
int in[] = { 12, 25, 30, 37, 40, 50, 60, 62, 70, 75, 87 };
int pre[] = { 50, 25, 12, 37, 30, 40, 75, 62, 60, 70, 87 };
Tree *root = build_tree (in, pre, 0, 10);
cout << "Inorder traversal\n";
printInorder (root);
return 0;
}
Output:
Inorder traversal 12 25 30 37 40 50 60 62 70 75 87
Explanation:
- The Tree class defines a node structure that stores an integer value and two pointers (left and right) to represent the left and right children of the node.
- The search() function finds the index of a given element in the inorder array, which helps in separating the left and right subtrees during tree construction.
- The build_tree() function recursively creates the binary tree using preorder and inorder traversals, where the preorder array decides the root node each time.
- A static index variable is used in build_tree() to keep track of the current root element from the preorder array as the recursion progresses.
- The printInorder() function performs an inorder traversal (Left → Root → Right) to display the constructed tree and verify that it matches the original inorder sequence.
Time and Space Complexity Table:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| search() | O(n) | O(1) |
| build_tree() | O(n²) | O(n) |
| printInorder() | O(n) | O(n) |
| Overall Program | O(n²) | O(n) |
Conclusion:
To reconstruct a binary tree from given inorder and preorder traversals, you leverage how these traversal orders reveal the structure of the tree. The preorder sequence always begins with the root, and the inorder sequence shows which nodes lie in the left and right subtrees relative to that root.
By repeatedly picking the next root from preorder and finding its position in inorder, you can recursively build left and right subtrees until the entire tree is formed. This method ensures the original binary tree is accurately reconstructed using both traversals.
FAQs
Inorder traversal helps determine the position of the root in the tree and separates the left and right subtrees. Without inorder traversal, we cannot identify how nodes are distributed around the root. It plays a crucial role in defining the structure of the tree.
No, preorder traversal alone is not sufficient to uniquely construct a binary tree. It only tells the order of node visits but does not provide information about left and right subtree boundaries. At least one traversal must be inorder to uniquely build the tree.
The time complexity is O(n) when we use a hash map to store the indices of inorder elements. Each node is processed once during recursion. Without optimization, it can increase to O(n²) due to repeated searching in the inorder array.
Preorder traversal follows the order Root → Left → Right. This means the first element of the preorder array is always the root of the tree or subtree. This property makes it very useful for constructing the tree step by step.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal Line by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric – C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
Introduction to Trees
Binary Trees
- Binary Tree in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Tree Traversals: Inorder Postorder Preorder : C | C++ | Java
- Inorder Postorder PreOrder Traversals Examples
- Tree Traversal without Recursion
Binary Search Trees
Traversals
- Traversal in Trees
- Tree Traversals: Breadth-First Search (BFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Tree Traversals: Depth First Search (DFS) : C | C++ | Java
- Construct a Binary Tree from Postorder and Inorder
B – Trees
AVL Trees
- AVL Trees
Complete Programs for Trees
- Depth First Traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Level Order Traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Inorder and Preorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Inorder traversals – C | C++ | Java
- Construct Tree from given Postorder and Preorder traversal – C | C++ | Java
- Find size of the Binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find the height of binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Find maximum in binary tree – C | C++ | Java
- Check whether two tree are identical- C| C++| Java
- Spiral Order traversal of Tree- C | C++| Java
- Level Order Traversal LIne by Line – C | C++| Java
- Hand shaking lemma and some Impotant Tree Properties.
- Check If binary tree if Foldable or not.- C| C++| Java
- check whether tree is Symmetric C| C++| Java.
- Check for Children-Sum in Binary Tree- C|C++| Java
- Sum of all nodes in Binary Tree- C | C++ | Java
- Lowest Common Ancestor in Binary Tree. C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment