Sum of Digits of a Number in Python
Find the sum of the Digits of a Number in Python
Given an input the objective to find the Sum of Digits of a Number in Python. To do so we’ll first extract the last element of the number and then keep shortening the number itself.
Example
Input : number = 123
Output : 6

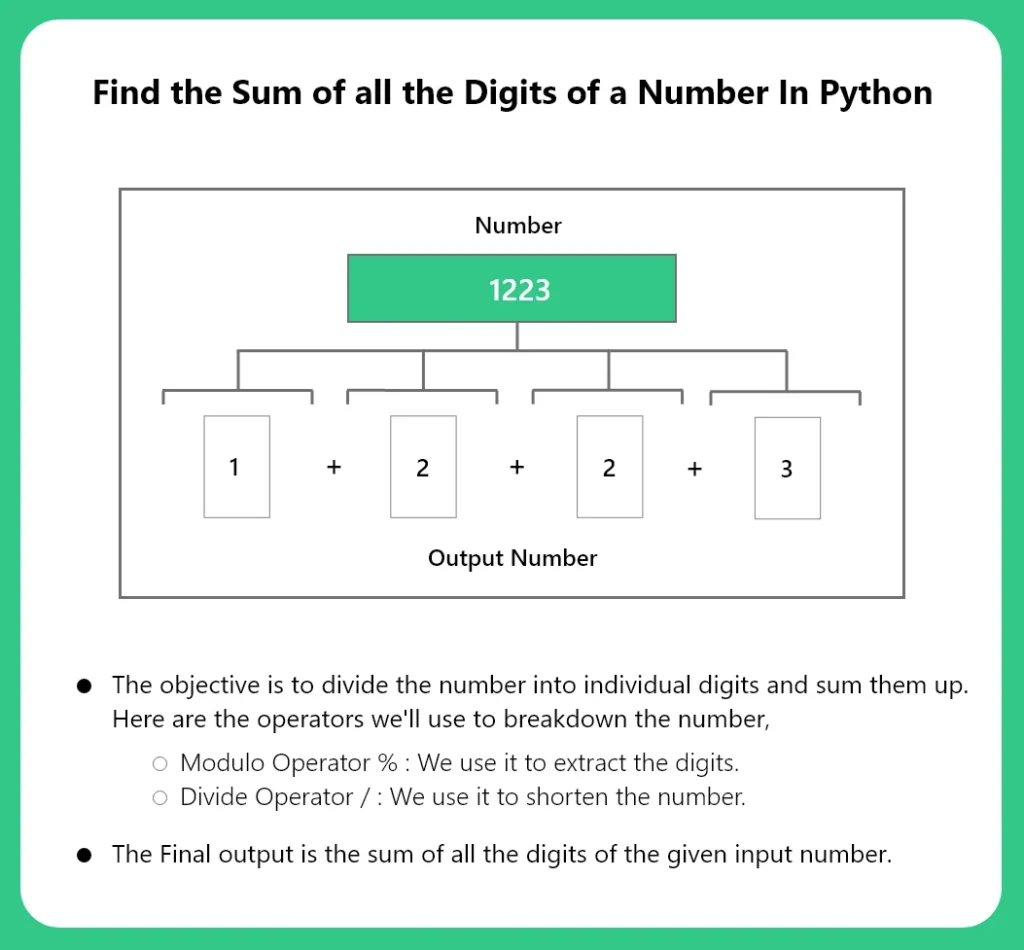
Find the sum of the Digits of a Number
Given a number as an input the objective is to calculate the sum of the digits of the number. We first break down the number into digits and then add all the digits to the sum variable. We use the following operators to break down the string,
- Modulo operator %: We use this operator to extract the digits from the number.
- Divide operator /: We use this operator to shorten the number after the digit has been extracted.
We use the above-mentioned operators to find the sum of the digits of the number. Here are some of the methods to solve the above-mentioned problem.
- Method 0: Using String Extraction method
- Method 1: Using Brute Force
- Method 2: Using Recursion I
- Method 3: Using Recursion II
- Method 4: Using ASCII table
- Method 5: Using map(), sum() and strip methods
- Method 6: One Line recursive function
- Method 7 : The cool method
We’ll discuss the above-mentioned methods in the upcoming sections.

Method 0: Using String Character Extraction
We will extract each character in the string input and convert it to an individual character’s integer equivalent.
num = input("Enter Number: ")
sum = 0
for i in num:
sum = sum + int(i)
print(sum)Output
Enter Number: 12345 15
Prime Course Trailer
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method 1: Using Brute Force
We extract each digit here by finding the modulus of the whole input by 10.
Python Code
num = 12345 sum = 0 while num!=0: digit = int(num%10) sum += digit num = num/10 print(sum)
Output
15
Method 2: Using Recursion I
Python Code
num, sum = 12345, 0
def findSum(num, sum):
if num == 0:
return sum
digit = int(num % 10)
sum += digit
return findSum(num / 10, sum)
print(findSum(num, sum))
Output
15
Method 3: Using Recursion II
Python Code
num = 12345
def findSum(num):
if num == 0:
return 0
return int(num % 10) + findSum(num / 10)
print(findSum(num))
Output
15
Method 4: Using ASCII Table
Please check the ASCII Table here
Python Code
num, sum = 12345, 0
for i in range(len(str(num))):
# ord methods helps with ASCII
sum += ord(str(num)[i]) - 48
print(sum)
Output
15
Method 5: Using map(), sum() and strip methods
Explain given in the code itself below –
Python Code
def getSum(n):
# convert into string
num_string = str(n)
# fetch each individual char using strip method
# find comparable int and store it in map
# covert it into list
list_of_number = list(map(int, num_string.strip()))
print(list_of_number)
# sum function returns the sum of all items in list
return sum(list_of_number)
n = int(input("Enter the number: "))
print(getSum(n))Output
Enter the number: 12345 15
Method 6: One Line recursive function
Let’s look at the function below –
def sumDigits(n):
return 0 if n == 0 else int(n % 10) + sumDigits(int(n / 10))
# Driver code
n = int(input("Enter the number: "))
print(sumDigits(n))Output
Enter the number: 12345 15
Method 7: The cool method
We kind of have discussed this method above. But its amalgamation of different python tricks –
n = [int(d) for d in input("Enter the number : ")]
print("the sum of digits is : ", sum(n))
Output
Enter the number: 12345 15
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
- Positive or Negative number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Even or Odd number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of First N Natural numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of N natural numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of numbers in a given range: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Greatest of two numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Greatest of the Three numbers: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Leap year or not: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Prime number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Prime number within a given range: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Sum of digits of a number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Reverse of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Palindrome number: C | C++ | Java | Python
- Armstrong number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Armstrong number in a given range : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Fibonacci Series upto nth term : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Find the Nth Term of the Fibonacci Series : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Factorial of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Power of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Factor of a number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Strong number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Perfect number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Automorphic number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Harshad number : C | C++ | Java | Python
- Abundant number : C| C++ | Java | Python
- Friendly pair : C | C++ | Java | Python
Login/Signup to comment





n = str(input())
sum= 0
for i in n:
sum = sum + int(i)
print(sum)
num=input(“Enter the number:”)
li=list(num)
li1=list(map(int,li))
sum=0
for i in range(len(li1)):
sum=sum+li1[i]
print(“sum of the digits:{}”.format(sum))
n=int(input(“enter the number”))
sum1=0
while(n>0):
a=n%10
sum1+=a
n=n//10
print(sum1)
n = int(input())
s = []
for i in range(a):
x = int(input())
s.append(x)
for i in s:
count = count + i
print(count)
#simple
num =str(input())
print(“The number is “,num)
sum = 0
for i in num:
sum = sum + int(i)
print(“The sum of digits is = “,+sum)
#SUM OF DIGITS OF GIVEN NUMBER
n=int(input())
n=list(map(int,str(n)))
print(sum(n))
from array import*
arr = array(‘i’,[])
n=int(input(“Enter the number of elements: “))
for i in range(n):
arr.append(int(input(“Enter the number: “)))
total =(sum(arr))
print(“The sum of these numbers are “,total)
from array import*
arr = array(‘i’,[1,2,3,4,5,6])
print(sum(arr))
n=int(input())
a=str(n)
c=0
for i in a:
c+=int(i)
print(c)
n=int(input())
sum=0
for i in str(n):
sum=sum+int(i)
print(sum)
number = [int(d) for d in input(“Enter number: “)]
print(sum(number))
n=12345
sum=0
while n>0:
temp=n%10
sum=sum+temp
n=n//10
print(sum)