C Menu
- Basics of C
- Basics of C Programming
- Features of C Programming
- Preprocessors in C Programming
- History of C Programming
- Low Level Programming
- Why C is Middle Level Language
- Introduction to C programming
- Structure of a C program
- Input-Output Functions
- Difference between Compiler and Interpreter
- Assembler v/s Compiler v/s Interpreter v/s Linker v/s Loader
- Basics to Code
- Operators in C
- Operators in C
- Precedence Associativity Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Ternary Operators in C
- Size of Operators
- Conditional Operators
- Comma Operators
- Format Specifiers in C
- Difference between %d and %i
- Difference between %f, %e, %E and %g
- How to print% using printf
- How to print \ using printf
- How to print “” using printf
- What is the use of %p in C
- Library Functions in C
- pow() in C
- sqrt() in C
- Storage Classes in C
- Conditional statements and Decision Making in C
- DataType & Functions in C
- Arrays, String, Structure, Union and Enum
- Pointer in C
- Library Function in C
- Library function in C
- math.h in c
- Library function math.h acos
- Library function math.h acosh
- Library function math.h asin
- Library function math.h asinh
- Library function math.h atan
- Library function math.h atan2
- Library function math.h atanh
- Library function math.h cbrt
- Library function math.h cell
- Library function math.h cos
- Library function math.h cosh
- Library function math.h exp
- Library function math.h fabs
- Library function math.h floor
- Library function math.h hypot
- Library function math.h log
- Library function math.h log10
- Library function math.h pow
- Library function math.h sin
- Library function math.h sinh
- Library function math.h sqrt
- Library function math.h tan
- Library function math.h tanh
- Library function studio.h clearerr
- Library function string.h strcat
- Library function string.h strcmp
- Library function string.h strcpy
- Library function string.h strlen
- File Handling
- Dynamic Memory Allocation
- Miscellaneous Topics in C
- Miscellaneous Coding Questions
PREPINSTA PRIME
Radix Sort in C
Radix sort
It is a sorting algorithm that is used to sort element. Radix sort is the method that many people begin to use when alphabetizing a large list of name or numeric number.Specifically ,
The list of names is first sorted according to the first letter of each name. That is, the names are arranged in 26 classes,where the first class consist of those name that begin with “A”, the second class consists of those name that begin with “B”,and so on.During the second pass, each class is alphabetized according to the second letter of the name.And so on.
- The time complexity of Radix sort is O(kn) and space complexity of Radix sort is O(k+n).the running time of Radix appears to be better than Quick Sort for a wide range of input numbers.
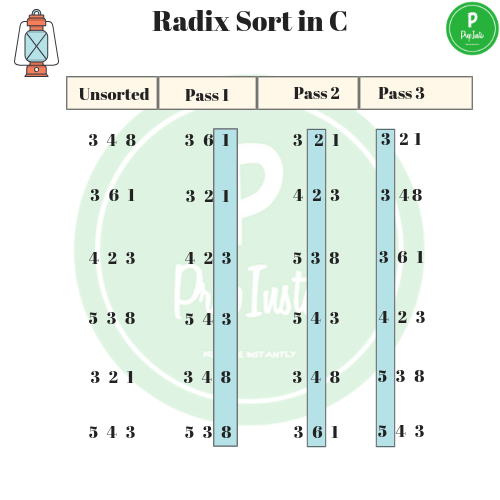
Implementation of Radix sort
Let us take an example of radix sort
Given to a list ,the numbers would be sorted in three phases. the list is (248,140,261,323,438,120,221,443,266).
(A)- In the first phase, the once digits are sorted into list.. The number are collected box by box ,from pocket 8 to 0.(Note 261 will now be at the bottom of the pile and 438 at the top of the pile.) The cards are now rein put to the sorter.
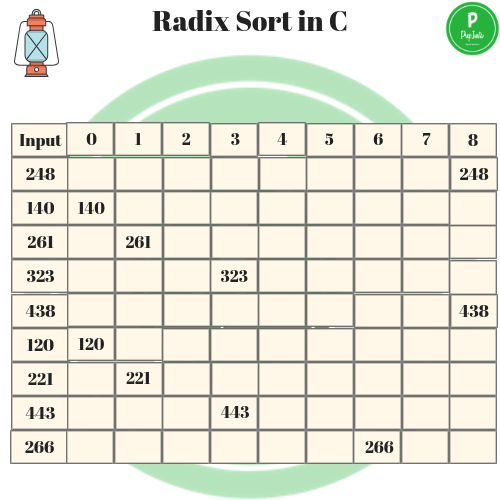
(B)- In the second phase, the tens digits are sorted into pockets,Again the card are collected pocket by pocket and rein put to the sorter.
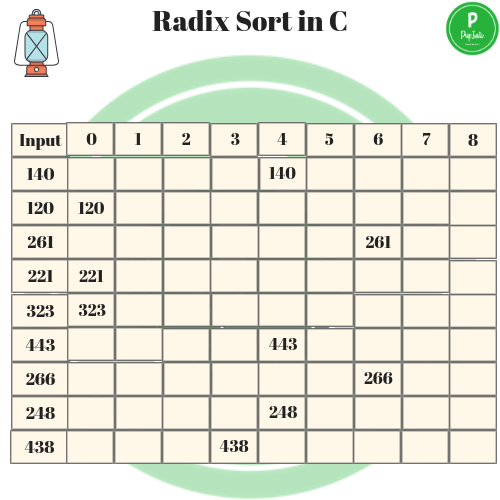
In the last phase and third phase, we will notify that the hundred digit are sorted into pockets.
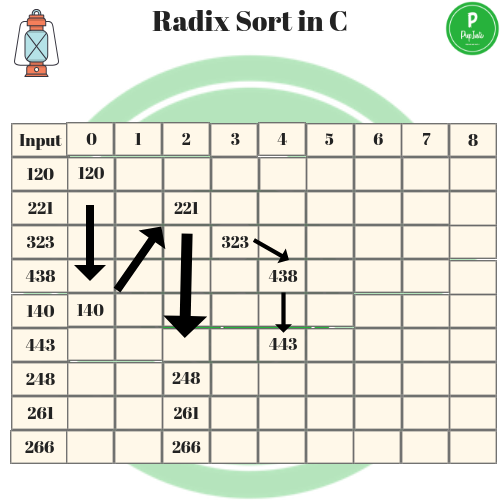
So the final list is by ascending order to sorted digits or number is (120,140, 221,248,261,266,323,438,443).
Algorithm of Radix sort
1- for i<-1 to d do
2-use a stable sort to array A on digit i
//counting sort will do the job
The code for radix sort assumes that each element in the n-element array A has d- digits,where digit 1 is the lowest -order digit and d is the highest-order digit.
Program for Radix Sort in C
#include<stdio.h> //including library files
int max(int a[]); //declaring functions
void radix_sort(int a[]); //declaring functions
void main() //defining main()
{
int i;
int a[10]={92,106,365,90,33,19,72,56,45,12}; //initializing array with values
radix_sort(a);
printf("\n The sorted list is: \n"); //printing the sorted list
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
printf(" %d", a[i]);
}
int max(int a[]) //giving the definition to max()
{
int max=a[0], i; //finiding the largest number
for(i=1;i<10;i++) { if(a[i]>max)
max = a[i];
}
return max;
}
void radix_sort(int a[]) //providing definition to radix_sort
{
int bucket[10][10], bucket_count[10]; //declaring variables
int i, j, k, remainder, NOP=0, divisor=1, maxi, pass; //declaring variables
maxi = max(a);
while( maxi>0)
{
NOP++;
maxi/=10;
}
for(pass=0;pass<NOP;pass++) // Initialization of the buckets
{
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
bucket_count[i]=0;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
// sort the numbers according to the digit at passth place
remainder = (a[i]/divisor)%10;
bucket[remainder][bucket_count[remainder]] = a[i];
bucket_count[remainder] += 1;
}
// collect the numbers after PASS pass
i=0;
for(k=0;k<10;k++)
{
for(j=0;j<bucket_count[k];j++)
{
a[i] = bucket[k][j];
i++;
}
}
divisor *= 10;
}
}Output:
The sorted list is: 12 19 33 45 56 72 90 92 106 365
Sorting
Sorting algorithms are easy to learn but are really important for college semester exams and companies offering package between 3 – 6 LPA would ask direct searching questions in online test/ interviews.


 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates

Login/Signup to comment