Insertion Sort in C++
What is Insertion Sort in C++?
Rearranging data in a logical order is known as sorting i.e. arranging of data in ascending or descending order. In this article, we will learn about insertion sort in C++.
Insertion sorting is done in the same way as we sort our cards in while we play games of cards
| Time Complexity | O(n2) |
| Best Case | Ω(n) |
| Worst Case | O(n2) |
| Aux. Space Complexity | O(1) |
| Best case when | Array is already sorted |
| Worst case when | Array is reverse sorted |

What is Insertion Sort in C++?
Rearranging data in a logical order is known as sorting i.e. arranging of data in ascending or descending order. In this article, we will learn about insertion sort in C++.
Insertion sorting is done in the same way as we sort our cards in while we play games of cards
| Time Complexity | O(n2) |
| Best Case | Ω(n) |
| Worst Case | O(n2) |
| Aux. Space Complexity | O(1) |
| Best case when | Array is already sorted |
| Worst case when | Array is reverse sorted |

Insertion Sort in C++
If there are n element and it requires (n-1) pass to sort them then, at each pass we insert current element in the appropriate position so that the element are in order. Some characteristics of insertion sort in C++.
- A sub-list is maintained which is always in sorted order.
- It is better then Selection Sort and Bubble Sort algorithms.
- It is efficient for smaller data sets but inefficient for larger data sets.
- Its space complexity is less.
- It does not change the relative order of elements which are equal.
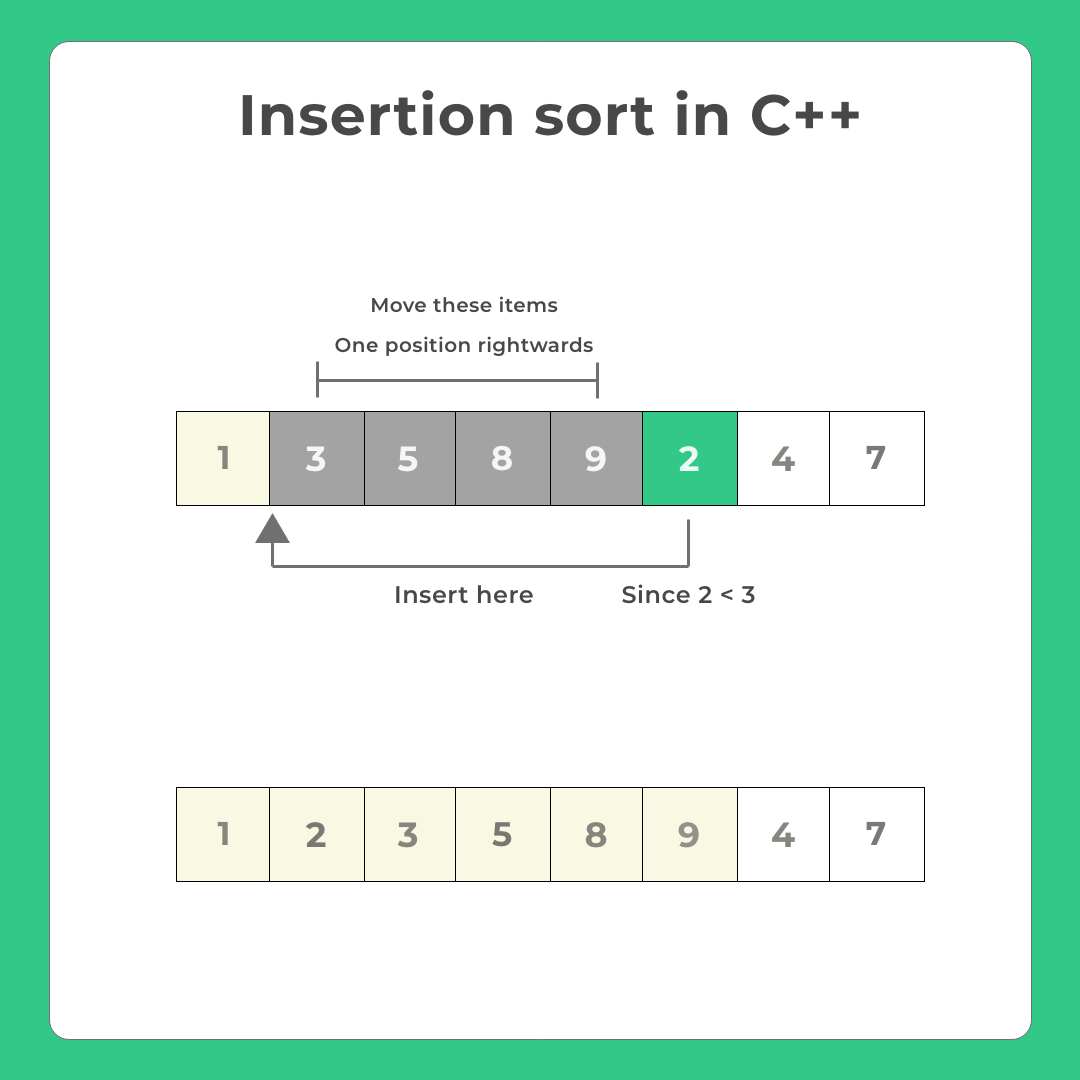

Execution of insertion sort in C++
- It’s almost similar to how we play cards.
- At any given time, one part of the array will be sorted and one part will be unsorted.
- We will pick the leftmost item from the unsorted part
- Insert this item at the correct position in the sorted array
You can check the implementation of the same below
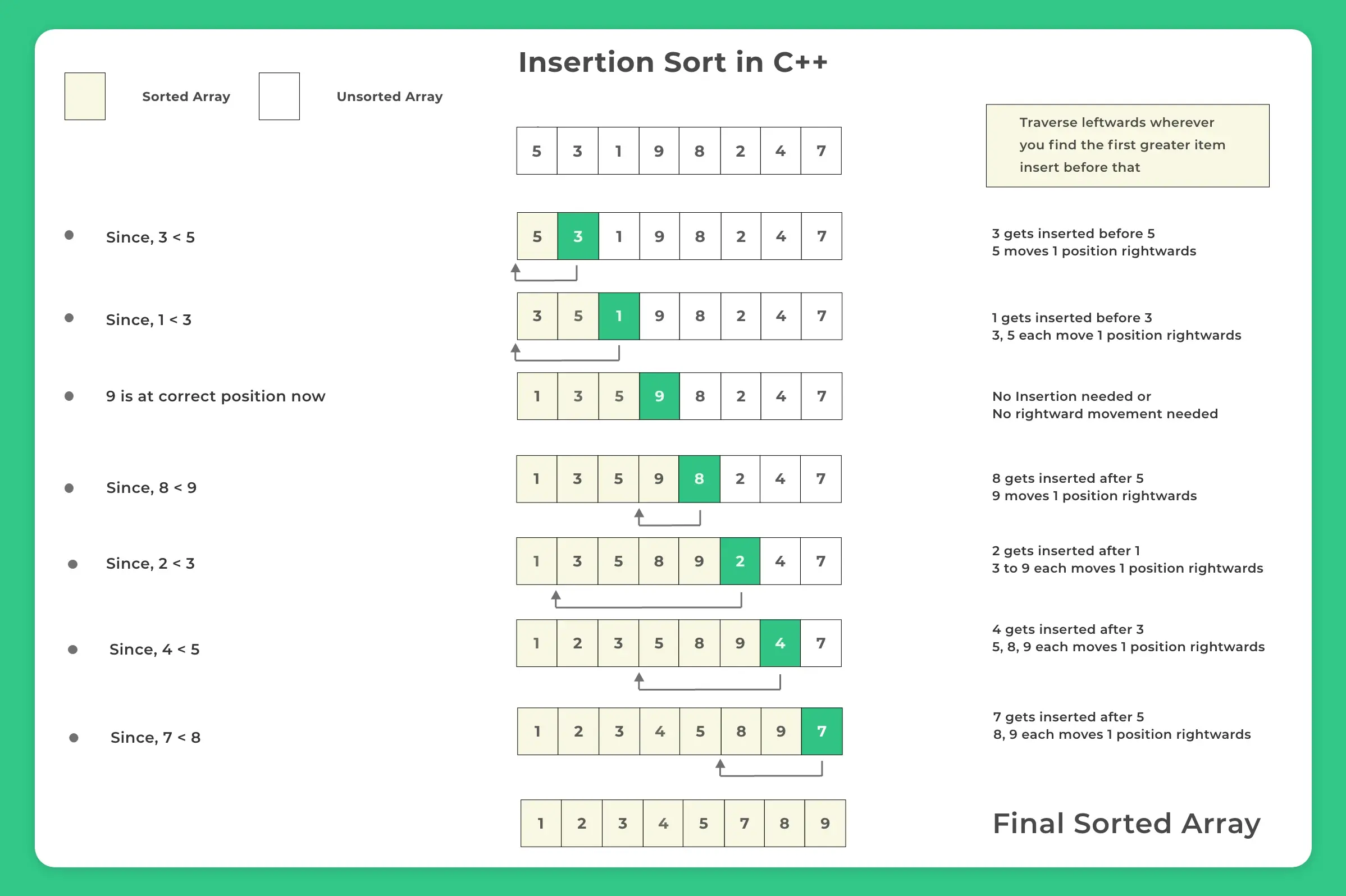

Algorithm for insertion sort in C++
- INSERTION-SORT(A)
- for i = 1 to n
- key ← A [i]
- j ← i – 1
- while j > = 0 and A[j] > key
- A[j+1] ← A[j]
- j ← j – 1
- End while
- A[j+1] ← key
- End for
Program for insertion sort in C++
// C++ Program for Insertion Sort
// Time Complexity : O(N^2)
// Space Compelexity : O(1)
// Best Case : When already Sorted, Worst Case : When reverse Sorted
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//Function to print array.
void display(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << "\t";
cout << "\n";
}
//Main function to run the program.
int main()
{
int array[] = {5, 3, 1, 9, 8, 2, 4,7};
int size = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);
cout << "Before Insertion sort: \n";
display(array, size);
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < size; i++) { key = array[i]; j = i - 1; /* Here the elements in b/w arrary[i-1 & 0] which are greater than key are moved ahead by 1 position each*/ while (j >= 0 && array[j] > key)
{
array[j + 1] = array[j];
j = j - 1; // moving backwards
}
// placing key item now
array[j + 1] = key;
}
cout << "After Insertion sort: \n";
display(array, size);
return 0;
}Output
Before Insertion sort: 5 3 1 9 8 2 4 7 After Insertion sort: 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9
Explanation:
- An integer array is defined and its length is determined.
- A function prints all elements of the array in a single line.
- Each element from the second position is selected for insertion into the sorted part.
- Elements larger than the selected key are moved one position ahead.
- The key is placed in its correct position within the sorted section.
- The array is shown before and after applying insertion sort.
Pros and Cons of Insertion Sort Algorithm
Pros
- Anyone can write it is moderately easy to understand
- Only O(1) space requirements
- For a smaller number of items in an array it’s quicker than merge sort
Cons
- Not so good average time complexity of O(n2)
- If there are large elements then it gives bad performance because of O(n^2) time complexity
- Shifting items because of insertion can be costly
Other information
- Best Case: If already sorted data set
- Worst Case: Sorted data set but in the opposite order
To Wrap It Up:
Insertion Sort is a simple and intuitive sorting technique in C++ that arranges elements in ascending or descending order. It works by dividing the array into a sorted and unsorted part, picking elements from the unsorted part, and inserting them into the correct position in the sorted part. It is efficient for small datasets and maintains the relative order of equal elements.
The algorithm is easy to implement, requires minimal extra space (O(1)), and performs well on nearly sorted arrays. However, its average and worst-case time complexity of O(n²) makes it inefficient for large datasets, and frequent shifting of elements can be costly.


Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
FAQs
Insertion Sort is a simple sorting algorithm that builds the final sorted array one element at a time by comparing and inserting elements into their correct position. It works similarly to sorting playing cards in hand.
The worst-case and average-case time complexity is O(n²), while the best case is O(n) when the array is already sorted.
Yes, Insertion Sort is stable because it does not change the relative order of equal elements, and it is in-place since it requires only a constant amount of extra memory.
Insertion Sort is preferred for small datasets or nearly sorted arrays because it has low overhead and performs efficiently in such scenarios.
Sorting
Sorting algorithms are easy to learn but are really important for college semester exams and companies offering package between 3 – 6 LPA would ask direct searching questions in online test/ interviews.

Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment