Counting Sort in Java
Counting Sort in Java
In this article, we’ll understand what Counting Sort in Java is, how it works, and how to implement it in Java with an example. We’ll also explain its algorithm in simple terms, discuss time and space complexities, and answer frequently asked questions.
Sorting is a common operation in programming that helps in organizing data in a specific order (ascending or descending). Java offers several sorting techniques like Quick Sort, Merge Sort, and Bubble Sort. However, when dealing with a limited range of non negative integers, Counting Sort is one of the fastest and most efficient sorting algorithms.

What is Counting Sort in Java?
Counting Sort is a non comparison based sorting algorithm. Unlike Merge Sort or Quick Sort, it does not compare elements to sort them. Instead, it counts the occurrences of each unique element and uses this information to place elements in the correct sorted position.
Counting Sort is most effective when:
- Input consists of non negative integers.
- The range of input values (max – min) is not significantly larger than the number of elements.
How Does Counting Sort Work?
The idea behind Counting Sort is:
- Count how many times each number appears.
- Modify the count array to store positions.
- Build the sorted output based on positions.
2. Average Case: O ( n + k )
3. Worst Case: O ( n + k )
Where:
n = number of elements in input array
k = maximum element in the array (range of input)
What is the Algorithm for Counting Sort?
Let’s understand the steps:
- Find the maximum value in the array (let’s call it max).
- Create a count array of size max + 1 to store frequencies of elements.
- Fill the count array by incrementing index based on array elements.
- Modify the count array such that each element at index i stores the sum of previous counts. This helps in placing elements directly at their sorted position.
- Create an output array to store sorted elements.
- Place elements into output array using the modified count array.
- Copy the output back to the original array.
Advantages of Counting Sort:
- Very fast for sorting small range of integers
- Linear time complexity in best conditions
- Stable sort (preserves the order of duplicates)
Limitations of Counting Sort:
- Not suitable for negative numbers (needs modification).
- Inefficient when the range (max – min) is much larger than the number of elements.
- Extra space usage (O(n + k)).
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Working of Counting Sort Technique
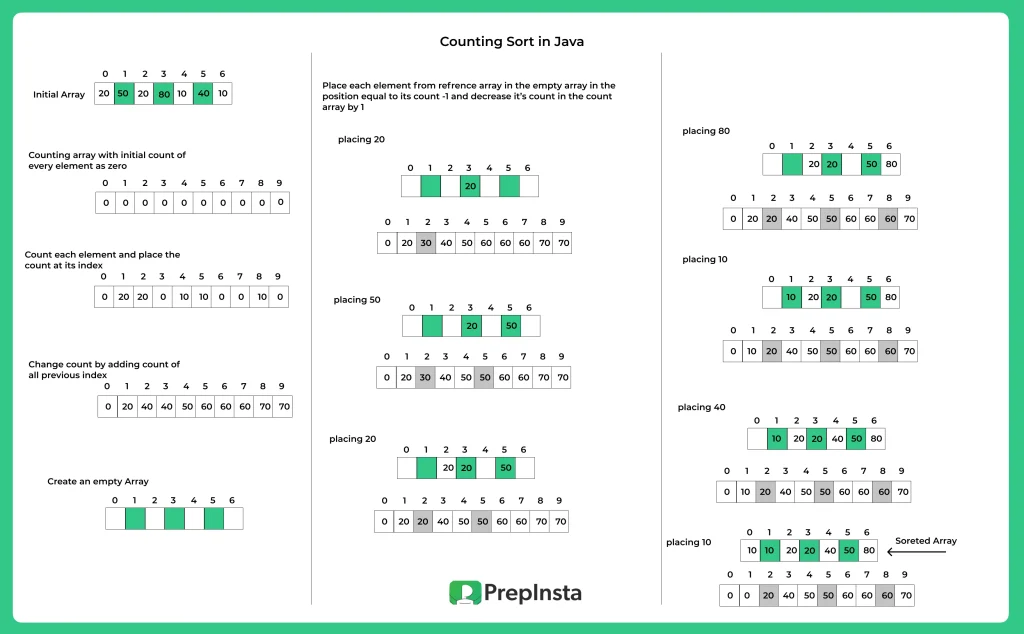
Working of Counting Sort Technique
public class CountingSort {
// Method to perform counting sort
public static void countingSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr.length == 0)
return;
// Step 1: Find the maximum element in the array
int max = arr[0];
for (int num : arr) {
if (num > max) {
max = num;
}
}
// Step 2: Create count array of size max + 1
int[] count = new int[max + 1];
// Step 3: Count each element
for (int num : arr) {
count[num]++;
}
// Step 4: Modify the count array
for (int i = 1; i < count.length; i++) {
count[i] += count[i - 1];
}
// Step 5: Create output array
int[] output = new int[arr.length];
// Step 6: Place the elements in sorted order (stable sort)
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[arr[i]] - 1] = arr[i];
count[arr[i]]--;
}
// Step 7: Copy the output to the original array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = output[i];
}
}
// Main method to test the counting sort
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1};
System.out.println("Original Array:");
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
countingSort(arr);
System.out.println("\nSorted Array:");
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
}
Output:
Original Array: 4 2 2 8 3 3 1 Sorted Array: 1 2 2 3 3 4 8
Conclusion:
Counting Sort is a powerful algorithm when applied to the right dataset. It’s fast, simple, and efficient when sorting non negative integers within a limited range.
Although not as general purpose as Merge Sort or Quick Sort, it’s a valuable tool for specific scenarios.
Understanding how Counting Sort works in Java with real code examples will help you improve your grasp of algorithm efficiency and help in competitive programming and system design alike.
FAQ's related to Counting Sort in Java
Answer:
Counting Sort is used to sort an array of Non negative integers efficiently when the range of elements is small. It’s ideal for use cases like sorting exam scores or ages in a dataset.
Answer:
Counting Sort can be faster than Quick Sort when the input size is small and the value range is limited. However, Quick Sort is generally more versatile and works better on larger and unsorted datasets with varied values.
Answer:
Basic Counting Sort does not handle negative numbers. To handle negatives, you must shift all values by the absolute minimum value before sorting and adjust accordingly.
Answer:
The time complexity is O(n + k), where:
- n is the number of elements in the input array.
- k is the maximum element in the array.
Answer:
Yes, Counting Sort is stable. It maintains the relative order of elements with the same value, which is useful in applications like radix sort or multi key sorting.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




For the information provided above about the counting array how comes the array size is taken as 10
Thanks a lot for answering Buddy?