Selection Sort in Java
Selection Sort in Java: Explained with Code
Sorting is a basic and important concept in computer science, one of the simplest sorting methods is Selection Sort in Java. It works by comparing elements and is easy to understand, which is why it’s often taught in schools and asked in interviews to explain how sorting works.
In this article, we will dive deep into Selection Sort in Java, covering everything from its working principle to space/time complexity, Java implementation, and real examples.

What is Selection Sort?
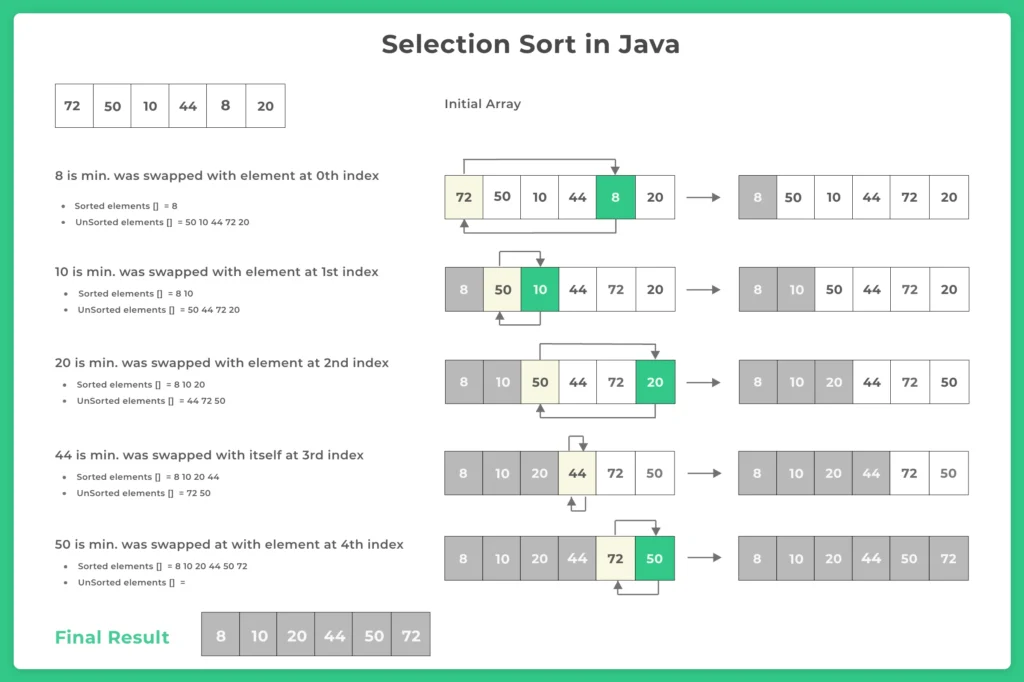
Selection Sort is a sorting algorithm that repeatedly selects the smallest (or largest) element from the unsorted part of the array and moves it to the beginning (or end) of the sorted part. This process continues until the entire array is sorted.
Unlike Bubble Sort or Insertion Sort, Selection Sort makes the minimum number of swaps (n – 1), which makes it slightly better in scenarios where write operations are costly.
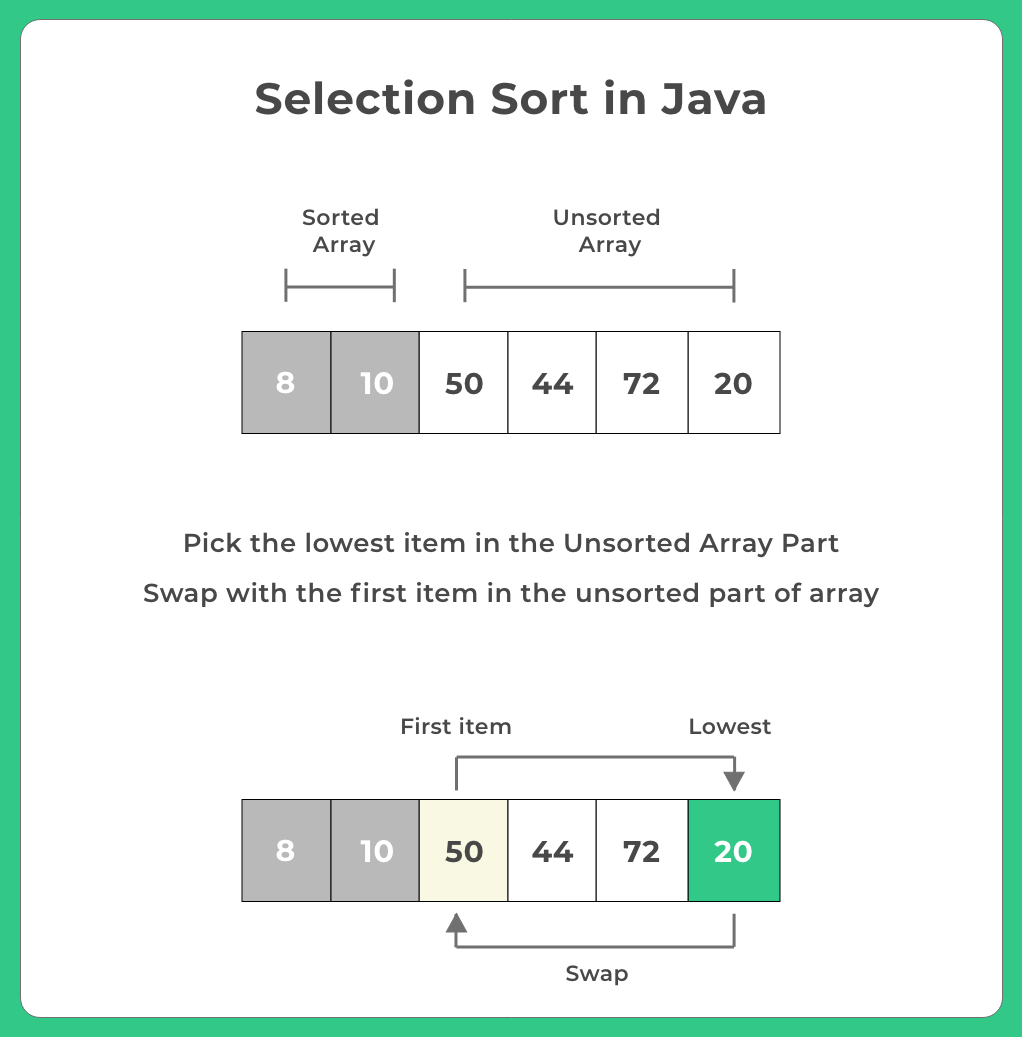
How Does Selection Sort Work?
The algorithm works in the following way:
- Divide the array into two parts: sorted and unsorted.
- Find the minimum element in the unsorted array.
- Swap it with the leftmost unsorted element.
- Move the boundary of the sorted part one step to the right.
- Repeat until the array is fully sorted.
Selection Sort Algorithm:
Here is the algorithm for Selection Sort:
for i = 0 to n-1:
minIndex = i
for j = i+1 to n-1:
if array[j] < array[minIndex]:
minIndex = j
Swap array[i] with array[minIndex]
Algorithm: SelectionSort(arr, n)
Input:
arr[] → An array of n elements
n → Size of the array
Output:
Sorted array in ascending order.
Procedure:
- Repeat steps 2 to 5 for i = 0 to n – 2:
- Set minIndex = i
- For j = i + 1 to n – 1:
- If arr[j] < arr[minIndex]:
- Set minIndex = j
- Swap arr[i] with arr[minIndex]
- End

Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
How Selection Sort Works?

Selection Sort using Java Programming
Below is a simple and clean implementation of the Selection Sort algorithm in Java:
public class SelectionSort {
// Method to perform selection sort
public static void selectionSort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// Find the index of the minimum element
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
// Swap the found minimum element with the first element
int temp = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
// Utility method to print an array
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int value : arr) {
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {64, 25, 12, 22, 11};
System.out.println("Input Array:");
printArray(numbers);
selectionSort(numbers);
System.out.println("Sorted Array:");
printArray(numbers);
}
}
Time Complexity: O(n2)
Input:
int[] numbers = {64, 25, 12, 22, 11};Output:
Input Array: 64 25 12 22 11 Sorted Array: 11 12 22 25 64
Advantages of Selection Sort
- Easy to understand and implement.
- Works well with small data sets.
- Minimizes the number of swaps.
Disadvantages of Selection Sort
- Bad time complexity for large arrays.
- Not adaptive: does not take advantage of partially sorted arrays.
- Unstable: does not preserve the relative order of equal elements.
However, with slight modification, it can be made stable by inserting the minimum element at the correct position without direct swapping.
Conclusion
Selection Sort in Java is one of the most basic sorting techniques that helps in building the foundation for understanding more complex sorting algorithms.
- While it may not be efficient for large datasets due to its O(n²) time complexity, it performs fewer swaps, making it useful in scenarios where memory write operations are costly.
- Understanding how Selection Sort works along with its Java implementation—enhances your fundamental programming skills and prepares you for interviews and algorithm design.

FAQ's related to Selection Sort in Java
Answer:
Selection Sort in Java is a sorting algorithm that repeatedly selects the minimum element from the unsorted array and places it at the beginning of the sorted portion.
Answer:
Time complexity of Selection Sort is O(n²) for best, average, and worst cases due to nested loops for comparison.
Answer:
By default, Selection Sort is unstable because it swaps elements, which may change the order of equal elements.
Answer:
Selection Sort is suitable for small datasets or situations where memory writes are expensive due to its minimal number of swaps.
Answer:
Space complexity is O(1) since Selection Sort is an In place sorting algorithm and doesn’t use extra space.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment