Merge Sort in C++
What is Merge Sort in C++?
Merge sort is one the sorting technique that is used to sort the data in a logical order. It uses divide and conquer approach for sorting the data. Merge sort repeatedly breaks down a list into several sub lists until each sub list consists of a single element and merging those sub lists in a manner that results into a sorted list. In this article, we will read more about merge sort in C++.
| Time Complexity | Θ(n Log n) |
| Best Case | Ω(n Log n) |
| Worst Case | O(n Log n) |
| Space Complexity | O(n) |

What is Merge Sort in C++?
Merge sort is one the sorting technique that is used to sort the data in a logical order. It uses divide and conquer approach for sorting the data. Merge sort repeatedly breaks down a list into several sub lists until each sub list consists of a single element and merging those sub lists in a manner that results into a sorted list. In this article, we will read more about merge sort in C++.
| Time Complexity | Θ(n Log n) |
| Best Case | Ω(n Log n) |
| Worst Case | O(n Log n) |
| Space Complexity | O(n) |

Merge Sort in C++
- A file of any size can be sorted using merge sort.
- Elements in the merge sort are divided into two sub list again and again until each sub-list contain only one element.
- After this, the elements are merged to make a sorted list.
- It requires more space and is less efficient
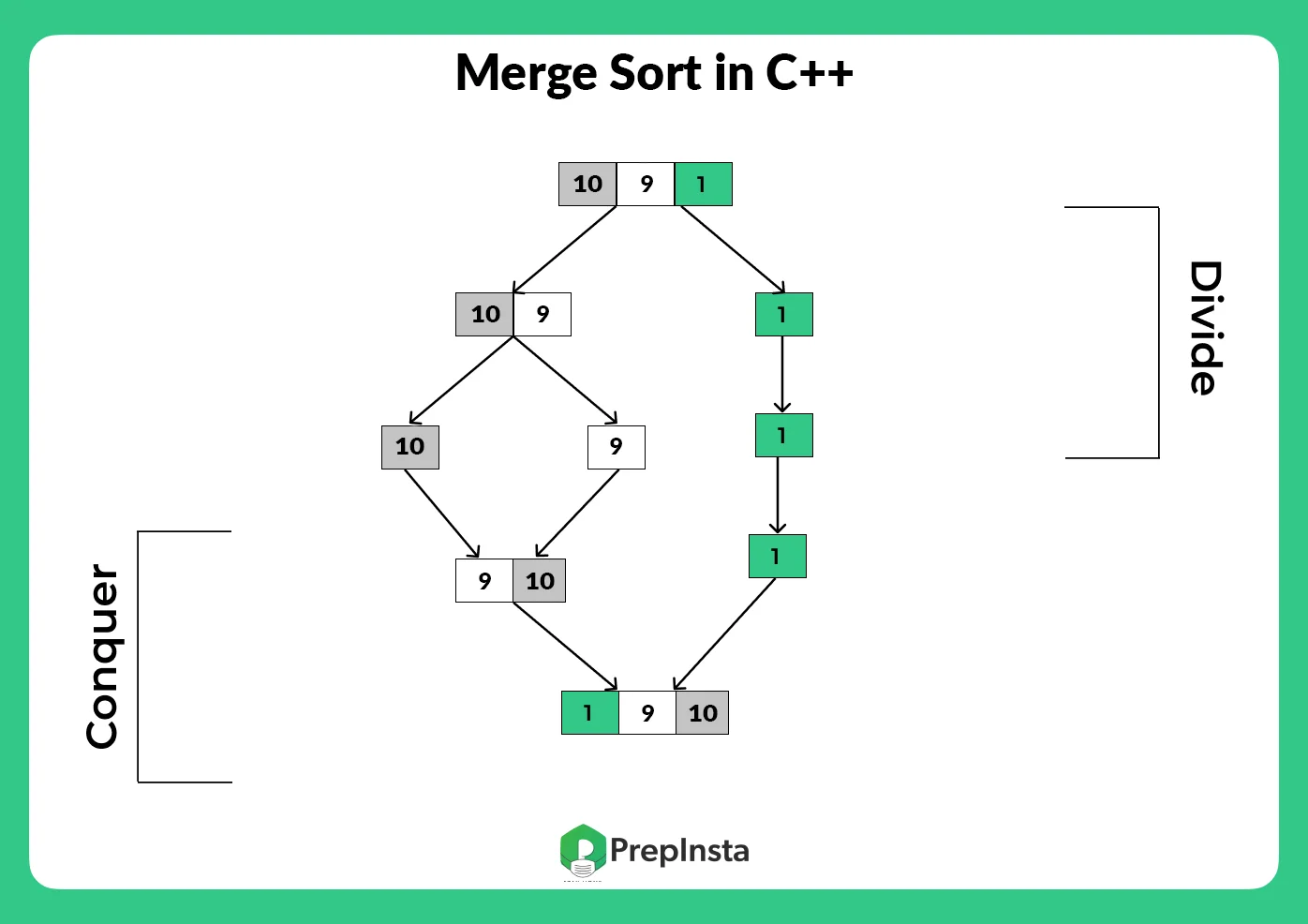

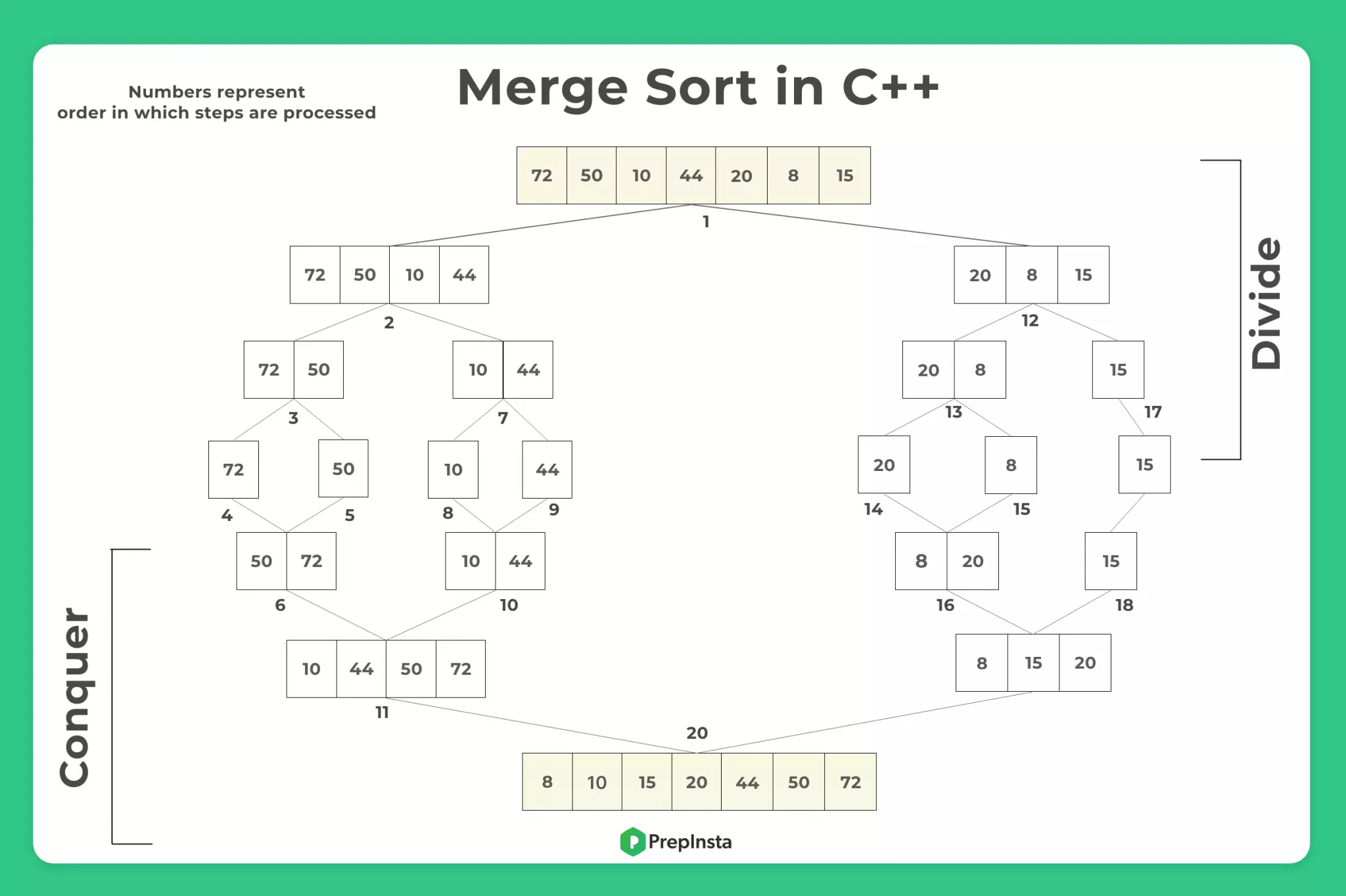
Execution of Merge sort in C++
Merge sort is executed in three steps:-
1.) Divide Step:
First of all the array will be divide in to N sub list, until each sub list contains only one element.
2.) Conquer Step:
Take two sub list and place them in logical order.
3.) Combine Step:
Combine the elements back by merging the two sorted sub list into a sorted sequence.

Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Program for merge sort in C++
We will look at two different methods, both have the same time complexity with the difference that –
- Method 1 – Uses two temp subarrays
- Method 2 – Uses 1 temp subarray
The combined size of two temp subarrays in method 1 is the same as the whole array in method 2. So the space complexity remains the same.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void mergeSort(int[],int,int);
void merge(int[],int,int,int);
void printArray(int arr[], int size){
int i;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int array[]= {8, 4, 5, 1, 3, 9, 0, 2, 7, 6};
int i;
int size = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);
printArray(array, size);
mergeSort(array, 0, size-1);
printArray(array, size);
}
void mergeSort(int a[], int left, int right)
{
int mid;
if(left < right)
{
// can also use mid = left + (right - left) / 2
// this can avoid data type overflow
mid = (left + right)/2;
// recursive calls to sort first half and second half subarrays
mergeSort(a, left, mid);
mergeSort(a, mid + 1, right);
merge(a, left, mid, right);
}
}
void merge(int arr[], int left, int mid, int right)
{
int i, j, k;
int n1 = mid - left + 1;
int n2 = right - mid;
// create temp arrays to store left and right subarrays
int L[n1], R[n2];
// Copying data to temp arrays L[] and R[]
for (i = 0; i < n1; i++)
L[i] = arr[left + i];
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++)
R[j] = arr[mid + 1 + j];
// here we merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r]
i = 0; // Starting index of L[i]
j = 0; // Starting index of R[i]
k = left; // Starting index of merged subarray
while (i < n1 && j < n2)
{
// place the smaller item at arr[k] pos
if (L[i] <= R[j]) {
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else {
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of L[], if any
while (i < n1) {
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of R[], if any
while (j < n2) {
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}Output
8 4 5 1 3 9 0 2 7 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void mergeSort(int[],int,int);
void merge(int[],int,int,int);
void printArray(int arr[], int size){
int i;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int array[]= {8, 4, 5, 1, 3, 9, 0, 2, 7, 6};
int i;
int size = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);
printArray(array, size);
mergeSort(array, 0, size-1);
printArray(array, size);
}
void mergeSort(int a[], int left, int right)
{
int mid;
if(left < right)
{
// can also use mid = left + (right - left) / 2
// this can avoid data type overflow
mid = (left + right)/2;
// recursive calls to sort first half and second half subarrays
mergeSort(a, left, mid);
mergeSort(a, mid + 1, right);
merge(a, left, mid, right);
}
}
void merge(int a[], int left, int mid, int right)
{
int i = left; // starting index of left subarray
int j = mid + 1; // starting index of right subarray
int index = left; // used to place items in temp[]
int temp[10];
while(i<=mid && j<=right)
{
// place the smaller item at temp[index]
if(a[i] < a[j]) { temp[index] = a[i]; i = i+1; } else { temp[index] = a[j]; j = j+1; } index++; } // i > mid would mean all items for left
// subarray were successfully placed, and there
// must be unplaced right subarray items
if(i>mid)
{
while(j<=right)
{
temp[index] = a[j];
index++;
j++;
}
}
// else all items of right subarray must have
// been placed and there must be
// unplaced items in the left-subarray
else
{
while(i<=mid)
{
temp[index] = a[i];
index++;
i++;
}
}
int p = left; // left index of subarray
// by now index would have reached right
// most index of right subarray
// placing all items of temp[] into actual array a[]
while(p < index)
{
a[p]=temp[p];
p++;
}
}Output
8 4 5 1 3 9 0 2 7 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Time and Space Complexity
- Time Complexity -O(n log n)
- Space Complexity – O(n)
Performance
Strengths
- With a good time complexity of O(n log n), merge sort is great !!!
- Good to learn Divide and conquer algorithm later used in Dynamic Programming concepts
Weakness
- Poor space complexity of O(n)
- Lots of overhead in copying data between arrays and making new arrays
To wrap it up:
Merge sort in C++ efficiently sorts data using the divide and conquer approach, breaking down arrays into smaller sublists and merging them back in order. Its consistent time complexity of O(n log n) makes it reliable for handling large datasets.
Although it ensures stable and predictable sorting, merge sort requires additional space for temporary arrays, which can make it less memory-efficient compared to other sorting techniques. Despite this, it remains a fundamental algorithm to understand recursive and divide-and-conquer strategies.
FAQs
Merge Sort is a divide-and-conquer sorting algorithm that splits an array into smaller subarrays, sorts them, and then merges them to get a sorted array.
The time complexity of Merge Sort is O(n log n) for all cases (best, average, worst), making it efficient for large datasets.
Yes, Merge Sort is stable because it maintains the relative order of equal elements while sorting.
Merge Sort requires additional memory for temporary arrays during merging, resulting in a space complexity of O(n).

Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




what is p,q,r?
Hey Rahul, we have taken these three variables, to denote the starting and ending point of the two sub arrays